Short Answer Questions: How Things Work | EVS for Class 4 (Our Wondrous World: New NCERT) PDF Download
Q1: What does spinning mean and give two examples of spinning objects?
Ans: Spinning means turning in circles around a central point. It can be seen in objects like a coin spinning on a table or a top rotating quickly. Other examples include a ceiling fan and a potter’s wheel, which also move in a circular motion when in use.
Q2: Why do some objects spin better than others?
Ans: Some objects spin better because of their shape, smooth surface, and balance. Round and flat objects like coins or bangles spin well because they can rotate smoothly. Uneven or soft objects, such as erasers, cannot spin effectively as they do not have the right balance or shape.
Q3: What happens when a spinning coin loses balance?
Ans: When a spinning coin loses balance, it begins to slow down, wobble, and then stops completely. This happens because the spinning motion is no longer steady, and friction with the surface reduces its speed until it can no longer rotate.
Q4: What is a Lattu and what is it made of?
Ans: A Lattu is a traditional spinning top used for play. It is usually made of wood or clay and has been used in India for thousands of years. When spun correctly, it balances on its pointed tip and rotates smoothly.
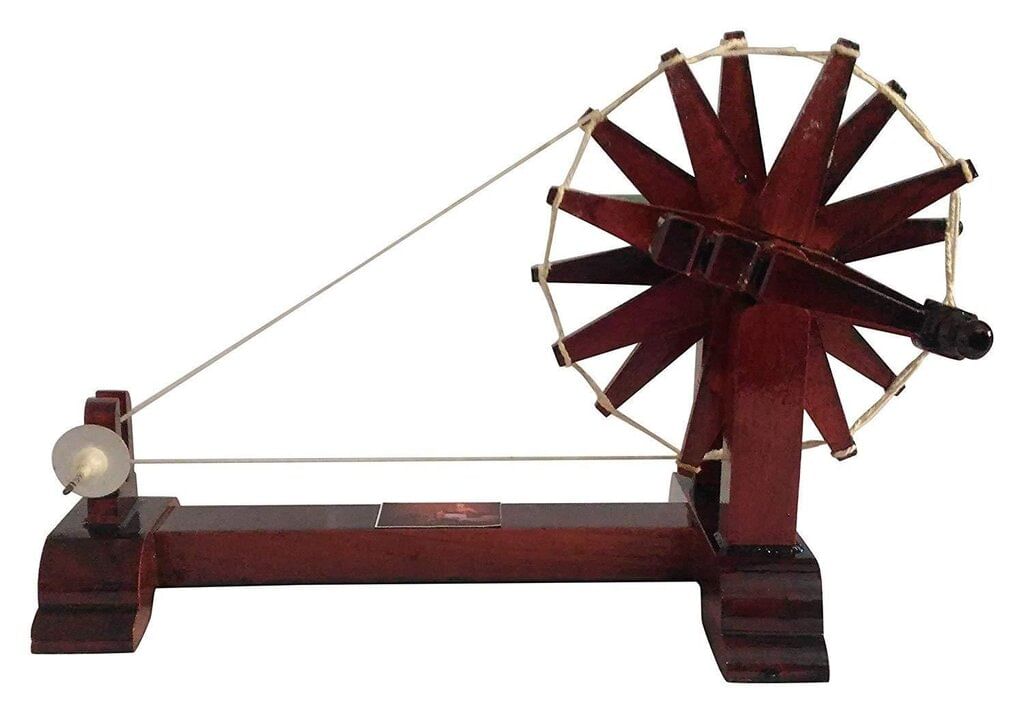
Q5: What is the purpose of a Charkha?
Ans: A Charkha is a spinning wheel used to twist cotton fibres into thread. It has a large wheel that spins when turned by hand. It is also a symbol of self-reliance and was famously used by Mahatma Gandhi for making handmade clothes.
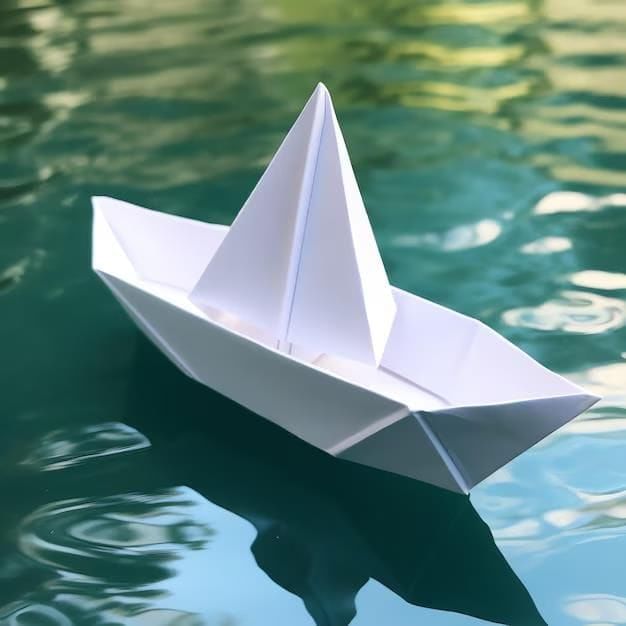
Q6: What is floating and how is it different from sinking?
Ans: Floating is when an object stays on the surface of water, while sinking is when it goes below the surface. For example, a paper boat can float on water, but a marble sinks to the bottom. The difference depends on weight, shape, and material.
Q7: Can all heavy objects sink? Give an example.
Ans: No, not all heavy objects sink. For example, a heavy empty bowl can float on water because it holds air inside, which makes it less dense than water. The air trapped inside helps it stay on the surface.

Q8: What are two factors other than weight that decide whether something floats or sinks?
Ans: Two important factors are the shape of the object and the material it is made of. For example, aluminium foil can float if shaped like a cup because it holds air, but the same foil will sink if tightly pressed into a ball.
Q9: Why does aluminium foil float when spread out?
Ans: Aluminium foil floats when spread out because it traps air and spreads its weight over a larger surface area. This makes it less dense than water, allowing it to stay on the surface instead of sinking.
Q10: Give two examples each of objects that float and objects that sink.
Ans: Objects that float include cork and leaves. Objects that sink include coins and marbles. Whether something floats or sinks depends on its density, shape, and the material it is made from.
Q11: How does balance help a boat float better?
Ans: A balanced boat stays upright and does not tip over easily. Good balance ensures that the weight is evenly distributed, preventing one side from dipping into the water, which helps the boat float more effectively and remain stable.
Q12: Why do some paper boats flip while others float well?
Ans: Some paper boats flip because they are not folded or shaped properly, making them unstable in water. Boats that are well-folded and balanced float better, as they can spread their weight evenly and resist tipping over.

Q13: How can you make a sinking object float?
Ans: You can make a sinking object float by changing its shape to hold more air or by attaching it to a floating material. For example, wrapping a marble in a piece of thermocol can help it stay on the water’s surface.
Q14: How do machines make paper different from handmade paper?
Ans: Machines make paper in large quantities using fast and automated processes, often producing smooth and uniform sheets. Handmade paper is made in smaller batches and can have a rougher texture, with unique patterns or natural fibres visible.
Q15: What are the 5Rs of waste management?
Ans: The 5Rs are Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Repurpose, and Recycle. These practices help in managing waste, saving resources, and protecting the environment by using materials wisely and avoiding unnecessary waste creation.
|
21 videos|198 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Short Answer Questions: How Things Work - EVS for Class 4 (Our Wondrous World: New NCERT)
| 1. What are the basic principles of how machines work? |  |
| 2. How do simple machines make work easier? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between potential energy and kinetic energy? |  |
| 4. How do electrical circuits work? |  |
| 5. What role do friction and gravity play in how things work? |  |





















