Short Answer Questions: The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Q1. What is the invisible living world?
Ans:
- The invisible living world refers to microorganisms that are too tiny to be seen with our naked eyes.
- These include bacteria, protozoa, some fungi, and algae.
- They can only be observed using magnifying instruments like magnifying glasses and microscopes.
- Though invisible, they play an important role in our lives — some are useful (e.g., in making medicines and food) while others can cause diseases.
Q 2. Write short notes on
(a) Bacteria
(b) Viruses
Ans.
(a) Bacteria: Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms.
- They can survive in all types of environments, ranging from ice-cold climates to hot springs and deserts to marshy lands.
- Bacteria can be seen under a microscope which enlarges their image from a hundred to a thousand times.
- They are of spiral shape or rod shape.
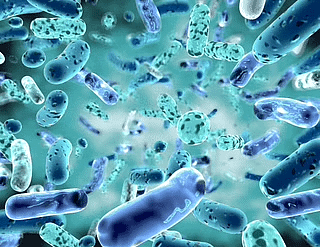 Bacteria: Rod Shaped
Bacteria: Rod Shaped
(b) Viruses:
- Viruses are microscopic infectious agents that act as non-living outside host cells and inside host cells become living and show reproduction.
- It can affect all kinds of an organism including animals, plants, and bacteria.
- Common ailments like cold, cough, and influenza (flu) are caused by viruses; serious diseases like chicken pox and polio are also caused by viruses.
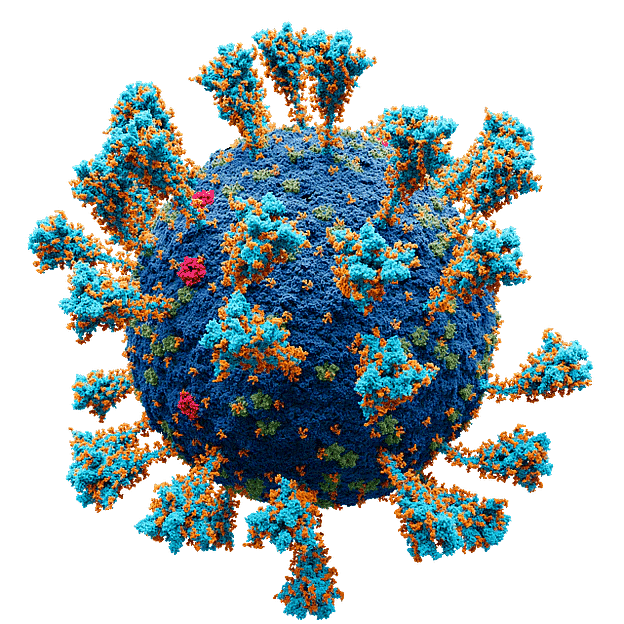 Virus
Virus
Q3. How does a magnifying glass make objects appear bigger?
Ans:
- A magnifying glass has a convex lens (curved outward).
- When we place it over an object, the lens bends the light rays.
- This bending of light makes the object look larger and clearer.
- It is useful to study very small objects like insects or tiny patterns on leaves.
Q 4. Write short notes on
(a) Protozoa
(b) Algae
Ans.
(a) Protozoa:
- Protozoa are unicellular animals.
- Some are free-living, and others are parasites.
- Several parasitic protozoans cause diseases in human beings, domestic animals, and plants.
- For example, Plasmodium, a protozoan, causes malaria.
(b) Algae:
- Algae are green substances that float on the surface of a pond, lake, river, stagnant water, moist soil, stones.
- They tend to grow on wet surfaces.
- Therefore, they can synthesize their own food.
- They are found in water or in very moist places.
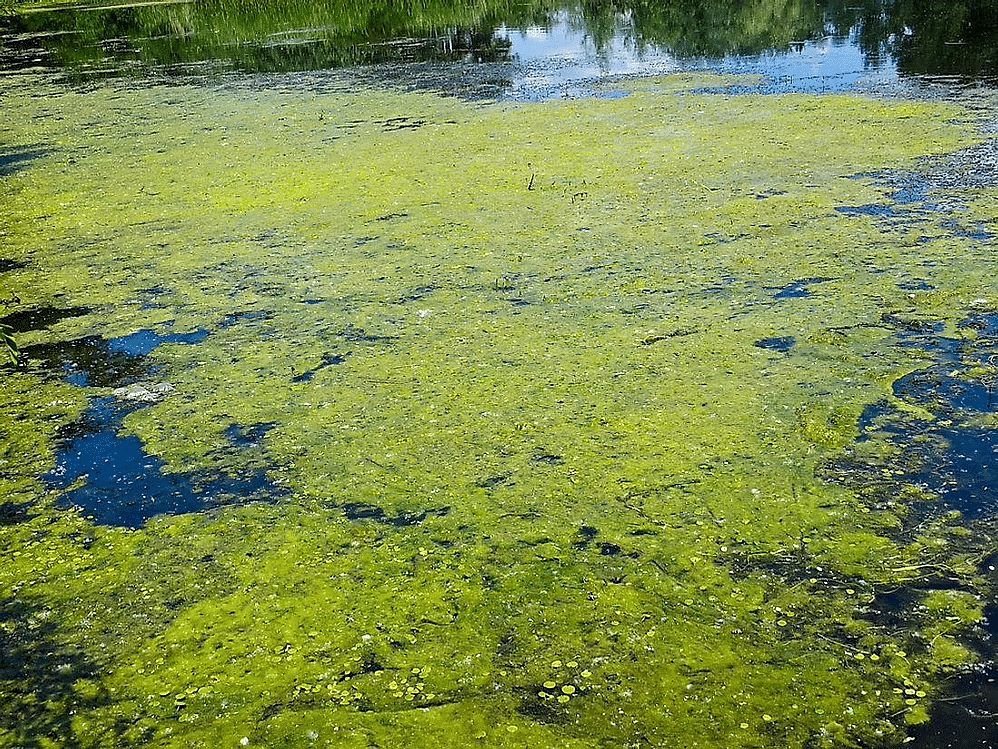 Algae
Algae
Q 5. What do you mean by friendly microbes?
Ans.
- In agriculture, microorganisms are used to increase soil fertility by nitrogen fixation.
- The bacterium Lactobacillus helps in the formation of curd.
- Bacteria are also involved in the making of cheese, pickles and many other food items.
- The microorganisms, yeast is used for the commercial production of alcohol and wine.
- Acetobacter acetic is used for producing acetic acid from alcohol.
Q 6. How is curd formed?
Ans.
- Milk is turned into curd by bacteria.
- Curd contains several microorganisms including Lactobacilli bacteria.
- It promotes the formation of curd from milk.
- When a little pre-made curd is added to warm milk, then Lactobacilli bacteria present in curd multiply in milk and convert the lactose sugar into lactic acid.
- This lactic acid then converts milk into curd.
Q 7. Why is yeast used in the baking industry for making bread, cakes, and pastries?
Ans.
- Yeast reproduces rapidly and produces carbon dioxide during respiration.
- Bubbles of gas fill the dough (a mixture of whole wheat flour or maida and some sugar and water) and increase its volume.
- This explains the use of yeast in the baking industry.
 Rised DoughQ 8. Define the process of fermentation and its application.
Rised DoughQ 8. Define the process of fermentation and its application.
Ans.
- Fermentation is a biological process in which sugars are converted into alcohol by the action of microorganisms, primarily yeast and bacteria.
- This process is widely used in the production of alcoholic beverages such as wine, beer, and cider.
- During fermentation, yeast is cultivated on natural sugars found in grains like barley, wheat, and rice, as well as in crushed fruit juices.
- The resulting products not only serve as drinks but also play important roles in food preservation and flavor enhancement.
Q 9. What are the three main parts found in all cells?
Ans:
Cell membrane –
A thin covering that surrounds the cell.
It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Cytoplasm –
A jelly-like substance present inside the cell.
It holds different cell organelles and is the site for many chemical reactions.
Nucleus –
The control centre of the cell.
It contains genetic material (DNA) and regulates cell activities like growth and reproduction.
Q 10. Write short notes on increasing soil fertility by the action of microorganisms.
Ans.
- Bacteria increase soil fertility through nutrient recycling such as carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus.
- Bacteria decompose dead organic matter and release simple compounds in the soil, which can be taken up by plants.
- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen and increase the nitrogen content of the soil, which can be readily absorbed by plants. They also improve soil structure and increase the water-holding capacity of the soil.
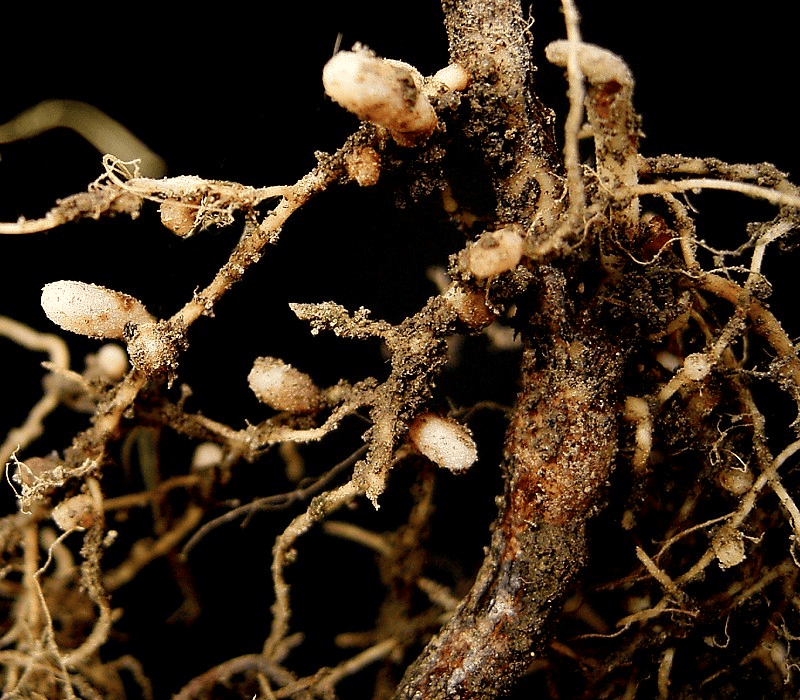 Rhizobium: Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria
Rhizobium: Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria
Q 11. How do microbes clean our environment?
Ans.
- The environment is cleaned up by microorganisms.
- Dead and decaying plant and animal materials are broken down by them into simpler components, that are then consumed by other plants and animals.
- They are therefore employed to degrade dangerous chemicals.
Q 12. Give two differences between plant cells and animal cells.
Ans:
Plant Cells:
Have a cell wall made of cellulose, which gives rigidity.
Contain plastids like chloroplasts (used in photosynthesis).
Have one or a few large vacuoles for storing water and maintaining shape.
Animal Cells:
Do not have a cell wall, only a flexible cell membrane.
Do not have plastids.
Have small or no vacuoles.
Q 13. What are the advantages of sealed air-tight packing for the storage of food items?
Ans.
- Prevents Microbial Growth: Sealed airtight packets effectively block the entry of microbes, reducing the risk of contamination.
- Preserves Freshness: They help maintain the freshness of food by preventing spoilage caused by air exposure.
- Increases Shelf Life: Airtight packaging extends the shelf life of food items, making them safe for longer periods.
- Prevents Toxins: By limiting exposure to air and moisture, these packets prevent the formation of harmful toxins.
- Reduces Waste: Longer shelf life means less food waste, benefiting both consumers and producers.
Q 14. How do we preserve cooked food at home?
Ans: We preserve cooked food at home by using preservatives like salt, sugar and edible oil. Common salt has been used to preserve meat and fish. It is also used to preserve amla, raw mangoes, tamarind, etc. Jams, jellies, and squashes are preserved using sugar. Vegetables, fruits, and pickles are often preserved by oil and vinegar.
 Pickles and Murabbas
Pickles and Murabbas
Q 15. Why a mango gets spoilt and rotten after few days but a mango pickle does not spoil for a long period of time?
Ans: A mango spoilt and rotten after a few days, but a mango pickle does not spoil for a long period of time because mango pickles contain salt, which acts as a preservative and prevents the growth of microorganisms in it.
Q 16. What are preservatives and their importance?
Ans: Preservatives are substances that help prevent the growth of microorganisms in food. They can be natural or synthetic. Here are some key points about preservatives:
- Common Examples: Salt and sugar are natural preservatives used in pickles to inhibit microbial growth.
- Synthetic Preservatives: Sodium benzoate and sodium metabisulphite are widely used in products like jams and squashes.
- Importance: Preservatives are crucial for extending the shelf life of food and preventing spoilage.
Q 17. How do microorganisms act as a cleaning agent of nature?
Ans. Microorganisms play a vital role in cleaning the environment by:
- Breaking down organic waste such as vegetable peels and animal remains into harmless substances.
- Decomposing dead plants and animals, which helps recycle nutrients back into the soil.
- Enhancing soil fertility by fixing nitrogen, which is essential for plant growth.
These processes contribute to a cleaner and healthier ecosystem.
Q 18. Explain the commercial use of microorganisms.
Ans. Microorganisms are used for large-scale production of alcohol, wine and acetic acid (vinegar). Yeast is used for commercial production of alcohol and wine. For this purpose, yeast is grown on natural sugar present in grains. Yeast converts the sugar into alcohol. This process is called fermentation. Microorganisms are also used to prepare medicines like antibiotics.
Q 19. Mention some beneficial effects of bacteria.
Ans. Beneficial effects of bacteria:
(i) They help fix nitrogen to increase soil fertility.
(ii) They are used to make vinegar, curd etc.
(iii) They help clean the environment by decomposing organic wastes.
(iv) They are also used to make medicines like antibiotics.
Q 20. Describe the role of blue-green algae and bacteria in the fertility of soil.
Ans. Some bacteria and blue-green algae are able to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere to enrich the soil with nitrogen and increase its fertility. These microbes are commonly called biological nitrogen fixers. In this way, bacteria and blue-green algae increase the soil fertility.

Q 21. Explain the cleaning action of microorganisms.
Ans. The microorganisms are called the cleaning agents of nature. Collect wastes from plants, vegetables, and fruits in your nearby surroundings. Put them in a pit meant for waste disposal. After some time, it decomposed and was converted to manure by the action of microorganisms. In this way, the waste products are converted into useful manure by the action of microbes. This is the way by which microorganisms act as cleaning agents of nature.
Q 22. How do microorganisms spoil food?
Ans. Microorganisms grow on the food materials and multiply rapidly. They release toxins in the food and make them unfit to consume. They break down food molecules into amines and change the taste, texture, and appearance of food.
Q 23. Why do muscle cells and nerve cells have different shapes?
Ans:
The shape of a cell is related to its function.
Muscle cells – Long and spindle-shaped so they can stretch and contract to bring about movement.
Nerve cells – Long and branched with extensions to carry messages quickly from one part of the body to another.
Different shapes help cells perform their specific tasks efficiently.
Q 24. What role does the vacuole play in plant cells?
Ans:
Vacuoles are storage sacs inside the cell.
In plant cells:
They store water, nutrients, and waste products.
They help maintain the shape and firmness (turgidity) of the cell.
They support growth by keeping the cell stretched.
In animal cells, vacuoles are smaller and mainly store food or waste temporarily.
Q 25. Arrange the levels of organization in living organisms from simplest to most complex.
Ans:
Cell – The basic structural and functional unit of life.
Tissue – A group of similar cells performing a specific function (e.g., muscle tissue).
Organ – Different tissues combine to form an organ (e.g., stomach).
Organ system – A group of organs working together (e.g., digestive system).
Organism – A complete living being made of various organ systems (e.g., human being).
Q 26. Give one example each of tissue, organ, and organ system in humans.
Ans:
- Tissue: Muscle tissue – made of muscle cells, helps in movement.
- Organ: Heart – pumps blood throughout the body.
- Organ System: Digestive system – includes organs like stomach, liver, and intestines, and is responsible for breaking down food and absorbing nutrients.
|
59 videos|235 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Short Answer Questions: The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are microorganisms and why are they important in our ecosystem? |  |
| 2. How do we observe microorganisms if they are not visible to the naked eye? |  |
| 3. What are some common diseases caused by microorganisms? |  |
| 4. How do microorganisms contribute to food production? |  |
| 5. What role do microorganisms play in biotechnology? |  |





















