Short Notes: Computer Organisation | Computer Science for Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Explain computer and its components.
OR
Explain basic computer organization
OR
Explain Structure of computer System
Computer is an electronic device that accept some input, process it and produces some output.
Several Components of computer system are:
- Input Unit
- CPU
- Memory Unit
- Secondary Storage
- Output Unit
These components of computer system are diagrammatically represented as :
Input Unit
This unit is used to provide data and instructions to computer. It converts data and instructions into binary form which is understandable by the computer.
Commonly used input devices are:
- Keyboard: It is the most commonly used input device to type alphabets, digit and symbols.
- Mouse: It is the most commonly used pointing device to move cursor and select different software components.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
CPU is also called brain of the computer. It is also known as processor. It is responsible for carrying out all activities in a computer. It is further divided into three parts:
- Control Unit (CU): This unit is responsible for flow of data and instructions between different units of computer. It decides whether data should go to ALU, registers, memory unit, secondary storage or output unit.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): This unit is responsible for arithmetic calculations and comparison.
- Registers: They are memory cells inside CPU to store data temporarily. They are mainly used to store frequently used data.
Memory Unit
Memory unit is used to store data and instructions. It stores data in machine language i.e. in the form of 0 and 1. The binary digits 0 and 1 are known as bits.
This unit is also termed as primary memory. It consists of three parts:
- RAM (Random Access Memory)
- ROM (Read Only Memory)
- Cache Memory
RAM (Random Access Memory)
It is used to store data and instructions temporarily. It retains data in it as long as the power is on. All the contents of RAM get cleared if power supply is turned off.
Whenever a software is opened, it automatically gets opened in RAM.
RAM is of two types:
- Dynamic RAM: It consists of capacitors and transistors. It uses electric charge to store the data.
- Static RAM: It consists of flip-flops. It stores data in binary form. They have faster access time compared to dynamic RAM.
ROM (Read Only Memory)
ROM stands for Read Only Memory. Data is permanently stored in ROM. ROM contains instructions needed to start up the computer and load operating system into RAM.
ROM is of three types:
- PROM (Programmable Read Only Memory) : It can be programmed once.
- EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory): It can be erased by keeping ROM chip using Ultraviolet light. It can be reprogrammed.
- EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Read Only Memory): It can be erased by electrical signal. It can also be reprogrammed.
Cache Memory
It is special memory used to compensate the speed difference between CPU(very fast) and RAM(very slow). It stores the copies of frequently used data from RAM. Hence it reduces the time required to access data from primary memory.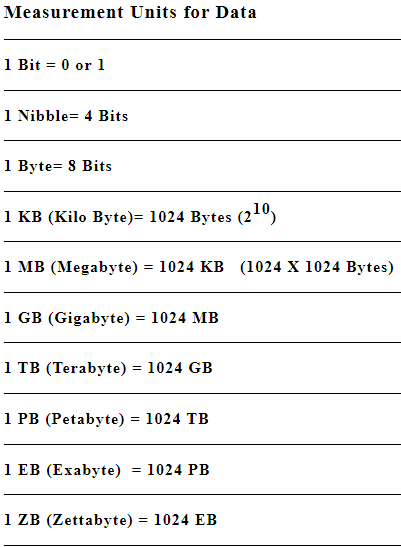
Secondary Storage unit
Secondary storage unit is used to store data permanently. It consists of different types of storage devices. Most commonly used storage devices are:
- Hard Disk : It is the most commonly used storage device to store data on a computer. It consists of multiple magnetic plates and heads to read and write data. Magnetic plates are further divided into tracks and sectors to store data.
Maximum capacity of hard disk is 15TB. - Compact Disk (CD): CD is an optical disk to store data. CD’s have a storage capacity of 700 MB. There are three types of CDs:
(i) CD-ROM (Compact Disk Read Only Memory): These are prerecorded CDs provided by manufacturers. Example: CDs containing softwares, games, ebooks etc.
(ii) CD-R (Compact Disk Recordable): Data can be recorded on these CDs only once.
(iii) CD-RW (Compact Disk Rewritable): These types of CDs can be erased and recorded multiple times. - Digital Versatile Disk (DVD):
DVD is an optical disk to store data. DVD’s have a storage capacity of upto 17 GB. There are three types of DVDs:
(i) DVD-ROM (Digital Versatile Disk – Read Only Memory): These are prerecorded DVDs provided by manufacturers. Example: DVDs containing movies etc.
(ii) DVD-R (Digital Versatile Disk – Recordable): Data can be recorded on these DVDs only once.
(iii) DVD-RW (Digital Versatile Disk – Rewritable): These types of DVDs can be erased and recorded multiple times. - Blu Ray Disk: Blu ray disk is optical disk that can store HD (High Definition) videos and data. They can store up-to 128 GB of data .
- Pen Drive: It is also called Flash memory. It is a solid state memory that can store more than 128GB of data.
Output Unit
This unit is used to get output from computer. This unit convert machine language to human understandable form. Most commonly used output devices are:
a. Monitor: It is used to display data just like TV screen.
b. Printer: It can be used to take printout of data stored on computer.
Explain software and its types
Software is defined as a collection of programs which are used for different purposes.
There are three types of software:
- Application Software
- System Software
- Utility Software
Application software:
Application software is used to perform specific operation on computer. They are of two types:
- General Purpose software: These softwares can be used by more than one type of user. Example: MS Word is a general purpose software that can be used by students, teachers as well as clerks.
- Special Purpose / Customized Software: These softwares can be used by only one type of user. Example: Banking Data Management software can be used only by bank employees.
System software
System software is used to perform functions related to general operations of computer system.. They are of two types:
- Operating System Software: It is an interface between user and computer. It takes instructions from user and further instructs hardware components to work. The results produced by hardware components are sent back to the user.
Example: Windows 10 , Unix, Linux, Android etc. - Language Translators: These softwares are used to convert the High Level Language instructions into Machine Language instructions.. They are of three types:
- Compiler: It converts High Level Language program into machine language in one go.
- Interpreter: It converts High Level Language program into machine language line by line.
- Assembler: It converts assembly language into machine language.
Utility Software
These softwares are used to take backup, remove outdated file, recover data and other tasks that assist in smooth operation of computer. Examples : Anti-Virus , Disk Defragmentation, Disk Clean, Backup, etc.
What is operating system? What are its functions?
Operating system is an interface between computer hardware and user. It is responsible for the management of activities and the sharing of the computer resources.
Operating system is divided into two parts:
- Shell: It accepts instructions from user and instructs kernel to perform further operations
- Kernel: It accepts instructions from shell and instructs hardware devices to perform operations.
Different functions of operating System are:
- Process management:- Operating System can create and delete processes. It also provides mechanism for communication among processes.
- Memory management:- Operating System allocates and de-allocates memory to different softwares.
- File management:- It manages storage, retrieval, naming, sharing, and protection of files.
- Device Management: It is responsible allocation and de-allocation of the hardware devices to different programs.
- I/O System Management: It takes care of allocation and de-allocation of Input/Output devices to different programs.
- Secondary-Storage Management: Operating Systems takes care of primary as well as secondary storage.
- Command interpretation: It interprets commands given by the user and further instructs hardware devices to perform operations according to the commands.
- Job accounting: It Keeps track of time & resource used by various programs and users.
- Communication management: It Coordinates the communication among different processes and hardware resources.
Explain architecture of Mobile Phone?
A mobile phone is composed of various parts. These parts are:

- RF Part: Every phone contains RF Unit which consists of various components amplify signal and convert baseband signal to RF frequency and vice versa.
- Baseband Part: Baseband part contains a digital signal processor (DSP) which processes received or transmitted signals. It also compresses and decompresses the signal along with error detection as correction.
- ADC and DAC: ADC(Analog to Digital Converter) and DAC(Digital to Analog Converter) is used to convert analog speech signal to digital signal and vice versa.
- RF Switch / Duplexer: RF switch is used to switch the RF path between transmitter and receiver. Duplexer is used to pass the transmitted signal and received signal at the same time through it.
- Application layer/CPU: It consists of protocols for process-to-process communication across an IP network. It includes audio, video and image/graphics applications. It provides many services like Simple Mail Transfer, Protocol, File transfer, graphics etc.
- Camera: Camera is used to click pictures and record videos. There are various mega pixel cameras for mobile available as 5 mega pixel, 13 mega pixel and even 41 mega pixel available in smartphones.
- Display: There are lot of display types used in mobile phones. They can be either color or monochrome. The color displays mostly use TFT displays. Touchscreen displays also use TFT technology. They are of two types:
- CAPACITIVE touchscreens work by sensing the electrical properties of the human body.
- RESISTIVE ones operate by sensing direct pressure applied by the user.
- Microphone: Microphone converts voice to electrical signal for further processing.
- Speaker: It converts electrical signal to voice. It comes with audio amplifier to amplify the audio signal. It also has volume control circuit to increase or decrease volume of audio signal.
- Antenna: An antenna converts electromagnetic radiation into electric signal and vice versa. In mobile phone, antenna is embedded inside so it is not visible to us.
- WiFi Module: This part is used for wireless connectivity to internet and other mobile phones or computers.
- Bluetooth Module: This part is used for Bluetooth connectivity between mobile phones and other devices within a limited area of upto few meters only.
- GPS: GPS(global positioning system) is used for location assistance and enables Google map to work efficiently.
- Sensors: In mobile phone, there are various kind of sensors like accelerometer, magnetometer, proximity sensor, light sensor, barometer, thermometer etc.
|
20 videos|20 docs|5 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Humanities/Arts exam
|

|
















