Class 10 Social Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2020-21) - 4 | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
Class - X
Social Science
TIME: 3 Hrs.
M.M: 80
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them :
1. The question paper comprises five sections - A, B, C, D and E. There are 32 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
2. Section A - Question no. 1 to 16 are Objective Type Questions of 1 mark each.
3. Section B - Question no. 17 to 22 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. The answer to each question should not exceed 80 words.
4. Section C - Question no. 23 to 26 are Source Based Questions, carrying 4 marks each.
5. Section D - Question no. 27 to 31 are Long Answer Type Questions, carrying 5 marks each. The answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
6. Section E - Question no. 32 is Map-Based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 32.1 from History (2 marks) and 32.2 from Geography (3 marks).
7. There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions has to be attempted.
8. In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section A
Q.1. Read the source given below and fill in the blank that follows: (1 marks)
The government has launched a major road development project linking Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai Mumbai and Delhi with a six-lane superhighway. The North-South Corridor linking Srinagar (Jammu & Kashmir) and Kanyakumari (Tamil Nadu), and East-West Corridor connecting Silchar (Assam) and Porbander (Gujarat) through a highway are part of this project.
These projects are being implemented by ___________ Complete the sentence.
Ans. National Highway Authority of India (NHAI)
Q.2. Which of the following agreements gave seats to the depressed classes in the Provincial and Central Legislative Council? (1 Mark)
(a) Poona Pact
(b) Lucknow Pact
(c) Gandhi – Irwin Pact
(d) None of these
Ans. a
Q.3. “When France sneezes, the rest of Europe catches a cold”. Who among the following said this popular line? (1 Mark)
(a) Giuseppe Mazzini
(b) Metternich
(c) Otto Von Bismarck
(d) Giuseppe Garibaldi
Ans. b
Q.4. Match the following items given in Column A with those in Column B. Choose the correct answer from the options given below: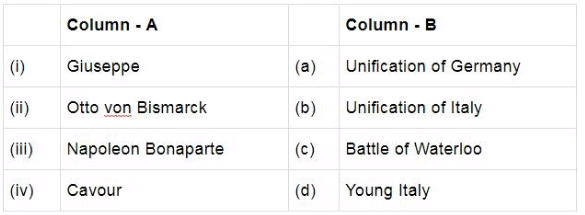
(a) (i) – (b), (ii) – (c), (iii) – (d), (iv) – (a)
(b) (i) – (d), (ii) – (c), (iii) – (b), (iv) – (a)
(c) (i) – (d), (ii) – (a), (iii) – (c), (iv) – (b)
(d) (i) – (a), (ii) – (d), (iii) – (b), (iv) – (c)
Ans. c
Q.5 Complete the following table with correct information with regard to alluvial soils: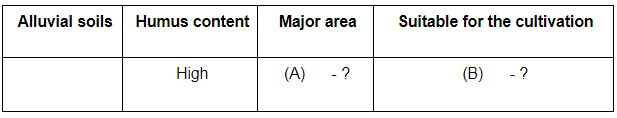
Ans. (A) Northern Plains
(B) Sugarcane/Paddy
Q.6. By which name is specialized cultivation of fruits and vegetables known? (1 marks)
Ans. Horticulture
OR
What is the full form of ICAR?
Ans. Indian Council of Agricultural Research.
Q.7. Which one of the following industries generates the largest amount of employment? (1 Mark)
(a) Cotton Industry
(b) Jute Industry
(c) Textile Industry
(d) Silk Industry
Ans. c
Q.8. Which one of the following means of transport is used for carrying solids in a slurry form? (1 Mark)
(a) Trucks
(b) Railways
(c) Pipelines
(d) Ships
Ans. c
Q.9. Limestone, silica, alumina and gypsum are the raw materials of _____ industry. (1 marks)
Ans. Cement
Q.10. Where did India conduct its first-ever nuclear test? (1 marks)
Ans. In Pokhran (Rajasthan)
OR
What status has been given to Hindi by the Constitution of India?
Ans. Official language of the country.
Q.11. At present, how many members are there in WTO? (1 Mark)
(a) 139
(b) 150
(c) 148
(d) 164
Ans. d
Q.12. In recent years, the central and state governments in India are taking special steps to attract foreign companies to invest in India. Industrial zones are being set up. Companies that set up production units in these zones do not have to pay taxes for an initial period of five years. (1 Mark)
Analyse the information given above, considering one of the following options correct:
(a) Industrial Zones
(b) Agricultural Zones
(c) Special Economic Zones
(d) Foreign Investment
Ans. c
Q.13. In the question given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option:
Assertion (A): Periodically, banks have to submit information to the Finance Minister on how much they are lending, to whom, at what interest rate, etc.
Reason (R): The Finance Minister monitors the banks in actually maintaining cash balance.
Options :
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(d) Both (A) and (R) are wrong.
Ans. d
Q.14. Find the incorrect option: (1 Mark)
(a) Secondary sector provides employment to a large number of people
(b) Secondary sector is also called the service sector
(c) Secondary sector uses mechanical power and modern use of labour
(d) Secondary sector produces goods for local and international consumers
Ans. b
Q.15. Which of the following option best signifies this cartoon? (1 Mark) (a) Challenge of dynastic succession
(a) Challenge of dynastic succession
(b) Challenge of lack of internal democracy within parties
(c) Challenge of the growing role of money and muscle power in politics
(d) None of the above.
Ans. c
Q.16 Which one of the following states was ruled by an Italian princely house before the unification of Italy? (1 Mark)
(a) Lombardy
(b) Kingdom of Two Sicilies
(c) Venetia
(d) Sardinia – Piedmont
Ans. d
Section B
Q.17. Why did Gandhiji start Non- Cooperation Movement? Explain. (3 Mark)
Ans. (i) Against the Rowlatt Act
(ii) Jallianwala Bagh incidence
(iii) Khilafat Andolan
Detailed Answer :
(i) Gandhiji launched the Non- Cooperation Movement with the aim of self-governance and obtaining full independence.
(ii) The Indian National Congress withdrew its support for British reforms against the Rowlatt Act and the Jallianwala Bagh incident.
(iii) Indian Muslims who had participated in the Khilafat Movement to restore the status of the Caliph (the spiritual leader of Muslims) gave their support to the Non- Cooperation Movement.
Q.18. Explain the measures and practices introduced by the French revolutionaries to create a sense of collective identity amongst the French people. (3 Mark)
Ans. (i) The ideas of La Patrie (the fatherland) and Le Citoyen (the citizen) emphasized the notion of a united community enjoying equal rights under a constitution.
(ii) A new French flag, the tricolour was chosen to replace the Royal Standard.
(iii) Estates General was elected by the body of active citizens and renamed the National Assembly.
(iv) New hymns were composed and martyrs commemorated all in the name of the nation.
(v) A centralized system of administration was introduced, uniform laws were made for all citizens.
OR
“Like Germany, Italy too had a long history of political fragmentation”. Explain.
Ans. (i) Italians were scattered over several dynastic states.
(ii) Sardinia-Piedmont was ruled by an Italian princely house.
(iii) Italy was unified in 1861 and Victor Emmanuel II was proclaimed King of United Italy.
(iv) Giuseppe Mazzini had sought to put together a programme for the unitary Italian Republic.
(v) The unification of Italy as a result of many wars, through a tactful diplomatic alliance with France by Chief Minister Cavour.
(vi) Garibaldi joined the fray.
Q.19. Suggest and explain any three ways to protect the land from degradation in various states of India. (3 Mark)
Ans. (i) Afforestation.
(ii) Proper management of grazing.
(iii) Planting of shelter belts of plants.
(iv) Stabilization of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes.
(v) Control of mining activities.
(vi) Proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment.
(vii) Any other relevant point
Detailed Answer :
(i) Afforestation and proper management of grazing can help to some extent.
(ii) Planting of shelterbelts, control overgrazing, stabilization of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes is some of the methods to check land degradation in arid areas.
(iii) Proper management of wastelands, control of mining activities, proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment can reduce land water degradation in industrial and suburban areas.
(iv) Control ploughing is another step to conserve land. The fields are ploughed, harrowed and sown along the natural contour of the hills.
Q.20. Describe any three steps taken by the government towards decentralization in the year 1992. (3 Mark)
Ans. (i) Constitution mandates to hold regular elections to local government bodies.
(ii) Reservation of seats in the elected bodies and the executive heads of these institutions for the Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes and Other Backward Classes.
(iii) Reservation of at least one-third of all positions for women.
(iv) Creation of an independent institution called the State Election Commission in each state to conduct panchayat and municipal elections.
(v) The state governments are required to share some powers and revenue with local government bodies.
OR
Describe any three federal features of Indian democracy.
Ans. (i) Division of powers between the centre and states.
(ii) There are three lists: Union List, State List, Concurrent List.
(iii) Residuary subjects.
(iv) Control of union territories with the Centre.
Detailed Answer :
(i) The Indian Constitution clearly provided a threefold distribution of legislative powers between the Union Government and the State Governments.
(ii) There are three lists: Union List, State List and Concurrent List.
(iii) Union List on which Centre can make laws such as defence, currency, etc.
(iv) State List on which State can make laws such as police, trade, agriculture, etc.
(v) Concurrent List on which both the Centre and State can legislate, such as education, marriage, etc.
(vi) Centre legislates on residuary subjects.
(vii) Centre also has special powers to control Union territories.
Q.21. Imagine yourself to be XYZ, a member of a women Self Help Group. Analyse the ways through which your group provides a loan to the members. (3 Mark)
Ans.
(i) Self Help Groups pool their savings.
(ii) A typical SHG has 15–20 members, usually belonging to one neighbourhood, who meet and save regularly.
(iii) Saving per member varies from ` 25 to ` 100 or more, depending on the ability of the people to save.
(iv) Members can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs.
(v) The group charges interest on these loans but this is still less than what the moneylender charges.
(vi) After a year or two, if the group is regular in savings, it becomes eligible for availing a loan from the bank.
Q.22. ‘The issue of sustainability is important for development.’ Examine the statement. (3 Mark)
Ans.
(i) Sustainable development aims at fulfilling the needs of today without compromising the needs of the future generation.
(ii) Sustainability is the capability to use the resources judiciously and maintain the ecological balance.
(iii) It lays emphasis on environmental protection and checks environmental degradation.
(iv) Any other relevant point.
Section C
Q.23. Read the source given below and answer the following questions :
Similar female allegories were invented by artists in the nineteenth century to represent the nation. In France, she has christened Marianne, a popular Christian name, which underlined the idea of a people's nation. Her characteristics were drawn from those of Liberty and the Republic - the red cap, the tricolour, the cockade. Statues of Marianne were erected in public squares to remind the public of the national symbol of unity and to persuade them to identify with it. Marianne images were marked on coins and stamps. Similarly, Germania became the allegory of the German nation. In visual representations, Germania wears a crown of oak leaves, as the German oak stands for heroism.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
23.1 What was the name given to the female allegory in France? (1 Mark)
(a) Germania
(b) Mary
(c) Flora
(d) Marianne
Ans. d
23.2 Germania became the allegory of _____________. (1 Mark)
(a) France
(b) Italy
(c) Germany
(d) Britain
Ans. c
23.3 What does the German oak stand for? (1 Mark)
(a) Liberty
(b) Heroism
(c) Justice
(d) Strength
Ans. b
23.4 ________ image were marked on coins and stamps. (1 Mark)
(a) Germania
(b) Marianne
(c) Mary
(d) Jesus
Ans. b
24. Read the source given below and answer the following questions :
Maize: It is a crop that is used both as food and fodder. It is a Kharif crop that requires a temperature between 21°C to 27°C and grows well in old alluvial soil. In some states like Bihar, maize Is grown in the rabi season also. The use of modern inputs such as HYV seeds, fertilisers and irrigation have contributed to the increasing production of maize. Major maize-producing states are Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and Madhya Pradesh.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
24.1 In which of the following states, maize ingrown in rabi season? (1 Mark)
(a) Uttar Pradesh
(b) Bihar
(c) Karnataka
(d) Telangana
Ans. b
24.2 Maize is used both as food and _________. (1 Mark)
(a) manure
(b) beverage
(c) fodder
(d) fibre
Ans. c
24.3 How much temperature is required for maize? (1 Mark)
(a) 21 °C to 27 °C
(b) 22 °C to 28 °C
(c) 18 °C to 22 °C
(d) 25 °C to 30 °C
Ans. a
24.4 Which of the following states is the largest producer of maize? (1 Mark)
(a) Telangana
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Andhra Pradesh
(d) Karnataka
Ans. d
25. Read the source given below and answer the following questions :
How many languages do we have in India? The answer depends on how one counts it. The latest information that we have is from the Census of India held in 2001. This census recorded more than 1500 distinct languages which people mentioned as their mother tongues. These languages were grouped together under some major languages. For example languages like Bhojpuri, Magadhi, Bundelkhand, Chhattisgarhi, Rajasthani, Bhili and many others were grouped together under 'Hindi'. Even after this grouping, the Census found 114 major languages. Of these 22 languages are now included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution and are, therefore, called 'Scheduled Languages'. Others are called 'non- Scheduled Languages'. In terms of languages, India is perhaps the most diverse country in the world.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
25.1 How many languages are spoken in India? (1 Mark)
(a) More than 1200
(b) More than 1100
(c) More than 1400
(d) More than 1300
Ans. d
25.2 Bhojpuri, Magadhi, ____________ , Rajasthani and many others were grouped under 'Hindi'. (1 Mark)
(a) Bundelkhandi
(b) Urdu
(c) Kashmiri
(d) Bengali
Ans. a
25.3 How many languages are included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution? (1 Mark)
(a) 18
(b) 20
(c) 21
(d) 22
Ans. d
25.4 In terms of __________, India is perhaps the most diverse country in the world. (1 Mark)
(a) population
(b) languages
(c) forests
(d) religions
Ans. b
26. Read the source given below and answer the following questions :
Besides banks, the other major source of cheap credit in rural areas is cooperative societies (or cooperatives). Members of a cooperative pool their resources for cooperation in certain areas. There are several types of cooperatives possible such as farmers cooperatives, weavers cooperatives, industrial workers cooperatives, etc. Krishak Cooperative functions in a village not very far away from Sonpur.
It has 2300 farmers as members. It accepts deposits from its members. With these deposits as collateral, the Cooperative has obtained a large loan from the bank. These funds are used to provide loans to members. Once these loans are repaid, another round of lending can take place. Krishak Cooperative provides loans for the purchase of agricultural implements, loans for cultivation and agricultural trade, fishery loans, loans for construction of houses and for a variety of other expenses.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
26.1 The passage given above relates to which of the following options? (1 Mark)
(a) Interest on the loan
(b) Formal source of credit
(c) Informal source of credit
(d) Krishak cooperative
And: b
26.2 How many members are there in the Krishak cooperative in a village near Sonpur? (1 Mark)
(a) 1200
(b) 2300
(c) 2100
(d) 200
Ans. b
26.3 Besides banks, what is the other source of cheap credit in rural areas? (1 Mark)
(a) Cooperative societies
(b) Moneylenders
(c) Friends
(d) Shopkeepers
Ans. a
26.4 Who provides loans to farmers for various agricultural activities? (1 Mark)
(a) Bank
(b) Moneylender
(c) Self Help Group
(d) Krishak cooperative
Ans. d
Section D
Q.27. Why did Mahatma Gandhi decide to call off the Civil Disobedience Movement? Explain. (5 marks)
Ans. Mahatma Gandhi decided to call off Civil Disobedience Movement because :
(i) Worried by the development of Civil Disobedience Movement, the colonial government began arresting the Congress leaders one by one.
(ii) This led to violent clashes in many places.
(iii) When Abdul Ghaffar Khan, a devout disciple of Mahatma Gandhi was arrested in April 1930, angry crowd demonstrated in the streets of Peshawar, facing armoured cars and police firing. Many were killed.
(iv) A month later, when Mahatma Gandhi was arrested; industrial workers in Solapur attacked police force, municipal buildings, law courts, railway stations and all other structures that symbolised British rule.
(v) A frightened government responded with the policy of brutal repression.
(vi) The peaceful satyagrahis were attacked, women and children were beaten and about 1 lakh people were arrested.
Under these circumstances Mahatma Gandhi called off the Civil Disobedience Movement.
OR
How did the peasants of Awadh use different methods to achieve their goal? Explain with examples.
Ans. (i) Peasants of Awadh were led by Baba Ramchandra, a Sanyasi. The movement was against talukdars and landlords.
(ii) The landlords and talukdars demanded exorbitantly high rents and other cesses. Peasants had to do begar and work at landlords farms without any payment.
(iii) As tenants, the farmers had no security of tenure. The peasant movement demanded a reduction of revenue, the abolition of begar and social boycott of oppressive landlords.
(iv) In many places, nai dhobi bandhs were organised by panchayats to deprive landlords of the services of barbers and washermen.
(v) Oudh Kisan Sabha was set up headed by Jawaharlal Nehru, Baba Ramchandra and few others. Within a month, over 300 branches were set up in the villages. The peasants developed in forms that the Congress leadership was unhappy with.
In 1921, the houses of talukdars and merchants were attacked. Bazaars were looted. Grain hoards were taken over.
Q.28. Explain any five differences between Public and Private sector. (5 marks)
Ans. Comparison between Private sector and Public sector:
(i) Most of the assets of public sector are owned by the government while private sector is owned by individuals or group of individuals.
(ii) Government provides all services in public sector, while in private sector it depends on private owner.
(iii) Government raises money for various activities through taxes while private sector collects money for the services they provide.
(iv) Activities in the private sector are guided by the motive to earn profits, while public sector is not just to earn profits.
(v) Railways, Post office are examples of public sector while Tata Steel and Reliance are examples of private sector.
Detailed Answer:
The following are the major differences between public sector and private sector:
(i) Public Sector is a part of the country's economy where the control and maintenance are in the hands of government. If we talk about Private Sector, it is owned and managed by the private individuals and corporations.
(ii) The aim of the public sector is to serve people, but private sector enterprises are established with the profit motive.
(iii) In the public sector, the government has full control over the organisations. Conversely, Private Sector companies enjoy less government interference.
(iv) The employees of the public sector have the security of the job, along with that they are given the benefits of allowances, perquisites, and retirement like gratuity, pension, superannuation fund, etc., which are absent in the case of the private sector.
(v) In the private sector, working environment is quite competitive which is missing in the public sector because they are not established to meet commercial objectives.
(vi) In general, Public Sector, uses the basis of Seniority for promoting employees, however, merit cum seniority is also taken as a base for promoting employees unlike the Private Sector, where performance is everything, and so merit is considered as a parameter to promote them.
Q.29. Elucidate some of the recent efforts taken in our country to reform political parties and its leaders. (5 marks)
Ans. (i) The Constitution was amended to prevent elected MLA's and MP's from changing parties. This was done because many elected representatives were indulging in defection in order to become ministers or for cash rewards. Now, if any MLA or MP changes parties, he or she will lose the seat in the legislature.
(ii) The Supreme Court passed an order to reduce the influence of money and criminals. Now, it is mandatory for every candidate who contests elections to file an affidavit giving details of his property and criminal cases pending against him. The new system has made a lot of information available to the public. But there is no system of check if the information given by the candidates is true.
(iii) The Election Commission passed an order making it necessary for political parties to hold their organisational elections and file their income tax returns.
(iv) The parties have started doing so but sometimes it is a mere formality. It is not clear if this step has led to greater internal democracy in political parties.
Q.30. “Democracy is based on the idea of deliberation and negotiation”. Examine the statement. (5 marks)
Ans. Democracy is based on the idea of deliberation and negotiation:
(i) Democracy gives importance to deliberation and public opinion.
(ii) The democratic government will take more time to follow procedures before arriving at a decision.
(iii) Its decisions may be both more acceptable to the people and more effective.
(iv) Democracy ensures that decision making will be based on norms and procedures.
(v) Transparency as people have the right and the means to examine the process of decision making.
(vi) It follows procedures and is accountable to the people.
(vii) The democratic government develops mechanisms for citizens to hold the government accountable.
(viii) Democratic government follows mechanisms for citizens to take part in decision making whenever they think fit.
OR
Describe any five outcomes of Democracy.
Ans. Five outcomes of Democracy:
(i) Accountable, responsive and legitimate government.
(ii) Economic growth and development.
(iii) Reduction of inequality and poverty.
(iv) Accommodation of social diversity.
(v) Dignity and freedom of the citizens.
(vi) Any other relevant point to be explained.
Detailed Answer:
Five outcomes of democracy :
(i) In a democratic nation, the government is accountable to the citizens. It is responsive to the needs and expectations of the citizens. Moreover, the government is efficient and effective. The democratic governments work on the principle of deliberation and negotiation, so delays take place.
(ii) In a democracy, decisions are based on norms and procedures. Decision making is transparent, i.e., every citizen has the right to examine the entire process of decision making.
(iii) In a democracy, the right to question the process of decision making is absent.
(iv) It is provided that a democratic government is accountable, but there isn't any mechanism to hold the government accountable and the decision making is not based on norms and procedures.
(v) Democracy is solely based on political equality. Every citizen has an equal weight in electing representatives. However, the same is not true in the economic field. In democratic countries, the poor usually become poorer and often find it hard to cater to the basic essentials of life like food, clothing, higher education, and health. Democracies have massively failed in this regard.
Q.31. Highlight any five features of Hazira-Vijaipur-Jagdishpur gas pipeline. (5 marks)
Ans. (i) This pipeline is about 1700 kms long.
(ii) Hazira-Vijaipur-Jagdishpur cross country gas pipeline links Mumbai High and Bassein with the fertilizer, power and industrial complexes in western and northern India.
(iii) This artery has provided an impetus to India's gas production.
(iv) The power and fertilizer industries are the key users of natural gas.
(v) Use of Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) for vehicles to replace liquid fuels is gaining wide popularity in the country.
OR
Explain with examples the conditions responsible for uneven distribution pattern of the railway network in India.
Ans. The distribution pattern of the railway network:
(i) The Northern Plains with their vast level land, high population density and rich agricultural resources provide the most favourable condition for their growth.
(ii) In the hilly terrains of the peninsular region, railway tracks are laid through low hills, gaps or tunnels.
(iii) The Himalayan mountainous regions too are unfavourable for the construction of railway lines due to high relief, sparse population and lack of economic opportunities.
(iv) It was difficult to lay railway lines on the sandy plains of western Rajasthan, swamps of Gujarat, forested tracks of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and Jharkhand.
(v) The contiguous stretch of Sahyadri could be crossed only through gaps or passes (Ghats).
(vi) The development of the Konkan railway along the west coast has facilitated the movement of passengers and goods.
Section E
Map-Based Questions
Q.32. (i) Two places A and B have been marked on the given outline map of India.
Identify them and write their correct names on the lines drawn near them.
(A) Indian National Congress session at this place in 1927 (1 Mark)
(B) Mahatma Gandhi organized a Satyagraha Movement at this place for indigo planters (1 Mark)
(ii) On the same outline map of India, locate and label any THREE of the following with suitable Symbols.
(a) Rana Pratap Sagar Dam
(b) Namrup Thermal Plant
(c) Bengaluru Software Technology Park
(d) Visakhapatnam Port
(e) Narora Nuclear Power Plant (3 Mark)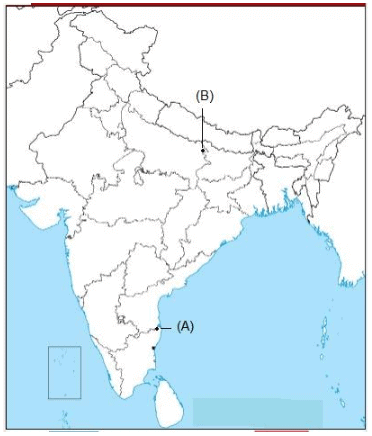 Ans. (i) & (ii)
Ans. (i) & (ii)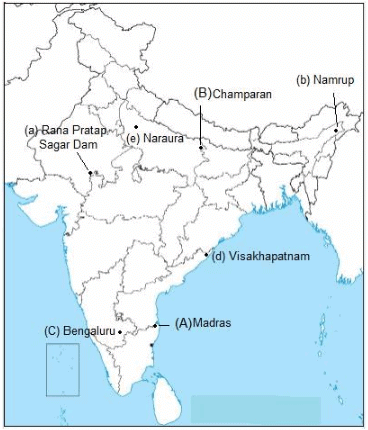
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Social Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2020-21) - 4 - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What is the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Class 10 Social Science? |  |
| 2. How can the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Class 10 Social Science help students? |  |
| 3. Are the questions in the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Class 10 Social Science the same as the actual exam? |  |
| 4. Can solving the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Class 10 Social Science guarantee good marks in the exam? |  |
| 5. Where can students find the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Class 10 Social Science? |  |





















