Class 10 Social Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2019-20) - 2 | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
SOCIAL SCIENCE (CODE 087)
CLASS X – SESSION 2019-20
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER
Time Allowed: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
i. The question paper has 35 questions in all.
ii. Marks are indicated against each question.
iii. Questions from serial number 1 to 20 are objective type questions. Each question carries one mark. Answer them as instructed.
iv. Questions from serial number 21 to 28 are 3 marks questions. Answer of these questions should not exceed 80 words each.
v. Questions from serial number 29 to 34 are 5 marks questions. Answer of these questions should not exceed 120 words each.
vi. Question number 35 is a map question of 6 marks with two parts - 35 a. from History (2 marks) and 35b. from Geography (4 marks).
SECTION – A VERY SHORT ANS. QUESTIONS
Q.1. In which of the following constitutional list subjects of national importance such as defence are included? (1 Mark)
(a) Residuary Subjects
(b) Union List
(c) State List
(d) Concurrent List
Ans: (b) Union List
Q.2. Why were the Dalits ignored by the Congress for a long time? (1 Mark)
(a) Fear of offending the sanatanis
(b) Fear from Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
(c) Fear from socialism
(d) Fear from industrialists
Ans: (a) Fear of offending the sanatanis
Q.3. Which of the following is a formal lender ? (1 Mark)
(a) Moneylender
(b) Trader
(c) Friends
(d) Bank
Ans: (d) Bank
Q.4. Arrange the following in correct sequence. (1 Mark)
(i) Salt March
(ii) Simon Commission
(iii) Champaran Satyagraha
(iv) Rowlat Act
Option:
A. (i), (iii), (ii), (iv)
B. (iii), (iv), (ii), (i)
C. (ii), (i), (iv), (iii)
D. (iv), (ii), (i), (iii)
Ans: B. (iii), (iv), (ii), (i)
Q.5. Who discovered America? (1 Mark)
Or
Where was 'Chutney Music' popular?
Ans: Christopher Columbus discovered the vast continent America.
Or ‘Chutney Music’ was popular in Trinidad and Guyana.
Q.6. Give an example of non-renewable resources. (1 Mark)
OR
Which cold desert is relatively isolated from the rest of the country ?
Ans: Coal Minerals.
OR Ladakh
Q.7. Which of the following states has the Lowest Infant Mortality Rate in India ? (1 Mark)
(a) Punjab
(b) Haryana
(c) Bihar
(d) Kerala
Ans: (d) Kerala
Q.8. Identify the ore with which the following ore mines are associated with : (1 Mark)
(a) Balaghat mines
(b) Kudremukh mines
Ans: (a) Balaghat mines - Copper
(b) Kudermukh mines - Iron or
Q.9. Study the picture and answer the question that follows : (1 Mark)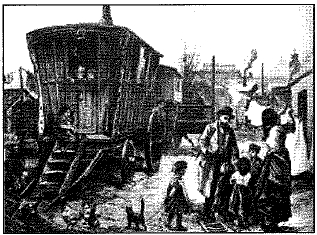
Which of the following aspect best signifies this image of 1879 AD ?
(a) People are working their house chores.
(b) People are enjoying some festivity.
(c) People are moving in search of work.
(d) Children are playing with their parents.
Ans: (c) People are moving in search of work.
Q.10. 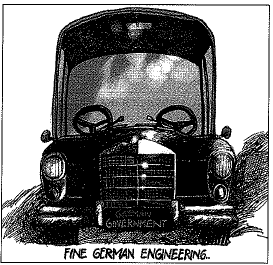
Which of the following option best signifies this cartoon ? (1 Mark)
(a) Problems of two party system
(b) A car with two steering
(c) Problems of a coalition government
(d) None of the above
Ans: (c) Problems of the coalition government
Q.11. After the introduction of refrigerated ships, animals were slaughtered for food at the starting point an d them transported as ________ . (1 Mark)
Ans. frozen meat
Q.12. The Constitution of India has given Hindi language, the status of_______. (1 Mark)
Ans: Official language
Q.13. Study the picture and answer the question that follows : (1 Mark)
Which of the following aspect best signifies this image of 'puppet theatre'?
(a) Prime Minister of Japan
(b) President of USA
(c) Prime Minister of Italy
(d) Prime Minister of Britain
Ans. (c) Prime Minister of Italy
Q.14. Development of a country can generally be determined by : (1 Mark)
(a) its per capital income
(b) its average literacy level
(c) health status of people
(d) All of the above
Ans: (d) All of the above
Q.15. (i)_________an American company is one of the world’s largest automobile manufacturer company with production spread over (ii)________countries of the world . (1 Mark)
Ans: (i) Ford Motors, (ii) 26
Q. 16. The sector in which government owns most of the assets and provides all services is called as________. (1 Mark)
Ans: Public Sector
Q.17. Correct the following statement and rewrite it.
Mahatma Gandhi found that salt was a powerful symbol that could unite the nation. He wrote a letter to viceroy Dalhousie urging twelve demands which included the demand to abolish the salt tax.
Or
In the country side, rich peasant communities like the Patidars of Uttar Pradesh and Jats of Haryana were enthusiastic supporters of the Civil Disobedience Movement. (1 Mark)
Ans: Mahatma Gandhi found that salt was a powerful symbol that could unite the nation. He wrote a letter to viceroy Irwin urging eleven demands which included the demand to abolish the salt tax.
Or
In the country side, rich peasant communities like the Patidars of Gujarat and the Jats of Uttar Pradesh were enthusiastic supporters of the Civil Disobedience Movement.
Q.18. Arrange the following in the correct sequence : (1 Mark)
(i) Harvesting the crop
(ii) Selling the surplus production in the market
(iii) Sowing the seeds in the soil
(iv) Cultivating the soil
Options: (a) (iii) - (i) - (ii) - (iv)
(b) (i) - (ii) - (iii) - (iv)
(c) (iv) - (iii) - (ii) - (i)
(d) (iii) - (iv) - (i) - (ii)
Ans: (d) (iii) - (iv) - (i) - (ii)
Q.19. What is the nature of Indian Federal System ? (1 Mark)
Ans: Indian federal system is an example of ‘holding together’ type of federalism.
Q.20. _________ is the process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries. (1 Mark)
Ans: Globalisation
SECTION – B SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Q.21. Which sector is called public sector? Give some examples. (3 Mark)
Or
What do you understand by organised sector? Also give its example.
Ans: The public sector refers to the part of the economy concerned with providing various government services. The composition of the public sector varies from country to country. In most countries, the public sector includes services like military, police, public transit and care of public roads, public education, healthcare etc. The public sector might provide services that a non-tax payer cannot be excluded from (such as street lighting) services. This sector benefits all of society rather than just the individual who uses the service.
Or
The organised sector covers those enterprises or places of work where the terms of employment are regular and people have, assured work. It is called organised because it has some formal processes and procedures. In organised sector, workers work for a fixed number of hours everyday. They get a weekly off day. In case of extra time for doing work is required, they are paid for it at double the normal rate. For e.g., a worker in a large factory, a clerk in a office, a doctor in a hospital etc.
Q. 22. Why was the Napoleonic rule over other regions unpopular with some sections of Europe? (3 Mark)
OR
Describe the ideology of liberalism during early 19th century.
Ans: Reasons of unpopularity of Napoleonic rule over other regions were :
(i) Administrative reforms did not go hand-in-hand with the political freedom. The newly annexed regions found themselves under the French rule..
(ii) The newly acquired territories had to face increased taxation and censorship.
(iii) The forced conscription into French army to conquer other parts of Europe was not popular with the new ly conquered people
OR
The Ideology of Liberalism during early 19th century:
(i) Liberalism in the early 19th century stood for freedom for the individual and equality to all before law for the new middle classes.
(ii) Politically, it emphasised the concept of government by consent.
(iii) It stood for the end of autocracy and clerical privileges.
Q.23. Which are the ideal conditions under which minerals may be mined ? (3 Mark)
Ans. The ideal conditions for mining of minerals are as given below :
(1) The mineral content of the ore must be in sufficient concentration to make its extraction commercially viable.
(ii) The type of formation determines the relative ease with which mineral ores may be mined.
(iii) This also determines the cost of extraction.
Q.24. Distinguish between the Coming Together Federations and,the Holding Together Federations. (3 Mark)
Ans: 
Q.25. How credit has its own unique role for development? State any three reasons. (3 Mark)
Or
Why the demand deposits are considered as money?
Ans: A major part of deposits is used as credit. Credit is an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods and services in return for the promise of future payment.
Credit has its own unique role for development because of the following reasons :
(i) Cheap and affordable credit leads to higher income and many people could then borrow cheaply for a variety of needs.
(ii) Farmers can buy agricultural inputs with credit or setup small scale and cottage industries.
(iii) People could setup new industries or trade as well. All these activities lead to development of the country.
Or
Due to following reasons the demand deposits are considered as money :
(i) Demand deposits can be withdrawn from the bank whenever it is required.
(ii) They are widely accepted as a means of payment, along with the currency, thus they are considered as money.
(iii) They are accepted widely as means of payment by way of a cheque instead of cash.
Q.26. How is Democracy a better form of government when compared with dictatorship or any other alternative government? (3 Mark)
Ans: Democracy is a better form of government when compared with dictatorship or any other alternative form of government because it:
(i) Promotes equality among citizens.
(ii) Enhances the dignity of the individual.
(iii) Improves the quality of decision making.
(iv) Provides a method to resolve conflicts.
(v) Allows room to correct mistakes.
Q.27. Describe any three functions of World Tirade Organisation. (3 Mark)
Ans: (i) With the liberalisation of foreign trade and investment, it is necessary to have an international organisation to supervise the trade between countries.
(ii) It sees that all the countries in the world liberalise their policies.
(iii) It allows free trade for all i.e., in developing and developed countries.
(iv) It implements the rules for trade in all the countries.
(v) WTO looks after to make globalisation more fair to create opportunities for all.
Q.28. "Credit is Useful as well Us harmful, it depends oh the risk involved.” Support the statement with examples. ; (3 Mark)
Or
Why should the banks and cooperative societies provide more loan fabilities to the rural households in India ? Give four reasons.
Ans. (i) Credit is a working capital which is required for production. The credit helps the farmers to meet the ongoing expenses of production, complete production on time, and thereby increase his earnings. Credit therefore plays a vital and positive role in, this situation.
(ii) The failure of crop may push the borrower into a situation from which recovery is very painful. InTmany cases farmers need to sell part of land to repay -the loan.
(iii) Whether the credit would be useful or not depends on the risks in the situation and whether there is some support in case of loss.
Or
(i) Most of the farmers are very poor, they do not have any surplus money.
(ii) Moneylenders charge very high rate of interest. This leads to increasing debt and debt trap.
(iii) Moneylenders use unfair means to get their money back.
SECTION – C LONG ANS. QUESTIONS
Q. 29. How was the history of nationalism in Britain unlike rest of the Europe? Briefly t trace the process of the unification of Britain. (5 Mark)
Ans: In Britain, the history of nationalism was different from rest of the Europe, There was no British nation before the 13th century. Different ethnic groups of people were there in the British isles, such as English, Welsh, Scot and Irish. Each of these ethnic groups had its own cultural and political traditions. Nationalism in Britain was.not the result of a sudden upheaval or revolution, it was due to a long drawn process.
The Act of Union (1707) between England and Scotland formed the United Kingdom of Great Britain. With the advent of English power, the English removed the cultural, political institutions of Scotland forcefully and the Scots were banned from speaking the Gaelic language and put on their national dress. There were two classes of the people in Ireland i.e. Catholics and Protestants.
The English liked the Protestants in comparison to Catholics. The English with the help of the Protestants suppressed the Catholics and forcibly United Ireland with the United Kingdom in 1801. The symbols of the new Britain are the National Flag (Union Jack), the National Anthem (God Save our Noble King) and the English language were actively promoted. Scotland and Ireland became the subordinate partners of the United Kingdom.
Q.30. Read the extract and answer the questions that follows: (5 Mark)
As you know, PDS is a programme which provides food grains and other essential commodities at subsidised prices in rural and urban areas.
India's food security policy has a primary objective to ensure availability of foodgrains to the common people at an affordable price. It has enabled the poor to have access to food. The focus of the policy is on growth in agriculture production and on fixing the support price for procurement of wheat and rice, to maintain their stocks. Food Corporation of India (FCI) is responsible for procuring and stocking foodgrains, whereas distribution is ensured by public distribution system (PDS).
The FCI procures foodgrains from the farmers at the government announced minimum support price (MSP). The government used to provide subsidies on agriculture inputs such as fertilizers, power and water. These subsidies have now reached unsustainable levels and have also led to large scale inefficiencies in the use of these scarce inputs. Excessive and imprudent use of fertilizers and water has led to waterlogging, salinity and depletion of essential micronutrients in the soil. The high MSB subsidies in input and committed FCI purchases have distorted the cropping pattern. Wheat and paddy crops are being grown more for the MSP they get. Punjab and Haryana are foremost examples. This has also created a serious imbalance in inter-crop parities.
(1) What is Public Distribution System?
(2) What are the objectives of India's food security policy?
(3) Describe any two ill-effects of subsidies on agriculture inputs.
Ans: (1) It is a programme which provides foodgrains and other essential commodities to the poor at subsidised prices in rural and urban areas.
(2) Objectives of India's food security policy:
(i) To ensure availability of foodgrains to the common people at an affordable price.
(ii) It has to enabled the poor to have access to food.
(iii) It also focuses on the growth in agriculture production and on fixing the support procurement of w heat and rice to maintain their stocks.
(3) All-effects of subsidies :
(i) These subsidies have now reached unsustainable levels and have also led to a large scale inefficiencies in the use of these inputs.
(ii) The high MSP subsidies in input and committed FCI purchases have distorted the cropping pattern.
Q.31. Describe the factors that are responsible for various objections against the multi-purpose projects. (5 Mark)
Ans: (i) Failure of the projects to achieve their objectives.
(ii) Some dams that were constructed to control floods, were responsible for the floods due to sedimentation in the reservoir.
(iii) Generally, big dams are not successful in controlling flood at the time of heavy and excessive rainfall because in such cases the release of water from dams aggravated the flood situation. This has happened in Maharashtra and Gujarat in 2006. The floods have not only devastated life and property but also caused extensive soil erosion.
(iv) Sedimentation deprived flood plains of silt, a natural fertiliser and was responsible for land degradation.
(a) Multi-purpose projects induce earthquakes, cause water-borne diseases and pests and pollution resulting from excessive use of water.
Or
Describe iron and steel industry with reference to its features, uses and method of production.
Ans. (i) Basic industry : Iron and steel industry is the basic industry because all the other industries depend on it for their machinery.
(ii) Production and heavy industry :
(a) It is a heavy industry because all the raw materials as well as finished goods are heavy and bulky entailing heavy transportation costs.
(b) Iron ore, coking coal and limestone are required in the ratio o f approximately 4 : 2 : 1 . (c) Some quantities of manganese are also required to harden the steel.
(iii) Uses : Steel is used to manufacture a variety of engineering goods, construction material, defence, medical, telephonic, scientific equipment and consumer goods.
Q.32. “Efficient means of transport are pre-requisites for the fast development.” Express your views in favour of this statement.
Or
Describe any five major problems faced by road transport in India. (5 Mark)
Ans: (i) Today, the world has been converted into a large village with the help of efficient and fast moving transport.
(ii) Transport has been able to achieve this with the help of equally developed communication system.
(iii) Today, India, is well-linked with the rest of the world despite its vast size, diversity and linguistic and socio-cultural plurality.
(iv) Railways, airways, waterways, newspapers, radio, television, cinema and internet, etc. have been contributing to its socio-economic progress in many ways.
(a) The trades from local to international levels have added to the vitality of its economy.
(vi) It has enriched our life and added substantially to growing amenities and facilities for the comforts of life.
Or
(i) The road network is inadequate in India and compared to demand and volume of traffic.
(ii) The condition of most of the roads is very poor, these become muddy during the rainy season.
(iii) They are highly congested in cities.
(iv) Most of the highways lack side amenities like telephone booths, emergency health services, police stations etc
(v) Most of the bridges and culverts are old and narrow
Q. 33. State any three differences between ferrous and non-ferrous minerals. ( 5 Mark)
Ans. Differences between ferrous and non-ferrous minerals are as follows:
Q.34. Explain why service sector is gaining more importance in the global economy. (5 Mark)
Ans: Tertiary sector in India has been growing rapidly for a number of reasons:
(i) In a developing country, the government has to take responsibility for the provision of basic services. For example, hospitals, educational institutions, post and telegraph services, police stations, courts, village administrative offices municipal corporations, defrence, transport, banks, insurance companies, etc.
(ii) The development of agriculture and industry led to the development of services such as trade, transport, storage, etc. Greater the development of the primary and secondary sectors, more would be the demand for such services.
(iii) As income levels rise, certain sections of people start demanding many more services, such as eating out, tourism, shopping malls, private hospitals, private schools, professional training, etc. This change is quite sharp in cities, especially in big cities.
(iv) Over the past decade or so, certain new services, such as those based on information and communication technology have become important and essential.
(v) Government policy of privatisation has also led to the growth of this sector.
MAP SKILL BASED QUESTION
Q.35. (a) On the given political outline map of India, mark and locate the following : (2 Mark)
(i) A place where Cotton Mill workers organised Satyagraha,
(ii) An incident took place here due to which the Non-cooperation Movement was called off.
(b) On the same outline map of India identify any four of the following with suitable symbols. (4 Mark)
(i) An international airport.
(ii) An iron and steel plant.
(iii) A software technology park in Jammu and Kashmir.
(iv) An iron ore mine.
(v) A major sugarcane producing state.
(vi) A dam on Narmada river.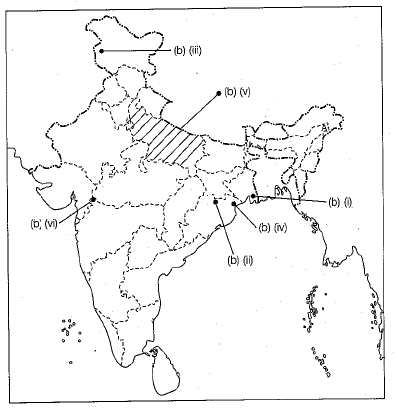
Ans: The answer map is given below ;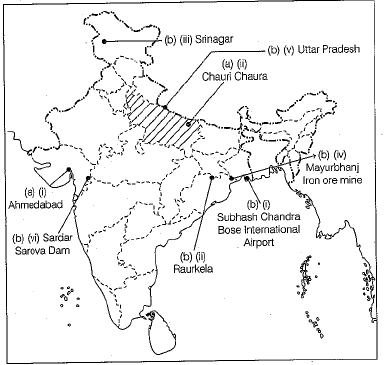
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Social Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2019-20) - 2 - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What is the importance of studying Social Science in Class 10? |  |
| 2. How can studying Social Science help in career development? |  |
| 3. What are the main topics covered in the Class 10 Social Science syllabus? |  |
| 4. How can I effectively prepare for the Class 10 Social Science exam? |  |
| 5. Are there any online resources available for studying Class 10 Social Science? |  |





















