Short Answer Type Question- Enterprise Growth Strategies | Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Franchising
Question.1: Give a brief history of Franchising.
Franchising began in 1850’s when Isaac Singer; the inventor of sewing machine wanted to distribute his machines outside of his geographical area, and also provide training to customers. Singer began selling licenses to entrepreneurs in different parts of the country. In 1955, Ray Kroc took over a small chain of food franchises and built it into today’s most successful fast food franchise known as McDonald’s. It has the most franchise units worldwide of any franchise system.
Question.2: State the features of franchise.
- The franchisor owns a trade or service mark and allows a franchisee to use it.
- The franchisee pays for the licence and becomes a part of the network.
- The franchisee makes an initial payment called licence fee. There may be an agreement of payment on percentage of sales or profit to be given monthly or annually by the franchisee to the franchisor.
- The franchisor provides all marketing support and proper equipments for doing business.
- The franchisee follows all the policies of the parent company, i.e., franchisor.
- The franchisor may give training to all the personnel working in the franchisees organization.
Question.3: Fizz and Lime is an established beverage company which started bottling:
Wheat Grass Juice; Bitter gourd with Jamun and Amla with Aloevera. It is planning to expand externally without compromising the unique taste of these drinks.
Belligio Juices got exclusive rights to manufacture and sell Wheat Grass and Amla, Aloevera under the name Fizz and Lime. Belligio Juice had to use only the ingredients supplied by Fizz and Lime to produce, bottle and distribute the two drinks.
(i) Identify and explain the form of external expansion adopted by Fizz and Lime.
(ii) State any one feature of this form of expansion.
(i) Manufacturing Franchise Opportunity. These types of Franchises provide an organization with the right to manufacture a product and sell it to the public, using the Franchisor’s name and trademark. This type of Franchise is found most often in the food and beverage industry.
(ii) Franchisee must use the ingredients given by the Franchisor to produce, bottle and distribute the soft drinks.
Question.4: Vimal Company Ltd. were earlier producing pencils, now they have decided to further venture into the field of notebooks and paper. What do you think is the company attempting to do? Identify and explain the concept.
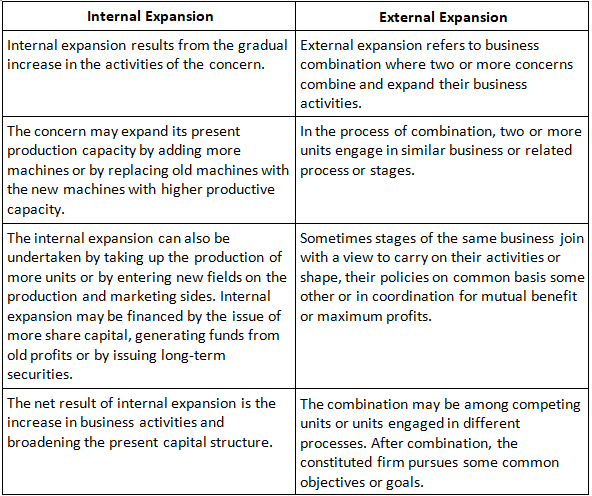
This is the case of growth through internal expansion. Internal expansion results from the gradual increase in the activities of the concern due to expansion of present production capacity by adding more machines or by modernising the technology or by taking up of the production of more units, or by entering new fields in the production and marketing side.
Question.5: Give any two disadvantages of franchising to the franchisee.
(i) The Franchisee loses the freedom to innovate the business as they have to work under the control of Franchisor.
(ii) The franchisee has to pay a huge amount of licence fee in the form of royalty which is nonrefundable.
Question.6: “Big brands make head towards franchising”. Why?
The big corporate houses have opted for a franchise route because:
- It considers franchising as an easy mode of expansion.
- Chances of success are higher due to high commitment level of the franchisor and the franchisees.
- It is a powerful and ideal way to expand business.
- It is best suited for a company which does not have any capital, manpower or time to build the network of company-owned outlets.
Question.7: Distinguish between internal expansion and external expansion.
Mergers, Acquisitions and Reasons for Failure
Question.1: Explain in brief the three ways in which an organisation can expand externally?
(i) Franchising: It is an agreement whereby the manufacturer or sole distributor of a trade marked product or service gives exclusive rights of local distribution to independent retailers in return for their payment of royalties and conformance to standardized operating procedures.
(ii) Mergers: It is a combination of two companies into one larger company. All the combining companies are dissolved and only the new entity continues to operate.
(iii) Acquisition: It is a corporate action in which a company buys most, if not all, of the target company’s ownership stakes in order to assume control of the target firm.
Question.2: If merger of Hindustan Computers Ltd., Hindustan Instruments Ltd., Indian Software Company Ltd. and Indian Reprographics Ltd. into an entirely new company called HCL Ltd. Identify the forms of merger and explain the same.
Merger through Consolidation/ Amalgamation. Meaning: A consolidation is a combination of two or more companies into a ‘new company’. In this form of merger, all companies are legally dissolved and a new entity is created. Here, the acquired company transfers its assets, liabilities and shares to the acquiring company for cash or exchange of shares.
Question.3: Beta Ltd. is a steel manufacturing company having its headquarters at Mumbai. It is the tenth largest steel manufacturing company of the world. Gama Ltd. are also steel manufacturers with their headquarters in Rangoon, the capital of Myanmar. For a long period the company (Gama Ltd.) had been facing workers unrest and it decided to sell its business to an international bidder. The highest bid for this was made by Beta Ltd. for ₹10 lakh crore. Afterwards Beta Ltd. realised that the assets of Gama Ltd. were overvalued and liabilities were under assessed and hence the price paid by them was higher. The employees of the two entities have different corporate cultures and styles of leadership which led to the problem of co-ordination. Ultimately Beta Ltd. had to close its business.
(i) Identify the growth strategy adopted by Beta Ltd.
(ii) Quoting lines from the above paragraph, explain any two reasons for the failure of Beta Ltd. after it took over the business of Gama Ltd.
(i) Acquisition
(ii) Reasons for failure of Beta Ltd.:
(a) Unrealistic Price paid: The process of M&A involves valuation of the target company and paying a price for taking over the assets of the company.
Lines : “The assets of Gama Ltd. ………… higher.”(b) Difficulty in the cultural integration: Every merger involves combining of two or more different entities. These entities reflect different corporate cultures, styles of leadership, differing employee expectations and functional differences.
Lines: The employees …… co-ordination
Question.4: Give some examples of Financial Synergy?
- Hindustan Unilever Company acquired Lakme, it helped HUL to enter the cosmetics market though an established brand.
- Glaxo and Smithkline Beecham merged, to gain market share and eliminate competition between each other.
- Tata Tea acquired Tetley to leverage Tetley’s international marketing strengths.
Question.5: The largest chocolate manufacturer ‘Cadibo in India merged with well-known Potato chips manufacturer ‘Best-Chips’. To impart a distinct identity to the merged company they decided to re-design their ‘Logo’ for their new brand name ‘Cadibo = Best – Chips.
(i) Identify and explain the ‘type of merger’ discussed above.
(ii) State one more type of merger in addition to the one identified in part (i)
(i) Product extension merger: Takes place between two business organizations that deal in products that are related to each other and operate in the same market. The objective of this merger is to group together their products and to have access to a bigger set of consumers, to earn higher profits.
(ii) Horizontal merger: Occurs between the firms which operate in the same space, often as competitors offering the same product or service. These mergers are common in industries with fewer firms as competition tends to be higher and synergies and potential gains in market share are much greater for merging firms.
Question.6: Kamal Ltd. are manufacturers of textiles, having their plant in Surat, a city of Gujarat. Vastra Ltd. are the manufactures of readymade garments and sell their products throughout the country. They also export their products to America and European countries. Vastra Ltd. source their textiles from Kamal Ltd. The management of the two companies decided to merge to have economies of large scale production.
(i) Identify the type of merger entered into by Kamal Ltd. and Vastra Ltd.
(ii) Also, explain a type of merger other than the one identified in (i) above.
(i) Vertical Merger
(ii) (a) Product extension merger: Takes place between two business organizations that deal in products that are related to each other and operate in the same market. The objective of this merger is to group together their products and to have access to a bigger set of consumers, to earn higher profits.
(b) Horizontal merger: Occurs between the firms which operate in the same space, often as competitors offering the same product or service. These mergers are common in industries with fewer firms as competition tends to be higher and synergies and potential gains in market share are much greater for merging firms.
Question.7: ‘Winber Motors Ltd.’ was a car dealer. It took over a car manufacturing plant ‘Speedcart & Co., and started a new business in the name of ‘Uniquecart Ltd.’ to synergise and capture a major share of the market and to maximize their profits. Like their competitors, they decided to sell their cars through company appointed dealers (retailers) in various parts of the country. This type of distribution network will enable the company to retain control over the distribution process.
(i) Identify and explain the type of expansion.
(ii) Also, explain the form of the type of expansion identified in (i) above.
(i) External Expansion: External expansion refers to business combination where two or more concerns combine and expand their business activities.
(ii) Acquisition: It could be acquisition of control, leading to takeover of a company. It could be acquisition of tangible assets, intangible assets, rights and other kinds of obligations. They could also be independent transactions and may not lead to any kind of takeovers or mergers.
Question.8: ‘Golden Sweets’ was a partnership firm, owned by Swati and Sushma. ‘Asam Sweets’ was another partnership firm owned by Vipan and Pranav. Swati and Sushma were sharing profits in 1 : 2 ratio and Vipan and Pranav were sharing profits in 2 : 3 ratio.
Both the firms were situated in a famous market of Guwahati and were doing competitive business. Pranav the partner of ‘Asam Sweets’ observed that many of their customers were from far off areas and if branches of ‘Asam Sweets’ are opened in other parts of the city, the firm may earn huge profits. Similar was the situation of ‘Golden Sweets’. One day in a function at a common friend’s house, the partners of both the firms met. The partners of both the firms knew that the internal expansion of their respective firms will be costly. Hence, they decided about the merger of the two firms. For this purpose they decided to meet again to finalise the conditions of the merger. Finally on 1.1.2016, their respective firms were merged and a new firm Ásam Golden Sweets’ was formed with all the four partners Swati, Sushma, Vipan and Pranav. Their new profit sharing ratio was 1 : 2 : 2 : 3. During the year ended 31.12.2016, the new firm opened four new branches in different parts of the city and earned a profit of 30% on sales.
(i) Identify the type of merger adopted by the two firms and also give its meaning.
(ii) Also give the names and meaning of two other types of mergers.
Type of merger took place is Horizontal merger:
- Horizontal mergers: These occur between companies in the same industry. It is a business consolidation that occurs between firms which operate in the same space, often as competitors offering the same goods or services.
- Other two types of mergers:
(a) Market extension mergers: These take place between two companies that deal in the same products but in separate markets. The purpose of this type of merger is to make sure that the emerging companies can get access to a bigger market and that ensures a bigger client base.
(b) Product extension mergers: These take place between two business organisations that deal in products that are related to each other and operate in the same market. This type of merger allows the merging companies to group together their products and get access to a bigger set of consumers.
(c) Vertical merger: A merger between two companies producing different goods or services for one specific finished product. It occurs when two or more firms, operating at different levels within an industry’s supply chain, merge operations.
(d) Conglomerate merger: Merger between firms that are involved in totally unrelated business activities.
There are two types of mergers : pure and mixed.
Pure conglomerate mergers involve firms with nothing in common.
Mixed conglomerate mergers involve firms that are looking for product extensions or market extensions.
|
19 videos|103 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Short Answer Type Question- Enterprise Growth Strategies - Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is franchising and how does it work? |  |
| 2. What are the benefits of franchising for both the franchisor and franchisee? |  |
| 3. What are some common reasons for failure in franchising? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between a merger and an acquisition? |  |
| 5. What are some common reasons for failure in mergers and acquisitions? |  |