Short & Long Question Answers: Timeline and Sources of History | Social Studies for Class 6 PDF Download
Short Question Answers
Q1: What does E.H. Carr say about history?
Ans: E.H. Carr describes history as an unending dialogue between the present and the past, linking today’s society with yesterday’s. He believes we can only fully understand our current world by exploring what happened before.
- For example, learning about early human hunting helps explain modern farming. History acts like a conversation, connecting old events, such as icy climates long ago, to life today.
- It’s a way to see how the past shapes the present, making it essential for understanding our world.

Q2: Who are the people that study the past and what do they do?
Ans:
- Geologists study Earth’s features like soil and mountains to learn about its history.
- Palaeontologists examine ancient fossils of plants and animals to understand past life. Anthropologists look at human societies and cultures from long ago to now.
- Archaeologists dig up remains like tools and bones to discover how people lived.
- Together, they uncover different parts of the past—Earth’s structure, ancient life, cultures, and daily activities—helping us build a complete picture of history.
Q3: How do we measure time with CE and BCE?
Ans: We measure time using the Gregorian calendar with CE, meaning Common Era, for years after Jesus Christ’s birth, like 1947 CE when India became independent. BCE, or Before Common Era, counts years backward before that, like 560 BCE for Buddha’s birth. There’s no year zero, so 1 BCE jumps to 1 CE. For example, from 2 BCE to 2 CE is 3 years because you add the numbers and subtract 1. This system helps us mark historical events worldwide.
Q4: What is a timeline and why does it matter?
Ans: A timeline is a tool that shows events in order, from early human times to today, like the end of icy periods or the start of cities.
- It helps us see when things happened and in what sequence, such as Buddha being born before Jesus.
- Timelines make history clear by showing how long ago events occurred without needing to know every date.
- They simplify the past, connecting it to the present, and help us understand the order of big changes.
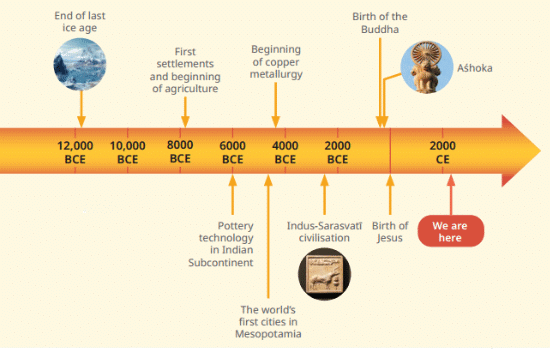
Q5: What are centuries and millenniums in history?
Ans: A century is a 100-year period, counted forward from 1 CE, like the 21st century from 2001 to 2100, or backward from 1 BCE, like the 3rd century BCE from 300 to 201 BCE.
- A millennium is 1,000 years, such as the 3rd millennium CE from 2001 to 3000, or the 1st millennium BCE from 1 to 1000 BCE.
- These terms help us organize long stretches of history, placing events like early farming into bigger time blocks for easier understanding.
Q6: How did early humans live before they started farming?
Ans: Early humans, called Homo sapiens, lived for 300,000 years as hunters and gatherers, chasing animals and picking plants for food. They stayed in groups in caves or shelters, used fire, and made tools like stone axes and arrowheads. They drew paintings on rocks showing animals and beliefs, and crafted beads from stones or shells. Facing tough nature, they moved often, spoke lost languages, and survived by helping each other, relying on teamwork for food and safety.
Q7: What changes happened for humans after the last Ice Age?
Ans: After the last Ice Age ended about 12,000 years ago, the Earth warmed, ice melted, and rivers grew, making life better for humans. They settled near rivers, growing grains and cereals and taming animals like cattle. Fertile soil helped farming, boosting food and group sizes. People moved from temporary camps to villages, starting agriculture instead of just hunting. This shift led to bigger communities, setting the stage for more settled lives near water and rich land.
Q8: What were the first crops and how did they change human life?
Ans: The first crops were cereals and grains, grown by humans after the Ice Age ended about 12,000 years ago.
- As the climate warmed, people settled near rivers with fertile soil and started farming these crops instead of just hunting. This change brought more food, letting groups grow bigger and live in one place.
- They also tamed animals like cattle, adding to their resources. Farming led to villages, replacing temporary camps, and set the foundation for larger communities, making life more stable and connected than before.

Q9: What new tools did early humans invent after settling down?
Ans: After settling, early humans invented pottery to make clay pots for storing food, and started using metals—first copper, then iron—for stronger tools and ornaments. These built on earlier stone tools like axes and blades used for hunting.
- Pottery helped with daily tasks, while metal tools made farming and building easier, supporting growing villages.
- These new skills improved life beyond fire and basic tools, helping communities expand and prepare for bigger societies.
Q10: How are Indian calendars different from the Gregorian calendar?
Ans: Indian calendars, like the pañchänga, track time using the sun and moon’s positions, setting months differently from the Gregorian calendar’s fixed 365 days and 12 months with leap years.
- Pañchangas predict eclipses, sunrise, sunset, weather, and festival dates, mixing astronomy with tradition. The Gregorian calendar, used globally, starts from Jesus’ birth and counts years simply.
- Indian calendars adapt to sky events, offering a cultural way to measure time alongside the worldwide CE and BCE system.
Long Question Answers
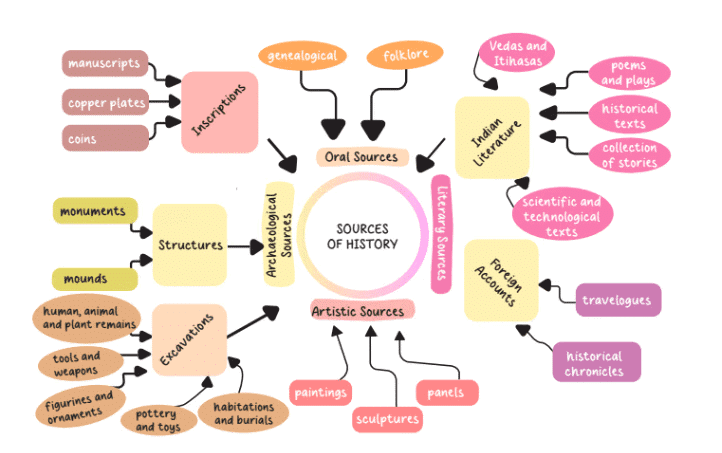
Q1: How do sources of history help us understand the past?
Ans:
- Objects: Coins, tools, and pots show what people used daily long ago.
- Rock Paintings: Drawings in caves reveal early human activities and beliefs.
- Writings: Old texts, studied by epigraphists, tell stories of kings or events.
- Fossils: Bones and plant remains show ancient life and environments.
- Newspapers: Recent papers report events from the last few centuries.
- Electronic Media: TV and internet give details on modern history.
- Science: Climate and genetics studies add facts about old times.
- Checking Sources: Historians compare them to see what matches or differs.
- Result: These build a picture of history, from hunting to cities, filling in gaps.
Q2: How do different experts work together to uncover the past?
Ans:
- Geologists: Examine Earth’s soil, mountains, and rivers to learn about its ancient state.
- Palaeontologists: Study fossils of old plants and animals to understand past life forms.
- Anthropologists: Look at human cultures and societies from early times to today.
- Archaeologists: Dig up tools, pots, and bones to find out how people lived.
- Historians: Write history by combining all these findings into a story.
- Epigraphists: Read ancient writings to add details from old texts.
- Scientists: Use studies of climate, chemicals, and genetics for new facts.
- Teamwork: They check if sources like tools or paintings match or differ, solving history’s puzzle.
- Result: Together, they reveal a full picture of the past, from Earth to human life.
Q3: Why is it important to measure time in history, and how do we do it?
Ans:
- Why It Matters: Measuring time shows the order of events, linking past to present.
- Gregorian Calendar: Uses CE for years after Jesus’ birth, like 1947 CE, and BCE for before, like 560 BCE.
- No Zero Year: 1 BCE jumps to 1 CE, so we add dates and subtract 1, like 560 + 2024 - 1 = 2,583 years.
- Timelines: Show events in sequence, like ice ages to cities, for easy understanding.
- Centuries: Group 100 years, like 21st century CE from 2001 to 2100.
- Millenniums: Cover 1,000 years, like 3rd millennium CE from 2001 to 3000.
- Indian Calendars: Use sun and moon, unlike Gregorian’s set days, for festivals.
- Example: Buddha’s birth before Jesus’ stands out clearly with these tools.
- Purpose: Time measurement makes history organized and meaningful.
Q4: How did early humans change from hunters to farming communities?
Ans:
- Hunting Life: For 300,000 years, humans hunted animals and gathered plants, living in caves.
- Early Tools: Used fire, stone axes, and blades to survive tough conditions.
- Rock Paintings: Drew animals and beliefs, showing their way of life.
- Ice Age: Faced cold climates until 12,000 years ago, staying mobile.
- Warming Up: After ice melted, rivers grew, and soil turned fertile for crops.
- Farming Start: Grew grains and tamed animals like cattle near rivers.
- Villages Form: More food led to settled groups, replacing camps.
- New Skills: Made pottery and metal tools, like copper and iron, for better living.
- Growth: These changes built bigger, stronger communities, ready for civilization.
|
23 videos|171 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Short & Long Question Answers: Timeline and Sources of History - Social Studies for Class 6
| 1. What is the importance of timelines in history? |  |
| 2. What are primary and secondary sources in historical research? |  |
| 3. How can we verify the accuracy of historical sources? |  |
| 4. What role do historians play in understanding history? |  |
| 5. Why is it essential to study history in school? |  |






















