Sentence & Phrase | English Grammar for Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Sentence? |

|
| What is a Phrase? |

|
| What is a Clause? |

|
| Kinds of Sentences |

|
| Affirmative and Negative Sentences |

|
What is a Sentence?
A sentence is a group of words that expresses a complete thought. It always contains a subject (the person or thing the sentence is about) and a verb (what the subject is doing or what is happening to the subject). For a sentence to make sense, the words must be arranged in the correct order.
Example:
- Incorrect: "Brother watch him his bought a."
- Correct: "His brother bought him a watch."
In the correct sentence, the words are arranged in an order that makes sense, giving us a clear and complete idea.
Three Important Rules for Sentences:
Complete Thought: A sentence must give a complete idea. For example, "She is reading" is a complete thought, whereas "She is" does not make complete sense by itself.
Capitalization: The first word of a sentence always starts with a capital letter. For example, "The cat is sleeping."
Punctuation: A sentence ends with a punctuation mark like a period (.), a question mark (?), or an exclamation mark (!). For example, "What time is it?" ends with a question mark because it is asking something.
Examples of Sentences:
- Statement: "My sister lives in Mexico."
This sentence states a fact. - Question: "Did you finish your homework?"
This sentence asks a question. - Command: "Close the door, please."
This sentence gives an order or request. - Exclamation: "Wow! That’s amazing!"
This sentence expresses a strong feeling.
What is a Phrase?
A phrase is a small group of words that makes some sense but does not express a complete thought on its own. Unlike a sentence, a phrase does not have both a subject and a verb.
Examples of Phrases:
- "In the morning" (This tells when something happens, but it doesn’t tell us what happens or who is doing something.)
- "Under the table" (This tells us where something might be, but it doesn’t give a complete idea.)
- "With a smile" (This tells us how someone might be doing something, but it doesn’t tell us what they are doing.)
Even though these groups of words give some information, they don’t tell the whole story. That’s why they are called phrases, not sentences.
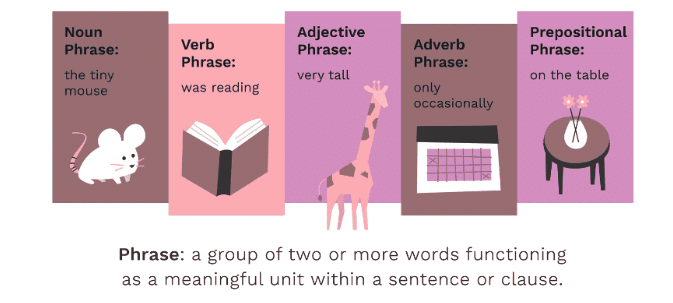
Types of Phrases:
- Noun Phrase: Acts like a noun in the sentence.
For example, "The tall boy" in "The tall boy is my friend." - Verb Phrase: Acts like a verb in the sentence.
For example, "is going" in "She is going to the park." - Adjective Phrase: Describes a noun.
For example, "full of life" in "She is a girl full of life." - Adverbial Phrase: Tells more about a verb, like when, where, or how something happens.
For example, "with great care" in "He did it with great care."
What is a Clause?
A clause is a group of words that has both a subject and a verb. A clause can either be a complete sentence on its own or part of a longer sentence.
Examples of Clauses:
- Independent Clause: "She ran fast."
This can stand alone as a sentence because it makes complete sense. - Dependent Clause: "When she ran fast..."
This cannot stand alone because it leaves us asking, "What happened when she ran fast?"
Types of Clauses:
- Independent (Main) Clause: A clause that can stand alone as a sentence. It makes complete sense by itself.
For example, "The dog barked." - Dependent (Subordinate) Clause: A clause that cannot stand alone as a sentence. It depends on the main clause to give complete meaning.
For example, "because the dog was scared" depends on a main clause like "The dog barked."
Examples:
- Main Clause: "The child returned."
This can stand alone as a sentence. - Subordinate Clause: "When the sun set."
This cannot stand alone and needs a main clause like "The child returned when the sun set."
Kinds of Sentences
Sentences can be categorized based on what they express. Here are the five main kinds:
Assertive Sentence (Declarative Sentence): This type of sentence states a fact or opinion. It can be positive (affirmative) or negative.
- Affirmative: "I love ice cream."
- Negative: "I do not like broccoli."
- Punctuation: Ends with a period (.)
Interrogative Sentence: This type of sentence asks a question.
- Examples: "What is your name?" "Are you coming to the party?"
- Punctuation: Ends with a question mark (?)
Imperative Sentence: This type of sentence gives a command, request, or advice.
- Examples: "Please pass the salt." (request) "Shut the door." (command) "Don’t talk during the movie." (advice)
- Punctuation: Ends with a period (.)
Exclamatory Sentence: This type of sentence expresses a strong emotion, such as surprise, joy, or anger.
- Examples: "Wow! That’s a huge cake!" "Oh no! I missed the bus!"
- Punctuation: Ends with an exclamation mark (!)
Optative Sentence: This type of sentence expresses a wish, hope, or prayer.
- Examples: "May you have a long life!" "I wish I could fly!"
- Punctuation: Often ends with an exclamation mark (!)
Affirmative and Negative Sentences
1. Affirmative Sentence:
- An affirmative sentence is a sentence that tells you something is true or correct.
- It makes a positive statement.
- Example: "He is honest."
This sentence is telling you that he is an honest person.
2. Negative Sentence:
- A negative sentence is a sentence that tells you something is not true or incorrect.
- It uses words like "no," "not," "don't," or "doesn't" to make the statement negative.
- Example: "Dogs do not chase after rats."
This sentence is saying that dogs do not do this action.
How to Change Affirmative Sentences into Negative Sentences
(i) Using Opposite Adjectives with Negative Words:
- You can turn an affirmative sentence into a negative one by using a negative word (like "not") and an opposite adjective.
- Examples:
- Affirmative: "Man is mortal."
Negative: "Man is not immortal." - Affirmative: "He is honest."
Negative: "He is not dishonest." - Affirmative: "Brutus loved Caesar."
Negative: "Brutus did not hate Caesar." - Affirmative: "Where there is fire, there is smoke."
Negative: "There is no smoke without fire." - Affirmative: "Everyone distrusts a liar."
Negative: "No one trusts a liar."
- Affirmative: "Man is mortal."
(ii) Using Degrees of Comparison:
- You can also change affirmative sentences to negative by comparing things in different ways.
- Examples:
- Affirmative: "He is as good as I am."
Negative: "I am not better than he is." - Affirmative: "He is the best student."
Negative: "No other student is as good as he is." - Affirmative: "As soon as the teacher arrived, the noise ceased."
Negative: "No sooner did the teacher arrive than the noise ceased."
- Affirmative: "He is as good as I am."
(iii) Other Ways to Change Affirmative to Negative:
- There are other methods to make a positive statement negative without changing the meaning.
- Examples:
- Affirmative: "Only the brave deserve the fair."
Negative: "None but the brave deserve the fair." - Affirmative: "He is too weak to walk."
Negative: "He is so weak that he cannot walk."
- Affirmative: "Only the brave deserve the fair."
|
49 videos|349 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Sentence & Phrase - English Grammar for Class 6
| 1. What is the difference between a sentence, a phrase, and a clause? |  |
| 2. What are the different kinds of sentences? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between affirmative and negative sentences? |  |
| 4. Can a phrase stand alone as a complete sentence? |  |
| 5. How can understanding the difference between a phrase and a clause help in writing clear and concise sentences? |  |
















