Short Notes: Business Environment | Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Introduction
The business environment refers to the sum of all external and internal forces, individuals, and institutions that influence the operations and performance of a business organisation. These include factors such as customers, competitors, government policies, economic conditions, and technological advancements that shape a firm's strategies and decision-making processes.
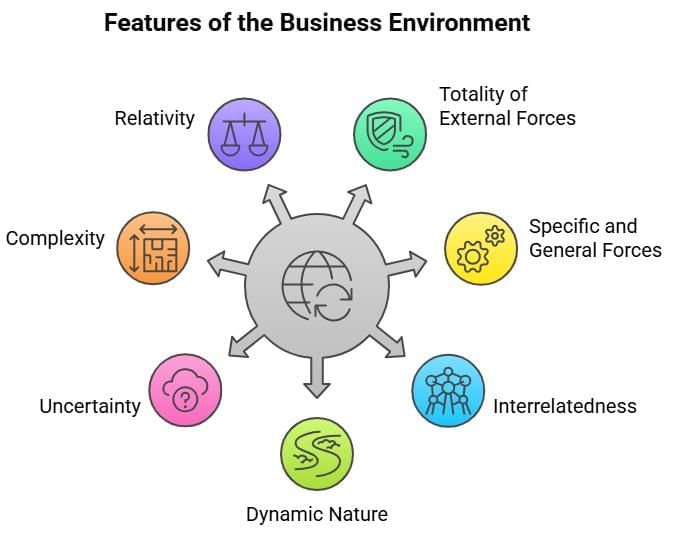
Features of Business Environment
- Totality of External Forces: Encompasses all external factors affecting a business, such as economic, social, and political forces.
- Specific and General Forces: Includes specific forces (e.g., customers, competitors, investors) that directly impact a firm and general forces (e.g., economic, political, technological conditions) that indirectly influence it.
- Interrelatedness: All forces are interconnected; for instance, increased health awareness boosts demand for organic food and roasted snacks.
- Dynamic: Constantly evolves due to changes in technology, consumer preferences, and market trends.
- Uncertainty: Predicting future changes and their impacts is challenging due to the unpredictable nature of the environment.
- Complexity: Easy to understand in parts but difficult to comprehend as a whole due to the interplay of multiple factors.
- Relativity: Impact varies across countries, regions, and firms; e.g., a shift from soft drinks to juices benefits juice companies but threatens soft drink manufacturers.
Importance of Business Environment
- Identification of Opportunities: Helps firms identify and capitalise on opportunities before competitors, gaining a first-mover advantage (e.g., early adoption of e-commerce by companies like Amazon).
- Identification of Threats: Enables firms to foresee threats and take corrective actions, like Bajaj Auto improving its two-wheelers when Honda entered the market.
- Tapping Useful Resources: Facilitates access to resources like capital, labour, and raw materials at economical prices.
- Coping with Rapid Changes: Continuous monitoring helps firms adapt to market changes effectively.
- Assistance in Planning and Policy Formulation: Supports strategic planning, as seen with ITC Hotels expanding due to a tourism boom.
- Improving Performance: Regular analysis enhances organisational performance and competitiveness.
Dimensions of Business Environment
- Economic Environment: Includes factors like interest rates, inflation, and income levels that directly impact business operations.
- Example: High inflation may reduce consumer purchasing power, affecting retail sales.
- Social Environment: Encompasses customs, beliefs, and lifestyle changes.
- Example: Growing health consciousness has increased demand for Diet Coke and mineral water while reducing tobacco sales.
- Technological Environment: Involves advancements in production and operational techniques.
- Example: Digital watches replacing traditional ones, and online ticket booking systems improving efficiency.
- Political Environment: Includes political stability and government attitudes toward business.
- Example: Supportive policies in Bangalore and Hyderabad have made them IT hubs.
- Legal Environment: Comprises laws and regulations affecting businesses.
- Example: Prohibition of alcohol advertisements and mandatory warnings on cigarette ads.
Economic Environment in India
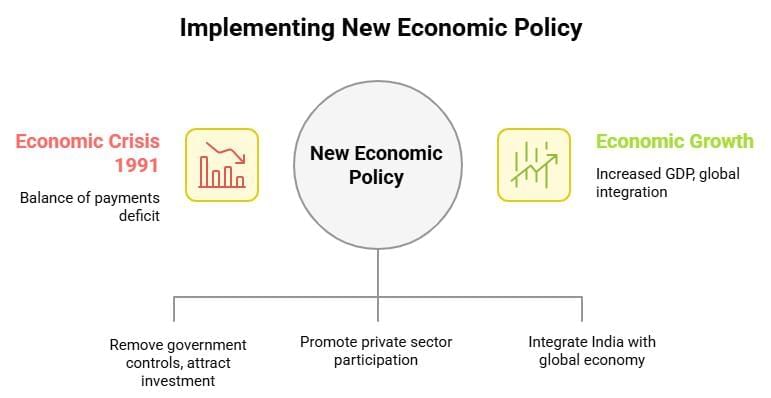
The economic environment in India significantly influences business operations through factors like monetary policies, inflation, and economic reforms. A pivotal moment was the introduction of the New Economic Policy (NEP) in July 1991, aimed at addressing the economic crisis and fostering growth.
New Economic Policy (NEP) 1991
The NEP focused on Liberalisation, Privatisation, and Globalisation to stimulate economic growth post the 1991 crisis, characterised by a balance of payments deficit and low foreign reserves.
- Liberalisation: Removed government controls, abolished licensing for most industries, reduced tax rates, and simplified procedures to attract foreign investment. This encouraged entrepreneurship and industrial growth.
- Privatisation: Reduced the role of the public sector, promoted private sector participation, and initiated disinvestment in public enterprises. The Board for Industrial and Financial Reconstruction (BIFR) was set up to revive sick public units.
- Globalisation: Integrated India with the global economy through trade liberalisation, export promotion, and foreign exchange reforms. The establishment of the Foreign Investment Promotion Board (FIPB) facilitated foreign direct investment (FDI).
Impact on Economic Growth: The NEP transformed India into a market-driven economy, attracting FDI, boosting industrial growth, and increasing GDP. It laid the foundation for India’s emergence as a global economic player, with sectors like IT and pharmaceuticals thriving due to liberalised policies.
Demonetisation (November 2016)
The demonetization of ₹500 and ₹1,000 notes aimed to curb black money, promote digitalisation, and enhance tax compliance. Its impacts include:
- Interest Rates: Increased liquidity in banks led to lower interest rates, encouraging borrowing and investment.
- Private Wealth: Reduced cash-based black money, impacting private wealth held in unreported cash.
- Public Sector Wealth: Enhanced government revenue through increased tax collections and deposits in public sector banks.
- Digitalisation: Accelerated adoption of digital payments, boosting platforms like UPI and mobile banking.
- Real Estate: Slowed down due to reduced cash transactions, impacting property prices and demand temporarily.
- Tax Collection: Improved as unreported income came under scrutiny, increasing direct tax compliance.
Impact of Government Policy Changes on Business and Industry
Increasing competition due to de-licensing and the entry of foreign firms has intensified the competitive environment for Indian businesses.
More demanding customers are now well-informed, making the market customer-oriented. Firms must tailor their products to meet specific customer needs.
Rapid technological change has improved production efficiency but poses challenges for small firms to keep up.
Necessity for change arises as fast-changing market forces require businesses to regularly adapt their policies and operations.
The need for human resource development has increased, as businesses now require skilled and committed employees to remain effective and efficient.
Market orientation has replaced the selling concept. Firms now focus on customer needs through marketing research, advertising, and after-sales service.
Reduction in budgetary support to public sector enterprises forces them to rely on their resources and improve operational efficiency.
Conclusion
The business environment is a critical determinant of organisational success, encompassing dynamic and interrelated forces that require continuous monitoring. Understanding its features and dimensions enables firms to seize opportunities, mitigate threats, and adapt to changes. The economic environment in India, particularly post-1991 reforms and demonetization, has significantly shaped business strategies, fostering growth, digitalisation, and global integration. By aligning with these environmental dynamics, businesses can enhance competitiveness and contribute to India’s economic progress.
|
51 videos|230 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Short Notes: Business Environment - Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What does reconstitution of a partnership firm involve? |  |
| 2. What is the process of admitting a new partner in a partnership firm? |  |
| 3. How is goodwill calculated when a new partner is admitted? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of goodwill in a partnership firm? |  |
| 5. What are the implications of reconstitution of a partnership firm on existing agreements? |  |
















