Sampling theorems | Engineering Mathematics for Electrical Engineering - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are the sampling methods or Sampling Techniques? |

|
| What is Probability Sampling? |

|
| What is Non-Probability Sampling? |

|
| Probability Sampling vs. Non-probability Sampling Methods |

|
What are the sampling methods or Sampling Techniques?
In Statistics, sampling methods involve studying the population by gathering and analyzing data. This forms the basis of vast sample spaces. Different sampling techniques exist, categorized into two groups, some targeting hard-to-reach groups.Types of Sampling Method
- Probability Sampling
- Non-probability Sampling
What is Probability Sampling?
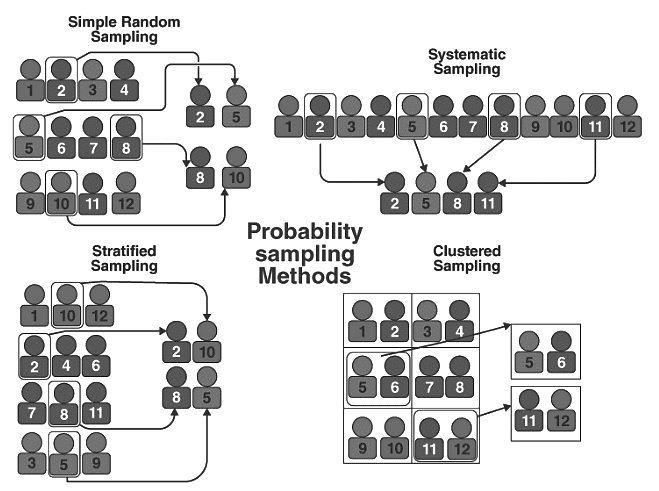
The probability sampling method involves random selection, where all eligible individuals have an equal chance of being selected from the entire sample space. It is more time-consuming and costly than non-probability sampling but ensures a representative sample of the population.- Probability Sampling Types: Probability Sampling includes simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and clustered sampling. Each method has specific characteristics and uses within research.
- Simple Random Sampling: Simple random sampling offers each item in the population an equal chance of selection, making it a method of chance selection. With a large sample size and random item selection, it ensures a representative sample. “Method of chance Selection”. As the sample size is large, and the item is chosen randomly, it is known as “Representative Sampling”.
Example: Suppose we aim to choose a random sample of 200 students from a school. We can assign a unique number to each student in the school's database ranging from 1 to 500. By using a random number generator, we can pick a sample of 200 numbers. - Systematic Sampling: In systematic sampling, items are chosen from the target population by selecting a random starting point and then picking every nth item where n is a fixed sample interval. This interval is determined by dividing the total population size by the desired sample size.
Example: Let's say there are 300 students in a school, and their names are listed in reverse alphabetical order. To perform systematic sampling, we start by randomly selecting a starting number, like 5. Starting from the 5th student, we then select every 15th student from the list. This process helps us form a sample of students. - Stratified Sampling: In stratified sampling, the total population is divided into smaller groups based on specific characteristics. Statisticians then randomly select samples from each group.
For instance, if we have three bags (A, B, and C) with different numbers of balls, such as 50 balls in bag A, 100 in bag B, and 200 in bag C, we might choose a sample proportionally—like 5 balls from bag A, 10 from bag B, and 20 from bag C. - Clustered Sampling: Clustered sampling involves forming groups with similar characteristics from the population. Each group has an equal chance of being selected. Simple random sampling is often used within these clusters.
For example, if an educational institution has ten branches across a country, each with a similar number of students, to collect data efficiently, researchers might use random sampling to select a few branches as clusters instead of visiting every unit.
What is Non-Probability Sampling?
- The non-probability sampling method involves the researcher choosing the sample based on personal judgment rather than random selection.
- In this method, not all members of the population have an equal chance to be part of the study.
Non-Probability Sampling Types
Non-probability sampling methods include:- Convenience sampling
- Consecutive sampling
- Quota sampling
- Judgmental sampling
- Snowball sampling
Convenience Sampling
- In convenience sampling, samples are chosen from the population based on their immediate availability to the researcher.
- The samples are selected easily, without ensuring they represent the entire population.
- Example:
- In a study on customer support services in a specific region, a few customers are asked to fill out a survey after making a purchase.
- This method is convenient for data collection but may not reflect the views of all customers in the area due to the limited sample selection.
Consecutive Sampling
- Consecutive sampling is akin to convenience sampling but with a slight twist. The researcher selects one person or a group and studies them for a period before moving on to another group if necessary.
Quota Sampling
- Quota sampling involves selecting individuals to represent the population based on specific traits. The subsets chosen provide a useful data collection that can generalize the entire population.
Purposive or Judgmental Sampling
- Purposive sampling relies solely on the researcher's knowledge for sample selection. This method aims for highly accurate answers with minimal error, also known as judgmental or authoritative sampling.
Snowball Sampling
- Snowball sampling, a chain-referral technique, involves identifying hard-to-find traits in samples. Each member found is asked to locate other units, all from the same target population.
Remember, each sampling method has its unique approach and application in research, influencing the quality and reliability of the data collected.
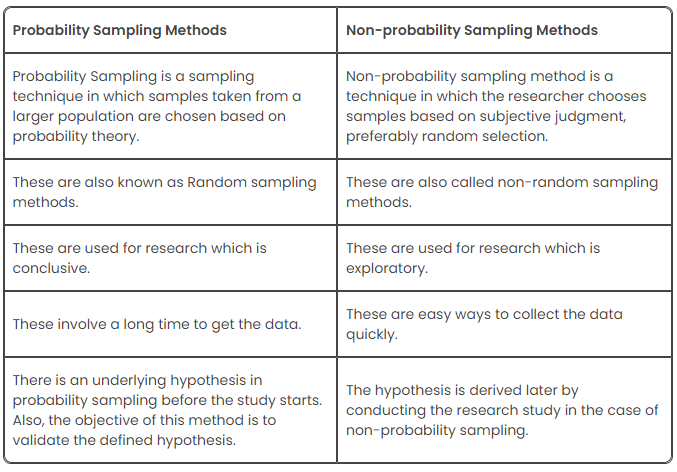
Probability Sampling vs. Non-probability Sampling Methods
The document Sampling theorems | Engineering Mathematics for Electrical Engineering - Electrical Engineering (EE) is a part of the Electrical Engineering (EE) Course Engineering Mathematics for Electrical Engineering.
All you need of Electrical Engineering (EE) at this link: Electrical Engineering (EE)
|
44 videos|109 docs|58 tests
|
Related Searches




















