Shear Strength of Soils | Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Shear Strength
Shear strength of a soil is the capacity of the soil to resist shearing stress. It can be defined as the maximum value of shear stress that can be mobilized within a soil mass.
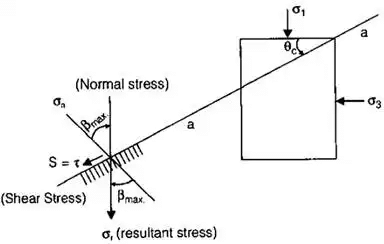
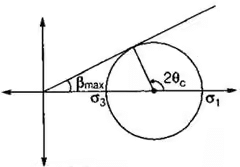
- Plane a-a is critical plane
- θc = Angle of critical plane (a-a)
- σ1 and σ3 are stresses on given planes
(i) where, βmax = Angle between resultant stress and normal stress on critical plane.
where, βmax = Angle between resultant stress and normal stress on critical plane.
= Friction angle of soil = ∅
θc = π / 4 + ∅ / 2
↓
for clay ∅ = 0
θc = π / 4
(ii)
(iii) , for C - ∅ soil.
, for C - ∅ soil.
(iv) τ = C, for C-soil (clays).
(v) for C-∅ soil.
for C-∅ soil.
(vi) , for φ-soil.
, for φ-soil.
(vii) for C-soil.
for C-soil.
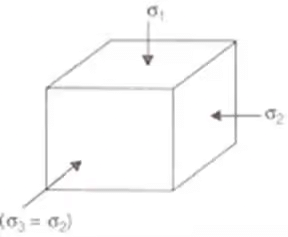
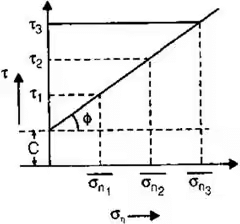
Mohr Coulomb's Theory
where, C' = Effective cohesion = Effective normal stress
= Effective normal stress
and ∅' = Effective friction angle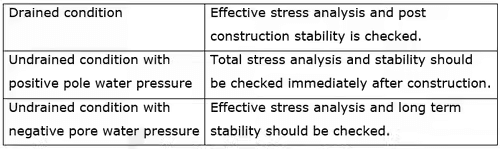
Direct Shear Test
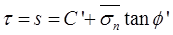
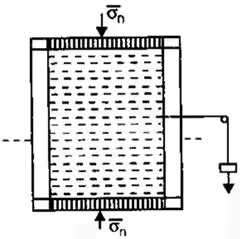
Results of Direct Shear Test
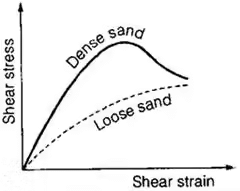
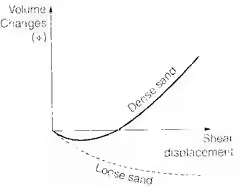
Drained conditions maintained, hence C taken as zero in results (as cohesion doesn't mobilizes in drained condition)
- σ1 = σ3 + σd


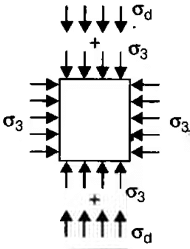
where, σ3 = Cell pressure or all-round confining pressure
σd = Deviator stress A = Area of failure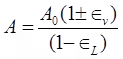 where, A0 = Area of beginning
where, A0 = Area of beginning
∈v = Volumetric strain
∈v = 0 for U - U - test
where, ΔV = Volume of water escaped out
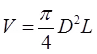 = Initial Volume
= Initial Volume
∈ = Axial strain
Important Points regarding Triaxial Test
- During triaxial, either pore water line is open (to get pore pressure) or Drainage line is open (to get volume change)
- UD (not possible in field)
- CD – Total = effective stress: To check long term stability of embankment which has been in existence since long ago.
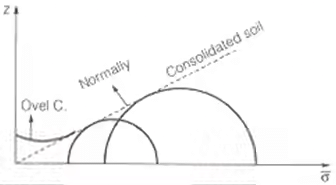
- With
 more σ1 required to canse failure hence mohr circle bigger. for normal consolidated soil, at σ3 = 0, τ = 0
more σ1 required to canse failure hence mohr circle bigger. for normal consolidated soil, at σ3 = 0, τ = 0 - But for OC soil, at σ3 = 0, τ have some value.CU – Undrained strength comes higher than in site due to isotropic confining pressure of lab and anisotripic confining in site soil.
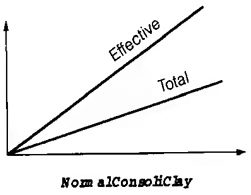
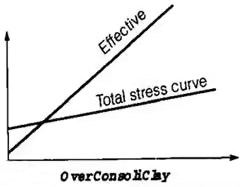
(Direct Shear) drained condition → C can't be modified
(unconfined undrained compression test) → ∅ can't be modified
UU Test
With ↑ in σ3, effective doesn't change hence no decrease in void ratio or increase in strength is noted, hence for all σ3, same incremental σ1, will come and only one Mohr's circle is obtained.
Unconfined Compression Test
- qu = (σ1)f where, qu = unconfined compressive strength. Here, σ3 = 0


 for clay's or c-soil.
for clay's or c-soil.- For clays as sand/coarse grained soil/can't stand in equipment with no lateral pressure.
- Used to rapidly assess clay consistency in field.
- To get sensitivity values of clay.
Vane Shear Test
- It is suitable for sensitive clays.
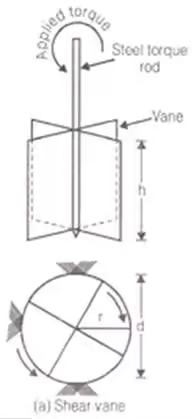
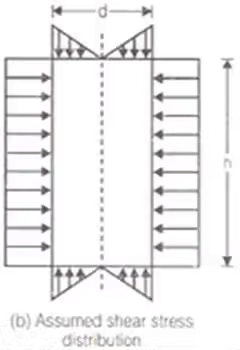
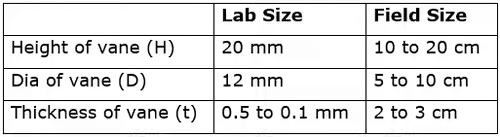
Shear Strength
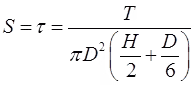
When top and bottom of vanes both take part in shearing.
When only bottom of vanes take part in shearing.
where sf = Sensitivity
Pore Pressure Parameter
(i) B = ΔUc / Δσc = ΔUc / Δσ3
where, B = Pore pressure parameter
ΔUc = Change in pore pressure due to increase in cell pressure
Δσc = Δσ3 = Change in cell pressure.
- 0 ≤ B ≤ 1
- B = 0, for dry soil.
- B = 1, for saturated soil.
(ii) 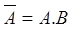 where A = Pore pressure parameter
where A = Pore pressure parameter
 ΔUd = Change in pore pressure due to deviator stress.
ΔUd = Change in pore pressure due to deviator stress.
Δσd = Change in deviator stress
ΔU = Change in pore pressure
(iii) ΔU = ΔUc + ΔUd
(iv) ΔU = B[Δσ3 + A(Δσ1 - Δσ3)]
|
30 videos|76 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Shear Strength of Soils - Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is shear strength of soils? |  |
| 2. How is shear strength of soils determined? |  |
| 3. What factors affect the shear strength of soils? |  |
| 4. Why is shear strength important in civil engineering? |  |
| 5. How can shear strength be improved in weak soils? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
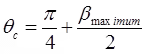 where, βmax = Angle between resultant stress and normal stress on critical plane.
where, βmax = Angle between resultant stress and normal stress on critical plane.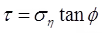
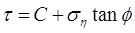 , for C - ∅ soil.
, for C - ∅ soil.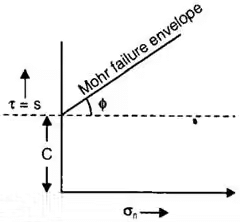
 for C-∅ soil.
for C-∅ soil.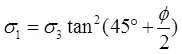 , for φ-soil.
, for φ-soil.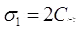 for C-soil.
for C-soil.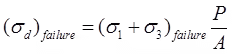

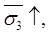 more σ1 required to canse failure hence mohr circle bigger. for normal consolidated soil, at σ3 = 0, τ = 0
more σ1 required to canse failure hence mohr circle bigger. for normal consolidated soil, at σ3 = 0, τ = 0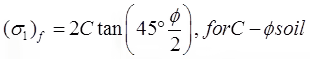
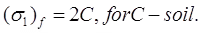
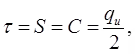 for clay's or c-soil.
for clay's or c-soil.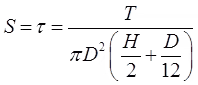
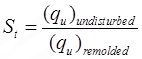
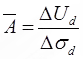 ΔUd = Change in pore pressure due to deviator stress.
ΔUd = Change in pore pressure due to deviator stress.
















