Atoms and Molecules Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 3
Introduction to Early Theories of Matter
- Ancient Indian and Greek philosophers speculated about matter's divisibility.
- Maharishi Kanad (500 BC): Proposed that matter can be divided until reaching indivisible particles called Parmanu.
- Pakudha Katyayama: Suggested these particles exist in combined forms, creating various matter.
- Democritus and Leucippus (Greek philosophers): Introduced the concept of atoms, the indivisible particles of matter.
- Ideas were based on philosophy, lacking experimental validation until the 18th century.
- By the late 18th century, scientists differentiated between elements and compounds.
- Antoine Lavoisier: Laid the foundation of modern chemistry with laws of chemical combination.
Laws of Chemical Combination
Given by Lavoisier and Joseph L. Proust as follows:
(a) Law of Conservation of Mass
Mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Example:
A + B → C + D
Reactants → Products
Mass of reactants = Mass of products
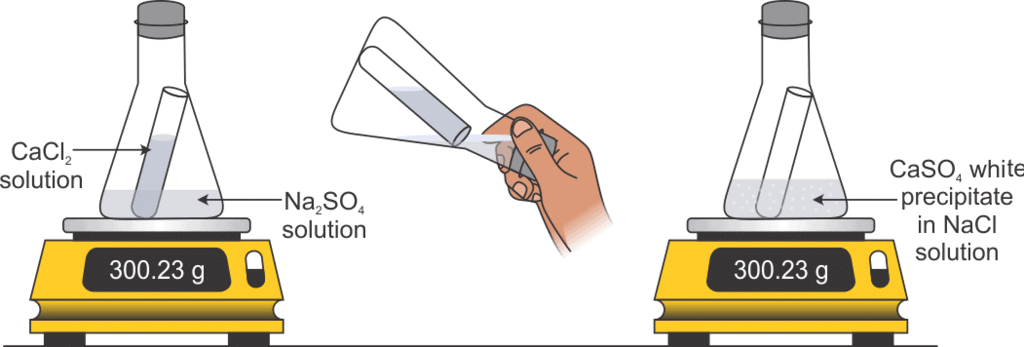 Mass of Reactants = Mass of Products
Mass of Reactants = Mass of Products
(b) Law of Constant Proportions
In a chemical substance, the elements are always present in definite proportions by mass.
Example: In water, the ratio of the mass of hydrogen to the mass of oxygen is always 1:8 respectively.
These laws lacked explanation. Hence, John Dalton gave his theory about the nature of matter. He said that the smallest particles of matter are called ‘atom’.
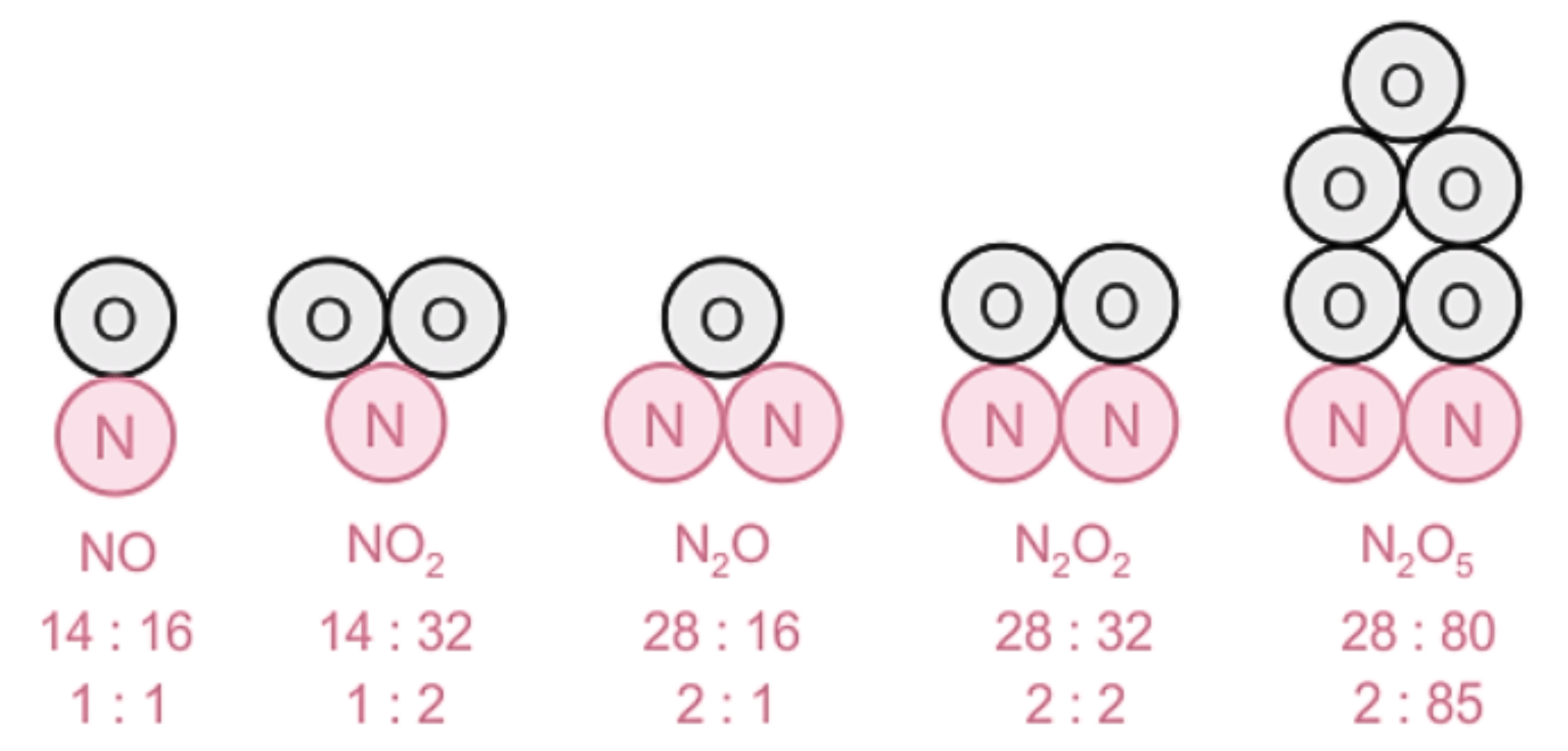 An illustration describing the mass ratio of elements in a few compounds.
An illustration describing the mass ratio of elements in a few compounds.
Dalton's Atomic Theory
- Every matter is made up of very small or tiny particles called atoms.
- Atoms are not divisible and cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- All atoms of a given element are the same in size, mass and chemical properties.
- Atoms of different elements are different in size, mass and chemical properties.
- Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
- The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
- Atoms are the smallest particles of an element that can take part in a chemical reaction.
Size of an Atom
Atomic radius is measured in nanometres.
1/109 m = 1 nm
1 m = 109 nm
Atomic radii of hydrogen atom = 1 × 10–10 m.
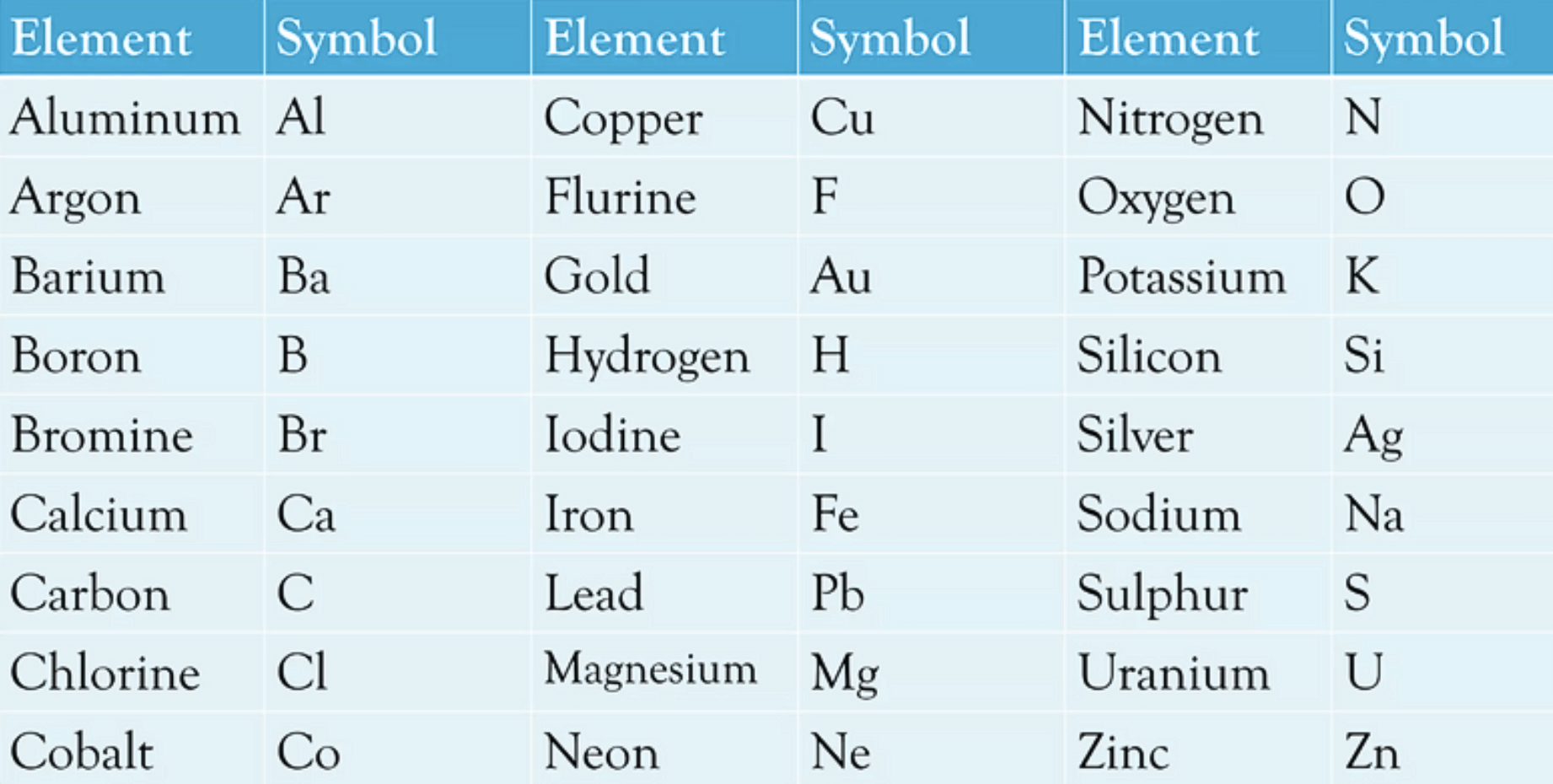
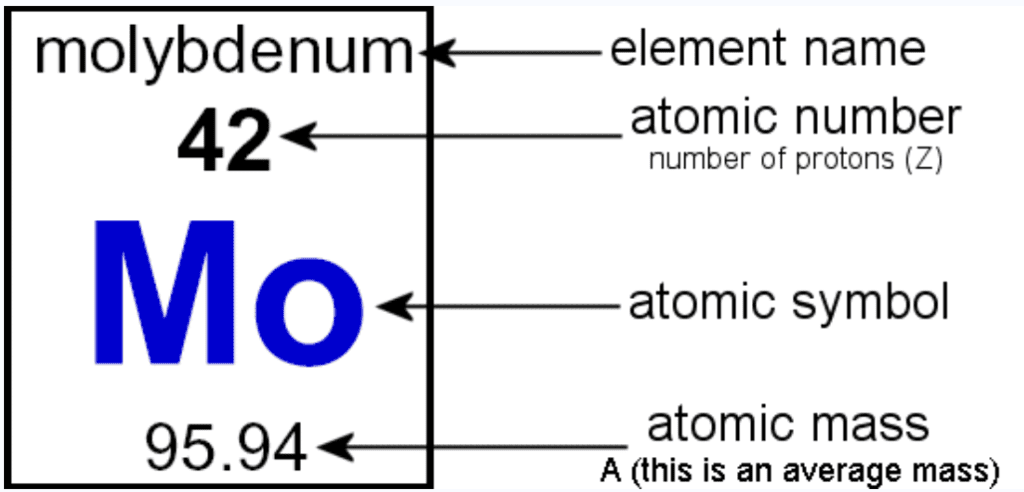
Symbols of Atoms
(a) Symbols for some elements as proposed by Dalton:
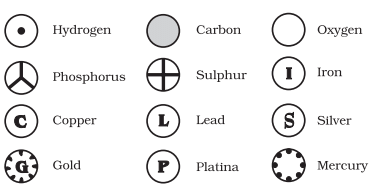 Symbols for Elements as Proposed by Dalton(b) Symbols of some common elements:
Symbols for Elements as Proposed by Dalton(b) Symbols of some common elements:
Atomic Mass
- Dalton proposed each element has a characteristic atomic mass.
- The theory explained the law of constant proportions and led to measuring atomic masses.
- Relative atomic masses were determined using chemical combinations due to the difficulty of measuring individual atomic masses. In carbon monoxide (CO), 3g of carbon combines with 4g of oxygen, showing carbon reacts with 4/3 times its mass of oxygen.
- The atomic mass unit (amu) was initially defined as 1/16th the mass of oxygen, chosen for its reactivity and whole number results.
- In 1961, carbon-12 became the standard reference, with 1 atomic mass unit (u) defined as 1/12th the mass of carbon-12.
- Relative atomic mass is the average mass of an atom compared to 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
Molecule
- It is the smallest particle of an element or a compound that can exist independently.
- Molecules of an element constitute the same type of atoms.
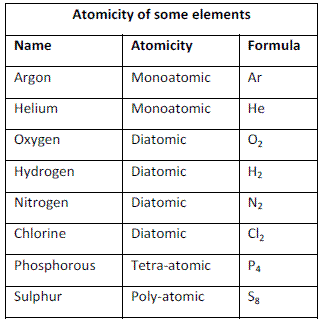
- Molecules may be monoatomic, di-atomic or polyatomic.
- In molecules of compounds atoms of different elements join together in definite proportions
- and constitutes a different type of atoms.
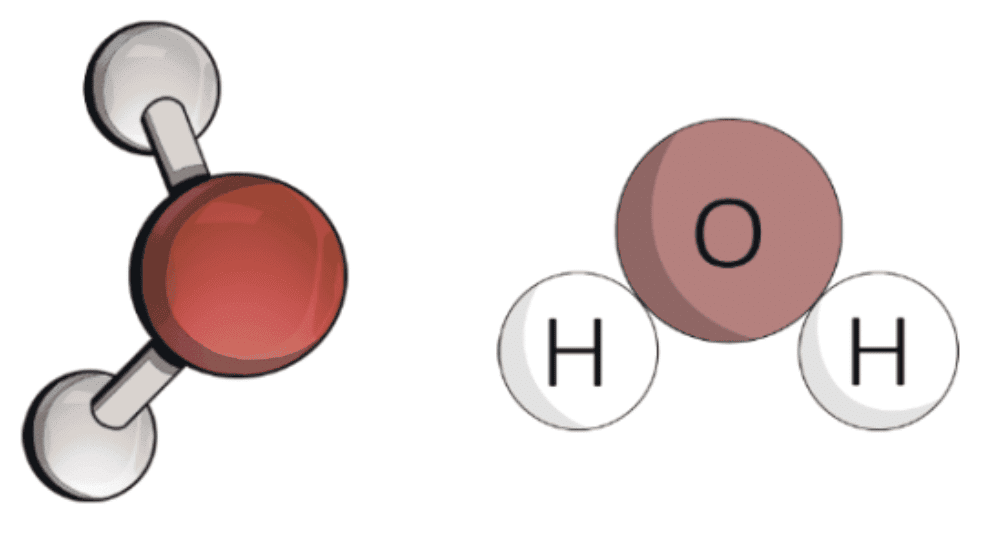 Water molecule
Water molecule
Atomicity
The number of atoms constituting a molecule is known as its atomicity.
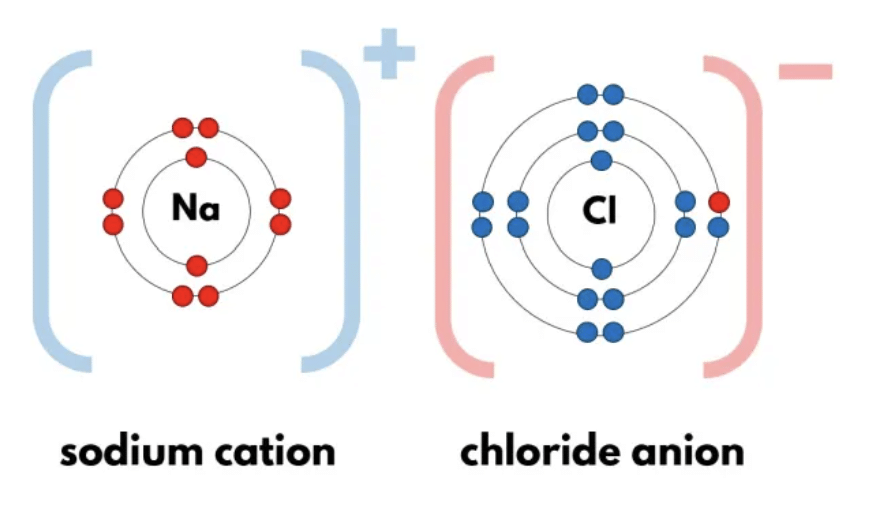
Ions
- The charged particles (atoms) are called ions, they are formed by attaining a positive charge or negative charge on them.
- A negatively charged ion is called anion (Cl–).
- A positively charged ion is called a cation (Na+).
Valency
The combining capacity of an element is known as its valency. Valency is used to find out how an atom of an element will combine with the atom of another element to form a chemical compound. (Every atom wants to become stable, to do so it may lose, gain or share electrons.)
- If an atom consists of 1, 2 or 3 electrons in its valence shell then its valency is 1, 2 or 3 respectively,
- If an atom consists of 5, 6 or 7 electrons in the outermost shell, then it will gain 3, 2 or 1 electron respectively and its valency will be 3, 2 or 1 respectively.
- If an atom has 4 electrons in the outermost shell then it will share these electrons and hence its valency will be 4.
- If an atom has 8 electrons in the outermost shell then its valency is 0.
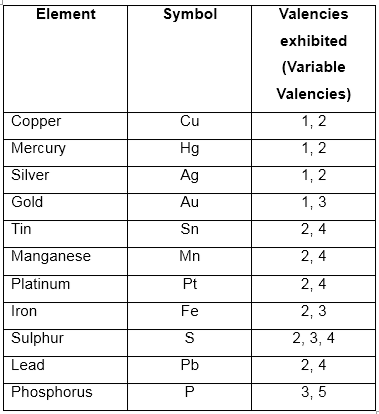 Some elements show more than one valency hence, termed variable valency.
Some elements show more than one valency hence, termed variable valency.
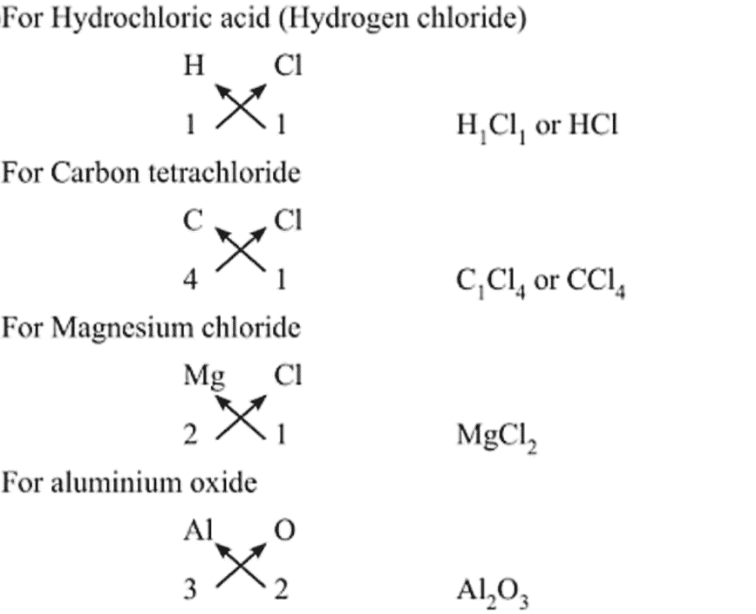
Writing Chemical Formulae
The chemical formula of a compound is a symbolic representation of its composition.
Rules
- The valencies or charges on the ion must balance.
- Metal and non-metal compound should show the name or symbol of the metal first.
Example: Na+ + Cl- → NaCl - If a compound consists of polyatomic ions. The number of ions present in the compound is indicated by enclosing the formula of ion in a bracket and writing the number of ions outside the bracket.
Example: (OH)- → Polyatomic radical
Mg2+ → Mg(OH)2
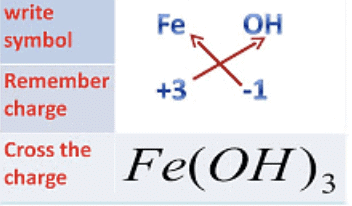 Fe (III) Hydroxide
Fe (III) Hydroxide
Chemical Formula of Some Simple Compounds
Molecular Mass
It is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance. It is expressed in the atomic mass unit (u).
E.g. The molecular mass of HNO3 = the atomic mass of H + the atomic mass of N+ 3 × the atomic mass of O
The molecular mass of HNO3 = 1 + 14 + 48 = 63 u
Formula Unit Mass
It is the sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in a formula unit of a compound. The constituent particles are ions.
E.g. sodium chloride has a formula unit NaCl. It's formula unit mass can be calculated as:
1 × 23 + 1 × 35.5 = 58.5 u
Mole Concept (Old Syllabus)
- Definition of Mole: It is defined as one mole of any species (atoms, molecules, ions or particles) is that quantity in number having a mass equal to its atomic or molecular mass in grams. 1 mole = 6.022 × 1023 in number
- Molar Mass : mass of 1 mole → is always expressed in grams and is also known as gram atomic mass.
1u of hydrogen has → 1 atom of hydrogen
1g of hydrogen has → 1 mole of hydrogen
= 6.022 × 1023 atoms of hydrogen
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Atoms and Molecules Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 3
| 1. What is atomic mass and how is it calculated? |  |
| 2. How do you write a chemical formula for a compound? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between an atom and a molecule? |  |
| 4. Why is understanding atomic mass important in chemistry? |  |
| 5. How do you determine the molecular formula from the empirical formula? |  |

















