Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
Class 1 Exam > General Knowledge for Young Learners > Flashcards: Sense Organs
|
52 videos|107 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Flashcards: Sense Organs Flashcard - General Knowledge for Young Learners - Class 1
| 1. What are the five sense organs? |  |
Ans. The five sense organs are the eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin. These organs enable us to perceive and interpret different sensory stimuli from the environment.
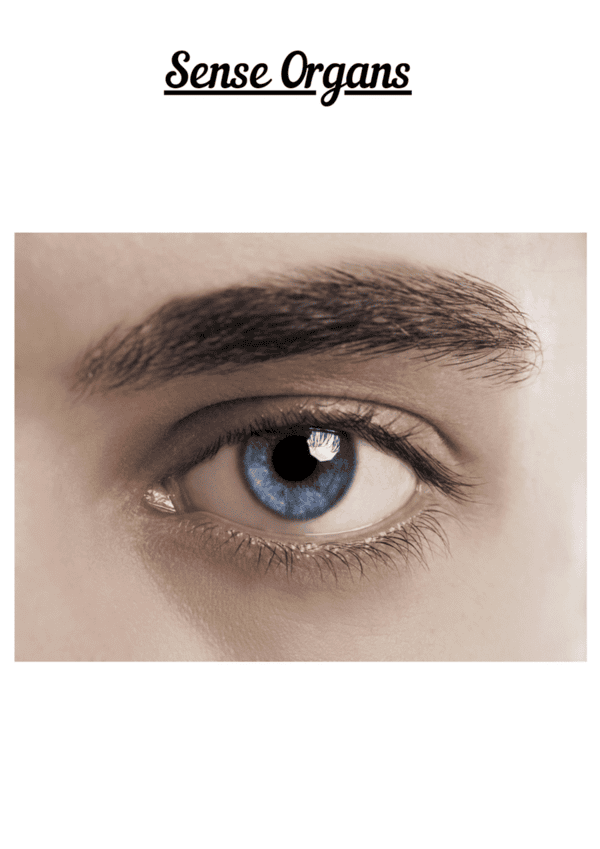
| 2. How do the eyes work as sense organs? |  |
Ans. The eyes are complex sense organs that allow us to see and perceive the visual world. They consist of various structures such as the cornea, iris, lens, and retina. When light enters the eye, it passes through the cornea and is focused by the lens onto the retina. The retina contains light-sensitive cells called photoreceptors, which convert light into electrical signals that are sent to the brain for interpretation.
| 3. What is the role of the ears as sense organs? |  |
Ans. The ears function as sense organs responsible for hearing and maintaining balance. The outer ear collects sound waves, which then travel through the ear canal and vibrate the eardrum. These vibrations are transmitted to the inner ear, where they stimulate hair cells in the cochlea. These hair cells convert the sound vibrations into electrical signals that are sent to the brain, allowing us to hear and perceive different sounds.
| 4. How does the nose function as a sense organ? |  |
Ans. The nose serves as a sense organ for smelling and detecting odors. It contains specialized cells called olfactory receptors, which are responsible for detecting different smells. When we inhale, odor molecules enter the nose and bind to these receptors. The receptors then send signals to the brain, where they are interpreted as specific smells.
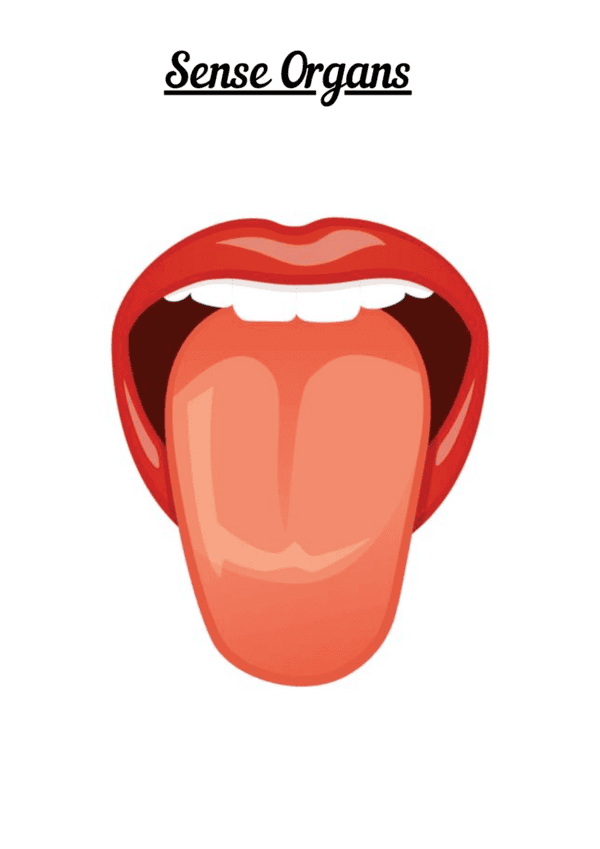
| 5. What is the role of the tongue as a sense organ? |  |
Ans. The tongue plays a crucial role in our sense of taste. It contains taste buds, which are sensory organs that detect different flavors. When we eat or drink, molecules from the food or drink stimulate these taste buds. The taste buds then send signals to the brain, allowing us to perceive and distinguish between different tastes such as sweet, sour, salty, and bitter.
Related Searches