Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Science Class 8 > Short Notes - Coal and Petroleum
Coal and Petroleum Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 3
What are Natural Resources?
Everything that nature provides is considered a natural resource.
- They contribute to a country's economy.
- Natural resources can be broadly categorised into two types based on the abundance of various resources in nature:
1. Inexhaustible Natural Resources: These resources are abundant in nature and are unlikely to be exhausted as a result of human activities. Sunlight and air are two examples.
2. Exhaustible Natural Resources: These resources are scarce and can quickly become depleted if they are overused. Forests, wildlife, minerals, coal, petroleum, and other natural resources are the examples.
What are Fossil Fuels?
- Coal, petroleum, and natural gas are examples of non-renewable natural resources.
- Millions of years ago, fossil fuels were produced from the dead remains of live species.
- Fossil fuels are finite resources that cannot be replenished.
Coal
- Coal is a black substance that is as hard as stone. One of the fuels used to prepare food is coal.
- It was once utilized in railway engines to generate steam to power them. It's also utilized to generate electricity in thermal power plants. Coal is also employed as a source of energy in a variety of sectors.
- Dead plants were slowly transformed into coal under intense pressure and high temperature. Carbonisation is the lengthy process of converting dead plants into coal because coal is primarily made up of carbon.
- Coal is classified as a fossil fuel since it was created from the leftovers of plants. When coal is burned in the presence of air, it burns and produces primarily carbon dioxide gas.
- In industry, coal is processed to produce useful products such as coke, coal tar, and coal gas.
Coke:
- It is a dark, rough, porous substance.
- It is a form of carbon that is practically completely free of impurities.
- Coke is used in the production of steel as well as the extraction of various metals.
Coal Tar:
- It is a dark, thick liquid with an unpleasant odor.
- It consists of almost 200 different chemicals.
- Uses of coal tar:
- As a starting material for substances like synthetic dyes, drugs, explosives, perfumes, plastics, paints, photographic materials, and roofing materials.
- To make naphthalene balls, which repel moths and insects.
- Bitumen, a petroleum product, is now the primary material used for road surfacing due to its availability and suitability, replacing coal tar in most cases. However, coal tar is still used in specific industrial applications, such as sealants and coatings.
Coal Gas:
- Coal gas is produced when coal is processed to make coke.
- Many companies near coal processing plants use coal gas as a source of energy.
- oal gas is created when coal is processed to make coke.
- Many companies near coal processing plants use coal gas as a source of energy.
- It was previously used for street illumination.
- Now, it is employed as a heat source rather than a light source.
Petroleum
- Petrol and diesel are made from petroleum, a natural resource.
- The word "petroleum" comes from Petra (rock) and oleum (oil), as it is obtained from rocks beneath the Earth.
Petroleum Formation
- Petroleum is formed from the remains of microscopic marine organisms, such as plankton and algae, which lived in ancient oceans and were buried under layers of sediment.
- When these organisms died, their remains sank to the seafloor and were covered by layers of sand and clay.
- Over millions of years, the absence of air, high temperature, and high pressure transformed the remains into petroleum and natural gas.
Refining of Petroleum
- Petroleum is a thick, viscous liquid with a dark color and an unpleasant odor.
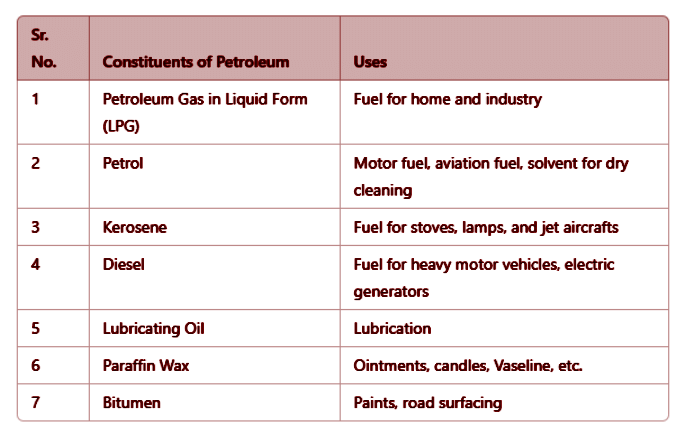
- It is composed of a variety of substances, including: Petroleum gas, gasoline, diesel, lubricating oil, paraffin wax, and more.
- Refining: The process of separating the various constituents (fractions) of petroleum.
- This process takes place in a petroleum refinery.
Details About Petroleum Constituents and Their Applications
Additional Information
- Petroleum and natural gas are used to make various useful compounds, called Petrochemicals.
- These are used in manufacturing products like detergents, fibers (e.g., polyester, nylon, acrylic), polythene, and other man-made polymers.
Petrochemicals
- Petroleum and natural gas are used to make a variety of useful compounds, known as Petrochemicals.
- These are used in manufacturing:
- Detergents.
- Fibers (e.g., polyester, nylon, acrylic).
- Polythene and other man-made polymers.
- Fertilizers are made from hydrogen gas derived from natural gas (e.g., urea).
- Petroleum is sometimes referred to as "Black Gold" due to its high commercial value.
Natural Gas
- Compressed Natural Gas (CNG):
- An essential fuel, easy to transport through pipes and store under high pressure.
- Does not pollute the environment and has a high calorific value.
- Used to generate electricity.
- It is now used as a transportation vehicle fuel.
- It is considered a cleaner fuel, producing less pollution compared to other fossil fuels.
Petroleum Conservation Research Association (PCRA) Recommendations
The Petroleum Conservation Research Association (PCRA) in India offers tips on how to save petrol and diesel when driving.
Recommendations:
- Drive at a consistent and moderate speed as far as feasible.
- Turn off the motor at traffic signals or other places where you must wait.
- Maintain proper tyre pressure.
- Ensure that the car is maintained on a regular basis.
The document Coal and Petroleum Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 3 is a part of the Class 8 Course Science Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
91 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Coal and Petroleum Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 3
| 1. What are natural resources? |  |
Ans. Natural resources are materials and components that can be found in the natural environment. They are essential for human survival and economic activity. Natural resources can be categorized into renewable resources, such as sunlight, wind, and water, and non-renewable resources, such as minerals and fossil fuels.
| 2. What are fossil fuels? |  |
Ans. Fossil fuels are natural substances formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals that have been subjected to heat and pressure over millions of years. The primary types of fossil fuels include coal, oil (petroleum), and natural gas. They are primarily used as energy sources for electricity generation, transportation, and heating.
| 3. What is coal and how is it used? |  |
Ans. Coal is a black or brownish-black sedimentary rock that is primarily composed of carbon along with various other elements. It is used mainly as a fuel source for electricity generation and in industrial processes, such as steel manufacturing and cement production. Coal can also be converted into gas or liquid fuels.
| 4. What are the main constituents of petroleum and their applications? |  |
Ans. Petroleum, or crude oil, is composed of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons and other organic compounds. Its main constituents include alkanes, cycloalkanes, and aromatic hydrocarbons. Applications of petroleum include the production of fuels (such as gasoline and diesel), lubricants, and raw materials for the petrochemical industry to make plastics, chemicals, and synthetic fibers.
| 5. Why are coal and petroleum important for the economy? |  |
Ans. Coal and petroleum are critical for the economy as they provide energy for various sectors, including transportation, manufacturing, and electricity generation. They also create jobs in extraction, processing, and distribution. Additionally, they serve as raw materials for numerous industries, contributing to economic growth and development.
Related Searches


















