Shallow Foundations - 2 | Foundation Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
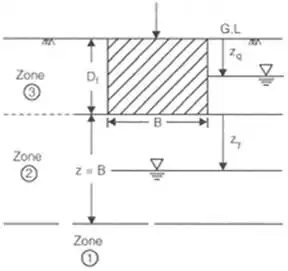
Effect of Water Table on Bearing Capacity of Soil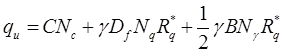
where Rq* and Ry* are water table correction factor.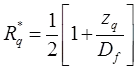
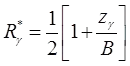
when 0 ≤ zq ≤ Df when 0 ≤ zγ ≤ B.
If Zγ > B they Rγ* = 1
If Zγ ≤ 0 they
If water table rise to G.L
Rq* = 1 / 2 and Rγ* = 1 / 2
Plate Load Test
- Significant only for cohesionless.
- Short duration test hence only results in immediate settlement.
(i) quf / qup = Bf / Bp
(ii) quf = qup
..for ∅ = soil … for C-soil
If plate load test carried at foundation level then
(iii)
(iv) Sf / Sp = Bf / Bp
… for dense sand. … for clays
(v) Sf / Sp = (Bf / Bp)n + 1
… for silts.
where,
quf =Ultimate bearing capacity of foundation
qup = Ultimate bearing capacity of plate
Sf = Settlement of foundations
Sp = Settlement of plate
Bf = Width of foundation in m
Bp = Width of plate in m
Housels Approach
QP = mAP + nPP
Qf = mAf + nPf
where, Qp = Allowable load on plate m and n are constant
P = Perimeter Ap = Area of plate
Af = Area of foundation
Standard Penetration Test
Significant for Granular Soils
 and
and 
where, N1 = Overburden pressure correction
N0 = Observed value of S.P.T. number.
= Effective overburden pressure at the level of test in kM/m2.- For Saturated
 fine sand and silt, when N1 > 15
fine sand and silt, when N1 > 15
N2 = 1/2(N1 - 15) + 15
where, N2 = Dilatancy correction or water table correction.
Nq + Nγ related to N value using peck Henson curve or (code method)
Teng's formula relate N value with reading capacity of granular soil.
Pecks Equation
qa net = 0.44NS = CwkN/m2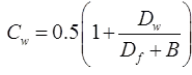
Dw = depth of water table below G.L
Df = Depth of foundation
B = Width of foundation
N = Avg. corrected S.P.T. no.
S = Permissible settlement of foundation
Cw = Water table correction factor
qa net = Net allowable bearing pressure.
Teng's Equations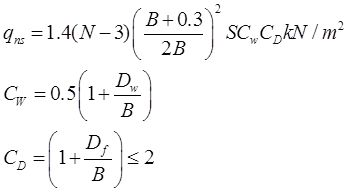
Cw =Water table correction factor
Dw = Depth of water table below foundation level
B = Width of foundation
Cd =Depth correction factor
S = Permissible settlement in 'mm'.
I.S Code Method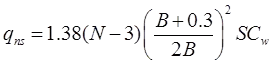
qns =Net safe bearing pressure in kN/m2
B = Width in meter.
S = Settlement in 'mm'.
I.S. Code Formula for Raft
qns = 0.88NSCw
Cw: Same as of peck Henson.
Meyer-Hoffs Equation
qns = 0.88NSCwCd
where, qns = Net safe bearing capacity in kN/m2.
B < 1.2 m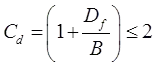
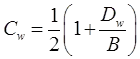
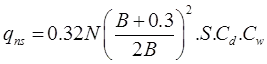
B ≥ 1.2 m (where qns is in kN/m2.
 |
Test: Terzaghi’s Analysis
|
Start Test |
Cone Penetrations Test
-
 where, = Static cone resistance in kg/cm2c = Compressibility coefficient
where, = Static cone resistance in kg/cm2c = Compressibility coefficient = Initial effective over burden pressure in kg/cm2.
= Initial effective over burden pressure in kg/cm2. -
 where, 'S' = Settlement.
where, 'S' = Settlement. - qns = 3.6qsRw B > 1.2 m.where, qns = Net safe bearing pressure in kN/m2.
- qns = 2.7qc.Rw B < 1.2 m.where, Rw = Water table correction factor.
|
18 videos|46 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Shallow Foundations - 2 - Foundation Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What are the different types of shallow foundations? |  |
| 2. What factors should be considered in the design of shallow foundations? |  |
| 3. How is the bearing capacity of a shallow foundation determined? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of using shallow foundations? |  |
| 5. What are the limitations of using shallow foundations? |  |
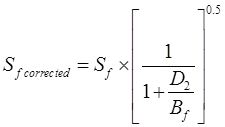
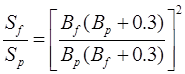

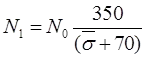 and
and 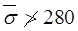
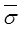 fine sand and silt, when N1 > 15
fine sand and silt, when N1 > 15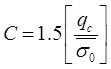 where, = Static cone resistance in kg/cm2c = Compressibility coefficient
where, = Static cone resistance in kg/cm2c = Compressibility coefficient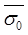 = Initial effective over burden pressure in kg/cm2.
= Initial effective over burden pressure in kg/cm2.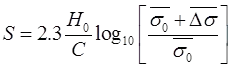 where, 'S' = Settlement.
where, 'S' = Settlement.




















