Short & Long Question Answers: Diversity in the Living World | Short & Long Answer Questions for Class 6 PDF Download
Short Question Answer
Q1. What are the two types of root systems in plants?
Ans: Plants have two main types of root systems: the fibrous root system and the taproot system. The fibrous root system consists of many thin roots spreading out from the base, commonly found in grasses. The taproot system has a single, thick main root with smaller branching roots, typical in plants like carrots.
Q2. What is the primary function of leaves in plants?
Ans: The primary function of leaves is photosynthesis, a process in which plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce food in the form of glucose. Leaves also help in gas exchange through tiny pores called stomata and play a role in transpiration, which regulates water loss and nutrient movement in plants.
Q3. What type of venation do wheat leaves exhibit?
Ans: Wheat leaves exhibit parallel venation, where veins run parallel to each other along the length of the leaf. This type of venation is typical in monocot plants, such as grasses, rice, and maize. Unlike reticulate venation found in dicots, parallel venation provides efficient water and nutrient transport in long, narrow leaves.

Q4. What is the definition of biodiversity?
Ans: Biodiversity refers to the wide variety of life forms found on Earth, including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. It encompasses the diversity of species, ecosystems, and genetic variations, playing a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance, supporting life processes, and providing essential resources for humans and the environment.
Q5. Name an animal that can live both in water and on land.
Ans: The frog is an example of an amphibian, a type of animal that can live both in water and on land. Frogs start their life as aquatic tadpoles with gills and later develop lungs and limbs for living on land. Other amphibians, like salamanders, also exhibit this dual habitat adaptation.
Q6. Explain the difference between fibrous and taproot systems with examples.
Ans: The fibrous root system has many thin, branched roots from the base of the stem, found in plants like wheat. This system enhances water absorption. In contrast, the taproot system, as seen in kidney beans, features a single, thick root growing straight down with smaller side roots, providing food storage and stability.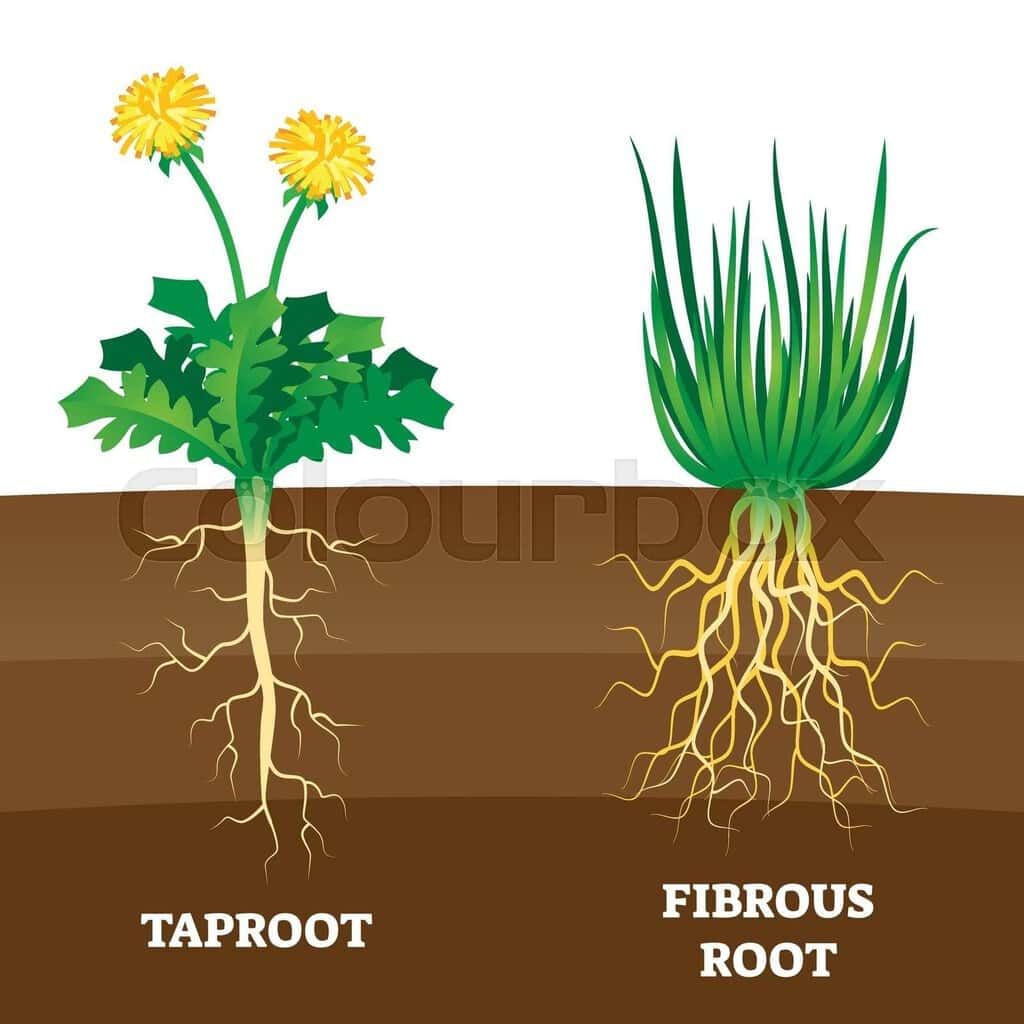
Q7. What are the similarities between terrestrial and aquatic animals?
Ans: Both terrestrial and aquatic animals have adapted features for their environments.
Terrestrial animals have lungs for breathing, while aquatic animals possess gills and streamlined bodies for swimming.
Q8. Describe the adaptation features of a mountain goat compared to a goat found in plains.
Ans: Mountain goats are adapted to rugged, cold environments with thick fur and shorter legs for navigating rocky terrains. Plains goats have thinner fur and longer legs, suited for flat, warmer areas, aiding their survival in respective habitats.
Q9. Explain the role of plants in maintaining ecological balance.
Ans: Plants are vital for ecological balance as they absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen via photosynthesis. They provide food and shelter for animals, maintain the water cycle, and prevent soil erosion by stabilizing the ground with their roots.
Q10: What adaptations help ducks swim effectively?
Ans: Ducks possess adaptations for effective swimming, including webbed feet that function like paddles, a streamlined body that minimizes water resistance, and feathers coated with oil for waterproofing. These features enable efficient movement in aquatic settings.
Long Question Answer
Q1: Discuss the different types of plant venation and their significance.
Ans: Plant venation is the arrangement of veins in leaves.
Parallel venation, found in wheat, features veins that run side by side, enhancing the transport of water and nutrients.
Reticulate venation, seen in kidney beans, has veins forming a network, which increases surface area for photosynthesis and improves water distribution.
Q2: Explain how animals can be classified based on their habitat.
Ans: Animals are classified into three main groups according to their habitats:
- Aquatic animals, like fish and whales, live in water.
- Terrestrial animals, such as horses and lions, inhabit land.
- Amphibious animals, like frogs and crocodiles, thrive both on land and in water. This classification reflects the animals' adaptation to their specific environments.
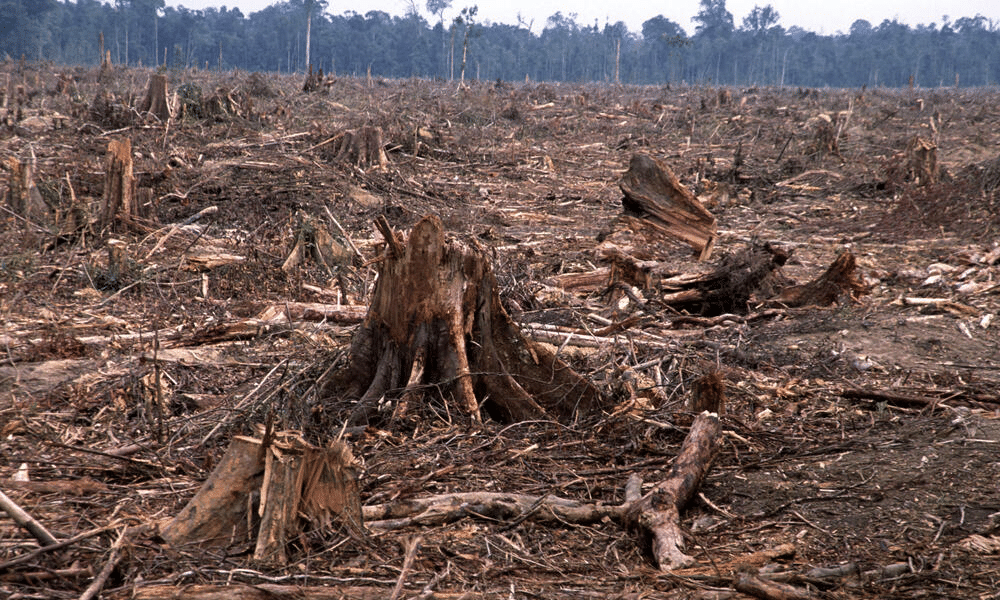
Q3. What is deforestation, and how does it affect the environment?
Ans: Deforestation is the clearing of forests for agriculture, urbanization, or logging. It leads to biodiversity loss, as many species lose their natural habitats. Deforestation also contributes to climate change by releasing stored carbon in trees, increasing carbon emissions. It causes soil erosion by removing plant cover, leading to poor soil stability. The water cycle is disrupted, affecting rainfall and water availability. Addressing deforestation requires reforestation, sustainable practices, and conservation efforts to protect ecosystems and maintain ecological balance.

Q4. What is biodiversity, and why is it essential for the environment?
Ans: Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. It is crucial for maintaining ecosystem stability, resilience to environmental changes, and essential services like pollination, nutrient cycling, and climate regulation. Biodiversity also provides resources such as food and medicine. Its loss disrupts ecosystems, affecting both nature and human well-being. Protecting biodiversity ensures a sustainable future.
Q5. Explain the process of photosynthesis and its importance for life on Earth.
Ans: Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose and oxygen. This occurs in chloroplasts, where chlorophyll absorbs sunlight to power the reaction. Photosynthesis is vital because it supplies oxygen for respiration, forms the foundation of the food chain, and helps regulate carbon dioxide levels. Without it, life on Earth could not be sustained.
FAQs on Short & Long Question Answers: Diversity in the Living World - Short & Long Answer Questions for Class 6
| 1. What is diversity in the living world? |  |
| 2. Why is biodiversity important? |  |
| 3. How do scientists classify living organisms? |  |
| 4. What are the main groups of living organisms? |  |
| 5. How does habitat loss affect biodiversity? |  |






















