Short & Long Question Answers: Beyond Earth | Short & Long Answer Questions for Class 6 PDF Download
Short Answer Questions:
Q1. Where do Yangdol and Dorjay live, and what do they enjoy about their surroundings?
Ans: Yangdol and Dorjay live in Nubra, a region in Ladakh, India. They enjoy the majestic mountain peaks, glaciers, and the clear night sky filled with stars.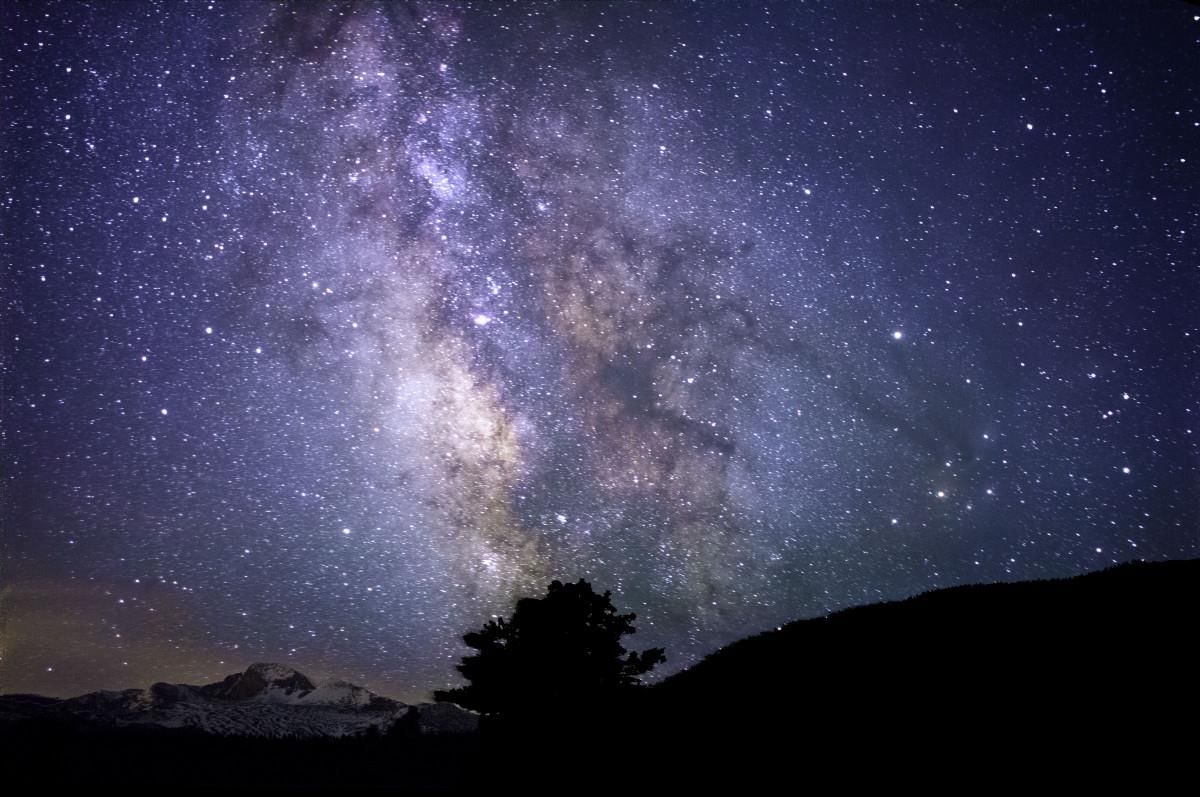
Q2. Why is the night sky in Nubra so clearly visible?
Ans: The night sky in Nubra is clearly visible due to the almost cloudless weather, with very little air or light pollution.
Q3. How do constellations help in navigation?
Ans: Constellations helped people in the past, especially sailors and travelers, by guiding them in finding directions, even before the invention of modern navigation tools like the compass.
Q4. What is the meaning of "constellation"?
Ans: A constellation is a group of stars that form a recognizable pattern in the sky. These patterns were often linked to myths, animals, or objects in ancient cultures.
Q5. How were constellations used in ancient times?
Ans: Constellations were used for navigation, helping people identify directions at sea or on land, particularly before the invention of the compass.
Q6. What is the Pole Star and why is it important?
Ans: The Pole Star, or Polaris, is a star that appears stationary in the Northern Hemisphere, helping people identify the North direction.
Q7. What are the Big Dipper and the Little Dipper?
Ans: The Big Dipper and Little Dipper are two prominent groups of stars in the sky, also known as constellations, which are used to locate the Pole Star.
Q8. What is light pollution and how does it affect our view of the night sky?
Ans: Light pollution is the excessive artificial light that makes it difficult to see stars and other celestial objects in the sky. It reduces the visibility of stars, especially in urban areas.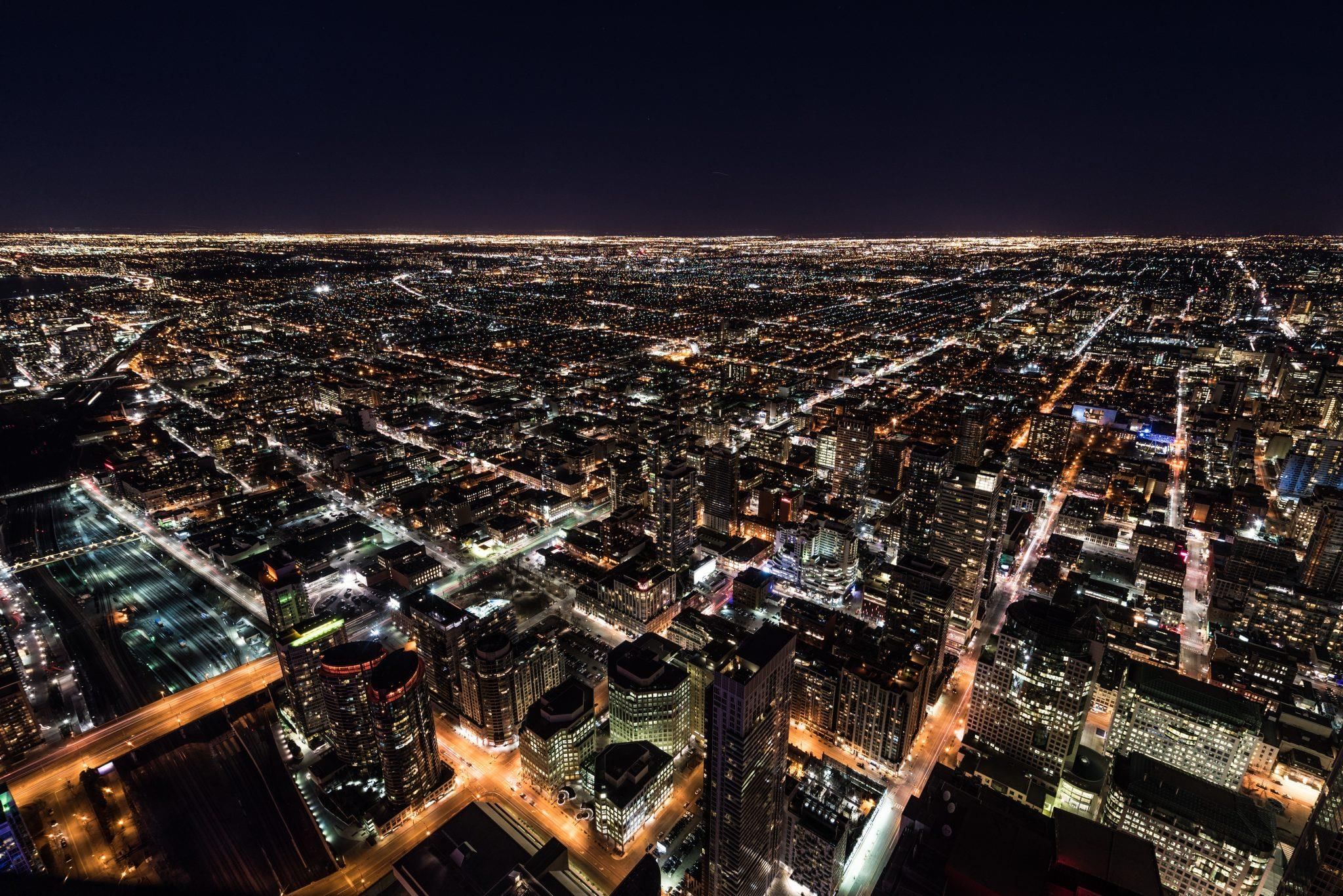
Q9. What is the Solar System, and what objects are included in it?
Ans: The Solar System is made up of the Sun, eight planets, their moons, and many smaller objects like asteroids and comets that revolve around the Sun.
Q10. What is the Milky Way Galaxy?
Ans: The Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that contains our Solar System. It consists of millions to billions of stars, including the Sun.
Long Answer Questions:
Q1. Explain how stars form constellations and the cultural significance of these patterns.
Ans: Stars form constellations by grouping together in specific patterns that are recognized in the night sky. Ancient cultures often named these groups based on their mythology, animals, or objects they resembled. For example, the constellation Orion is depicted as a hunter. These constellations helped ancient people identify stars and directions in the sky, serving as important tools for navigation, especially for sailors. Over time, these constellations became integral to various cultures' storytelling and traditions.
Q2. How did people in ancient times use the stars for navigation?
Ans: In ancient times, people relied on the stars to find directions, especially when they were traveling across seas or deserts. The North Star (Polaris) was used to find the North, while other constellations helped determine East, West, and South. The patterns in the sky were like a map, guiding travelers and sailors at night. This method of navigation was especially useful before the invention of the compass and modern technology.
Q3. Discuss the role of the Sun in sustaining life on Earth.
Ans: The Sun plays a crucial role in sustaining life on Earth by providing the necessary heat and light for plants to undergo photosynthesis. This process creates food for plants and oxygen for animals. The Sun also regulates the Earth's climate, influencing weather patterns, seasons, and the water cycle. Its energy is responsible for maintaining the temperature necessary for life and driving atmospheric processes like winds and ocean currents.
Q4. Describe the different types of planets in our Solar System.
Ans: The eight planets in our Solar System can be divided into two types: the inner planets and the outer planets. The inner planets—Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars—are small, rocky, and have solid surfaces. The outer planets—Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune—are much larger, mostly made of gases, and are often referred to as gas giants. The outer planets have multiple moons and ring systems, while the inner planets are closer to the Sun and have fewer moons.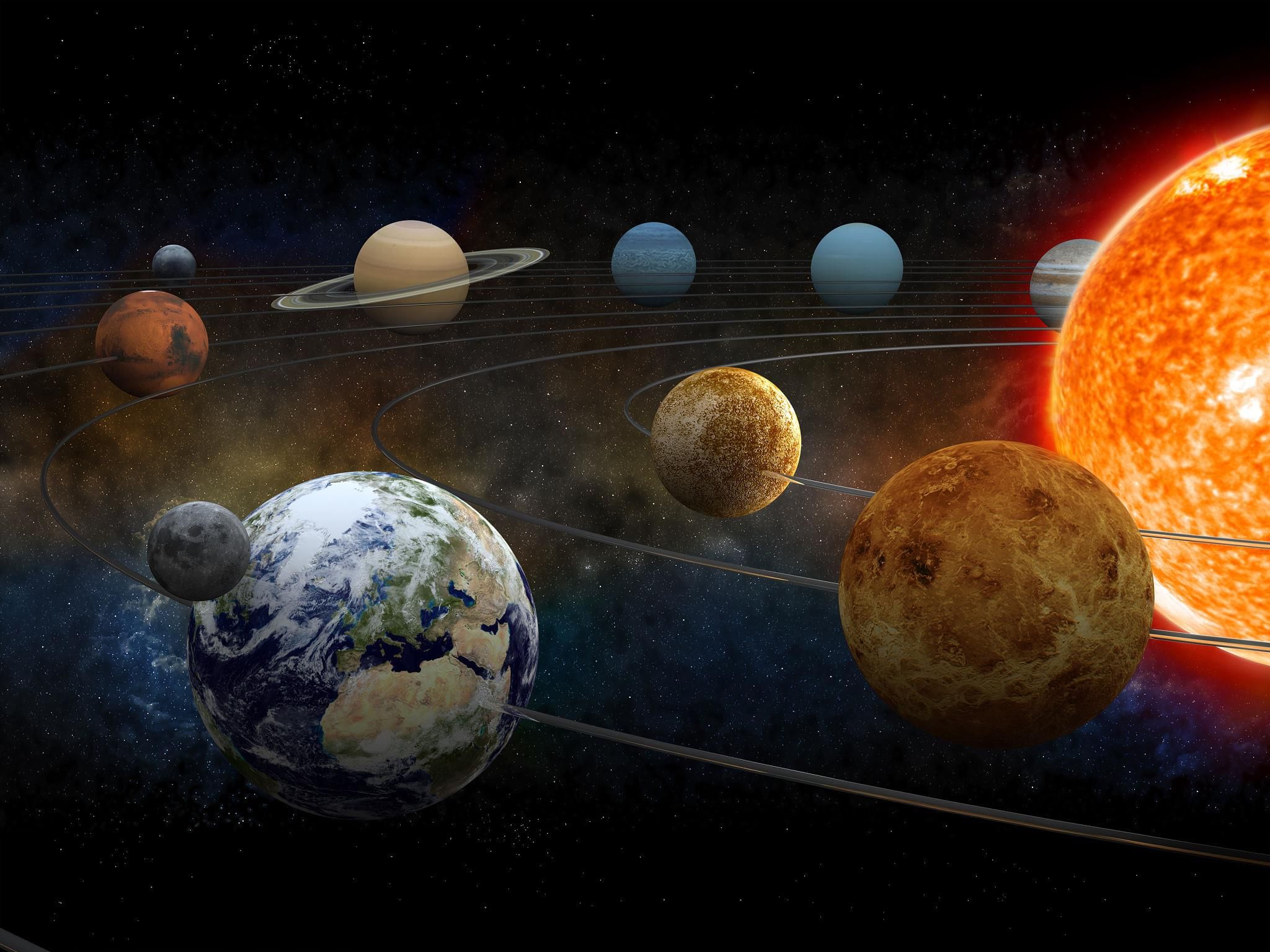
Q5. What are asteroids and comets, and how do they differ from planets?
Ans: Asteroids are small, rocky objects that orbit the Sun, mainly in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. They are irregularly shaped and much smaller than planets. Comets, on the other hand, are icy objects that have long, bright tails when they come close to the Sun, due to the evaporation of their frozen material. Unlike planets, asteroids and comets do not have a fixed, spherical shape and are often considered small celestial bodies that occasionally cross the path of planets.
FAQs on Short & Long Question Answers: Beyond Earth - Short & Long Answer Questions for Class 6
| 1. What are the main components of our solar system? |  |
| 2. How do planets in the solar system differ from one another? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Sun in our solar system? |  |
| 4. What are asteroids and where can they be found? |  |
| 5. Can humans live on other planets in the solar system? |  |
















