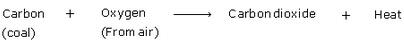Sample Paper 1 with Solution - Term- 1 Social Science, Class 8 | Social Studies (SST) Class 8 PDF Download
Section A
Q 1. Identify the correct sequence of events carried out in preparation of soil. (1)
(a) Ploughing →Levelling of soil → Watering of dry soil → Breaking the crumbs.
(b) Watering of dry soil → Breaking the crumbs → Ploughing → Levelling of soil.
(c) Breaking the crumbs → Ploughing → Levelling of soil → Watering of dry soil.
(d) Watering of dry soil →Ploughing → Breaking the crumbs →Levelling of soil.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The correct sequence of events carried out in preparation of soil is as follows:
(a) Ploughing → Breaking the crumbs → Levelling of soil → Watering of dry soil.
- Ploughing: The first step in preparing the soil is ploughing. This involves using a plough to loosen and turn over the soil. Ploughing helps break up compacted soil, improves aeration, and promotes better water penetration.
Ploughing
- Breaking the crumbs: After ploughing, the soil may form large clumps or crumbs. These clumps need to be broken down into smaller particles to create a finer and more uniform soil texture. This can be done using various tools such as a rake or a harrow.
- Levelling of soil: Once the clumps have been broken down, the next step is to level the soil surface. Levelling involves smoothing out any irregularities or bumps in the soil, ensuring a flat and even surface. This helps in uniform water distribution and facilitates proper seedbed preparation.
- Watering of dry soil: After levelling, if the soil is dry, it is important to provide adequate moisture. Watering the dry soil helps in rehydrating it, promoting microbial activity, and preparing it for seed germination. It is crucial to ensure that the soil is not waterlogged, as excess water can hinder plant growth.
Q 2. Which of the following is false about antibiotics? (1)
(a) Antibiotics should be taken only on the advice of a qualified doctor.
(b) Taking antibiotics when not needed or in wrong doses may make the drug less effective when you may need it in the future.
(c) Antibiotics taken unnecessarily may kill the beneficial bacteria in the body.
(d) Antibiotics are highly effective for curing diseases caused by viruses.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Antibiotics are specifically designed to target and eliminate bacterial infections, not viral infections. Antibiotics are ineffective against viruses, such as the common cold or influenza. Viral infections usually resolve on their own, and taking antibiotics for viral infections can contribute to antibiotic resistance and unnecessary side effects. Therefore, option (d) is the false statement.
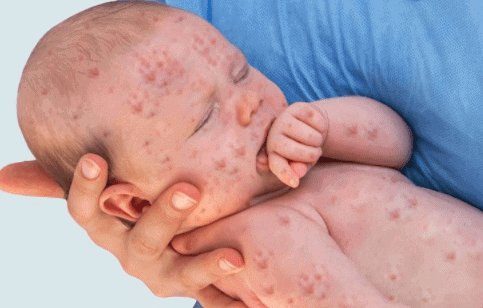
Q 3. Citrus canker and measles are both: (1)
(a) Water-borne diseases
(b) Insect-borne diseases
(c) Air-borne diseases
(d) Seed-borne diseases
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Citrus canker is a bacterial disease that affects citrus trees and is primarily spread through infected plant material, including seeds. Measles, on the other hand, is a highly contagious viral disease that is primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets from an infected person. It is not directly related to seeds, so option (d) is not applicable to measles. However, for citrus canker, the correct option is (d) as it is a seed-borne disease.
Citrus CankerMeasles
Q 4. What is false about deforestation? (1)
(a) It reduces the biodiversity of the area.
(b) It ensures better survival of animals of the area.
(c) It uproots several organisms from their habitat.
(d) It is carried out by humans to use the land for other purposes.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Forests serve as essential natural habitats for numerous animal species. A significant concern is the destruction of these habitats due to deforestation, which may result in the unfortunate vulnerability of these animals to predation and consequent death.
Q 5. Which of the following is an endangered species of animals? (1)
(a) Dinosaur
(b) Asiatic lion
(c) Irish deer
(d) Hyena
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The Asiatic lion, which once had an extensive range across southwest Asia, now has a drastically reduced population that is limited to India's Gir Forest. This rare species is struggling to survive in this last remaining habitat, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts to protect and preserve these majestic animals.
Q 6. Rayon is chemically made by the treatment of _________ (1)
(a) Protein
(b) Cellulose
(c) Fats
(d) Amylase
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Rayon is a versatile fabric derived from wood pulp, which is primarily composed of cellulose obtained from plants. This natural polymer provides the foundation for creating a wide range of textiles with unique properties and applications.
Q 7. A comb is an example of _______ (1)
(a) Thermosetting plastic
(b) Thermoplastic
(c) Natural polymer
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Thermoplastics possess the unique property of becoming pliable and easily deformed when heated, allowing them to be effortlessly bent and reshaped as desired. This characteristic makes them highly versatile and widely used in various applications.
Q 8. Which of the following metals can be easily cut with a knife? (1)
(a) Aluminium
(b) Sodium
(c) Copper
(d) Iron
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Sodium is a metal which is soft and can be easily cut with a knife.
Q 9. A purple colour liquid of a non-metal is applied on wounds as an antiseptic. The nonmetal is (1)
(a) Chlorine
(b) Bromine
(c) Iodine
(d) Carbon
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Iodine, a non-metallic element, is commonly employed as a topical antiseptic for treating various skin conditions and preventing infection.
Q 10.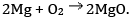 Which type of oxide is magnesium oxide? (1)
Which type of oxide is magnesium oxide? (1)
(a) Basic
(b) Acidic
(c) Neutral
(d) Mixture of all
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Metals, such as magnesium, readily combine with oxygen to form basic oxides, like magnesium oxide (MgO). This reaction typically occurs when metals are exposed to air, resulting in the formation of a thin oxide layer on the metal's surface, which helps protect it from further corrosion.
Q 11. A box is subjected to two forces as shown in the figure below. In which direction will the box move? (1)
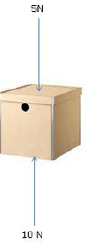 (a) Downwards
(a) Downwards
(b) Upwards
(c) Towards the left
(d) Towards the right
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The net force is 10 n − 5 n = 5 n (upwards).
Q 12. The example of the contact force is (1)
(a) Pulling a rope.
(b) Magnets attracted to each other.
(c) Electrostatic attraction.
(d) Gravitational pull of the Earth.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Pulling a rope necessitates the exertion of muscular force, which is classified as a contact force. In contrast, forces involved in various other scenarios have the ability to operate effectively from a distance.
Q 13. Gym and tennis shoes have soles made of rubber rather than leather because (1)
(a) A rubber sole is lighter than a leather sole.
(b) A rubber sole can be easily washed and cleaned.
(c) Rubber gives a better appearance.
(d) Rubber provides more friction than leather.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Gym and tennis shoes have rubber soles rather than leather because rubber provides more friction than leather.
Q 14. Sound quality is also termed (1)
(a) Pitch
(b) Frequency
(c) Oscillation
(d) Timbre
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Timbre or quality of sound is a characteristic by virtue of which we can distinguish between two sounds of the same pitch and loudness.
Q 15. Sounds having frequencies lower than 20 Hz are called (1)
(a) Ultrasonic sound
(b) Infrasonic sound
(c) Audible sound
(d) Periodic vibrations
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Sounds with frequencies lower than 20 Hz are below audible level and hence are called infrasonic sound.
Section B
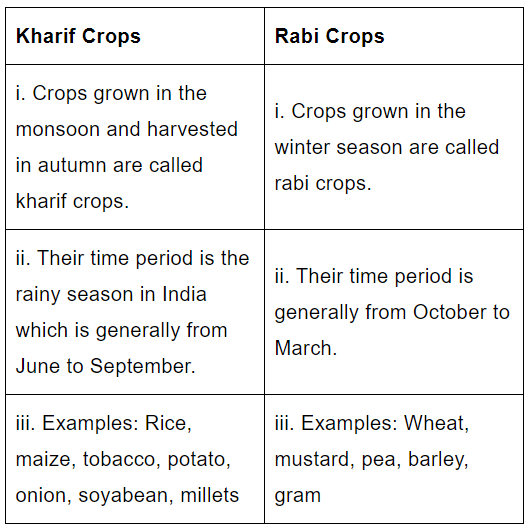
Q 16. Differentiate between Kharif and Rabi crops. (2)
Q 17. How are the modern methods of irrigation more efficient than traditional methods? (2)
Modern methods of irrigation help us to use water economically, i.e. it prevents wastage of water. These methods also help to save time and labour. Hence, they are more efficient than traditional methods of irrigation.
Q 18. Mention the important uses of microorganisms in agriculture and medicine. (2)
- Uses of microorganisms in agriculture: Microorganisms help in manure formation and in increasing soil fertility.
- Uses of microorganisms in medicine: Microorganisms are used to prepare antibiotics and vaccines.
Q 19. Plastics are replacing metals in the car industry. Give two possible reasons to support your answer. (2)
Plastics are replacing metals in the car industry because
- They are cheaper than metals.
- They can be easily moulded in various shapes.
Q 20. You are given some substances. Just by looking, can you classify those as metals and non-metals? Which physical property will you be using to classify? (2)
Yes. We can classify substances like metals and non-metals based on lustre. Metals have a shiny lustre, while non-metals generally do not have a shiny lustre.
Q 21. Identify the action as 'push' or 'pull' in each of the instances given below. (2)
(a) A cricket ball hit by a batsman
(b) Planting a pin on the pinboard
(c) Plucking the nail off the wall
(d) Picking up a shopping bag
(a) Cricket ball hit by a batsman: Push
(b) Planting a pin on the pinboard: Push
(c) Plucking the nail off the wall: Pull
(d) Picking up a shopping bag: Pull
Q 22. Explain why sliding friction is less than static friction. (2)
Friction is because of irregularities of two surfaces in contact. In sliding friction, the time given for the interlocking of the irregularities of the two surfaces is small, and that is why sliding friction is less than static friction.
Section C
Q 23. (i) State any three significant points of a biosphere reserve.
(ii) How does carbon dioxide cause global warming? (4)
(i) Significance of a biosphere reserve is as follows:
- To provide opportunities to conduct studies on different plants and animals.
- To protect the tribal people living in the area.
- To maintain the ecological balance of the area.
(ii)
- Carbon dioxide is known as a greenhouse gas.
- Plants absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide to carry out the process of photosynthesis.
- Deforestation, human activities and pollution have to lead to an increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide.
- CO2 traps the heat rays reflected by the Earth which leads to an increase in the average temperature of the Earth and causes global warming.
Q 24. (i) A farmer has carried out the harvest of his crop. He now wants to store these grains for a month before selling them to an appropriate buyer. What steps should he take to store the harvest?
(ii) How does the lowering of temperature help in increasing the shelf-life of food? (4)
(i) A farmer needs to carry out the following steps in order to ensure the safe storage of the harvest:
- The fresh crop should be properly dried in the Sun to reduce the moisture in them so as to prevent the attack by moulds and fungi.
- The grains should be stored in jute bags or metallic bins to protect them from pests.
- Specific chemical treatments must be carried out for storing large quantities of grains in big godowns to protect them from pests and microorganisms.
(ii) Lowering of temperature slows down the growth of bacteria, yeast and moulds, and inhibits the action of enzymes present in the food material and helps to increase the shelf-life of food.
Q 25. (i) Explain any three methods of food preservation.
(ii) Name any two common preservatives. (4)
(i) Three methods of food preservation are as follows:
- Preservation by common salt: Meat and fish are preserved by covering with dry salt. Salting prevents the growth of bacteria. Salting is also used in the preservation of amla, pickles, tamarind etc.
- Preservation by oil and vinegar: Vinegar to prevents the growth of bacteria. Hence, it is used in pickles, vegetables, fruits and fish.
- Heat and cold treatments: Some bacteria cannot thrive at high temperature and at low temperatures. Hence, certain food items (e.g. milk) are boiled, and food is stored in the refrigerator.
(ii) Sodium benzoate and sodium metabisulphite are two common preservatives.
Q 26. What is meant by biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials? Give examples of two biodegradable and two non-biodegradable materials. (4)
- A material which gets decomposed through natural processes (such as the action of bacteria) is called a biodegradable material.
Examples: Peels of vegetables and fruits, wood.- A material which is not easily decomposed by natural processes (such as the action of bacteria) is called non-biodegradable material.
Examples: Plastics, glass
Q 27. (i) What is coal?
(ii) ‘Coal is a source of energy’. Explain.
(iii) What is the real source of energy of coal? (4)
(i) Coal is a hard, black combustible mineral which consists mainly of carbon.
(ii) Coal is a source of energy:
- Coal is mainly carbon. When heated in air, coal burns and produces mainly carbon dioxide gas. A lot of heat energy is also produced during the burning of coal.
This can be written as- Coal is important because it can be used as a source of heat energy (just by burning it), or it can be converted into other forms of energy such as coal gas, coke or electricity.
(iii) The real source of energy of coal is solar energy (or the Sun's energy). This is because the plants and trees which decomposed to form coal grew on the Earth by absorbing sunlight energy during the process of photosynthesis.
Q 28. (i) Define balanced and unbalanced forces.
(ii) Which materials are considered brittle? Give two examples of brittle and nonbrittle substances. (4)
(i) Balanced Forces: When the resultant of all the forces acting on a body is zero, the forces are said to be balanced forces.
Unbalanced Forces: When the resultant of all the forces acting on a body is not zero, the forces are unbalanced forces.
(ii) The materials which break easily when force is applied to them are considered brittle.
Example: Ceramic and Glass.
Objects made of plastic and wood are non-brittle in nature.
Q 29. (i) With the help of diagrams, explain how the use of oil reduces friction between two surfaces in contact with each other.
(ii) Name two common lubricants. (4)
(i) When the oil is applied between the two surfaces in contact, a thin layer of oil is formed between the two surfaces. This layer separates the two surfaces a little bit due to which their interlocking is reduced to a large extent when they rub against each other.
(ii) Grease and oil are two commonly used lubricants.
Q 30.
(i) Define:
(a) Amplitude
(b) Time period
(c) Frequency
(ii) State whether the following statement is true or false:
Sound can travel through liquids and gases but not through solids. (4)
(i)
(a) Amplitude: The maximum displacement from the mean position during an oscillation is called the amplitude of the oscillation.
(b) Time period: The time taken to complete one oscillation is called the time period of the oscillation.
(c) Frequency: The number of oscillations per second is called the frequency of oscillation.
(ii) False. Sound can travel through solids, liquids and gases.
Q 31. What does LPG stand for? What are the advantages or characteristics which make LPG a good fuel? (4)
LPG stands for liquefied petroleum gas.
LPG is a good fuel because of its following advantages:
- LPG burns easily.
- LPG has a high calorific value. Due to this, a given amount of LPG produces a lot of heat.
- LPG burns with a smokeless flame and hence does not cause air pollution.
- LPG does not produce any poisonous gases on burning.
- LPG does not leave behind any solid residue on burning.
Section D
Q 32. State at least five beneficial effects of microorganisms. (5)
Some of the beneficial effects of microorganisms are as follows:
- In the making of curd, bread, and cake.
- In the production of alcohol, wine, vinegar, etc.
- In the preparation of medicines or drugs such as antibiotics.
- Microorganisms such as Rhizobium are used in agriculture to increase the fertility of the soil by fixing atmospheric nitrogen.
- Microorganisms clean up the environment by decomposing the organic matter of dead plants, dead animals, and animal wastes into harmless and useful simple substances.
Another synthetic fibre C is made of a polymer which consists of several glucose units joined one after the other.
(a) Which fibre could be:
(i) Terylene
(ii) Rayon
(iii) Nylon
(b) Which fibre (A, B or C) is prepared from a natural raw material?
(c) Which fibre (A, B or C) contains the same types of groups as those in a PET jar? (5)
(a)
(i) Terylene: B
(ii) Rayon: C
(iii) Nylon: A
(b) C (Rayon)
(c) B (Terylene)
Q 34. (i) What happens when we rub a plastic object such as a pen or a comb with hair? Which type of force is operating in this case?
(ii) Why are skis used to glide over snow? (5)
(i) When we rub a plastic object such as a pen or a comb with hair, it gets electrically charged. When such an object is brought close to bits of paper, the bits of paper get attracted to the object. This is due to the electrostatic force.
(ii) Skis are constructed such that they have a large surface area which helps to reduce the pressure on snow. This ensures that the skis do not sink in too far in the snow.
|
87 videos|558 docs|53 tests
|