Fractions and Decimals Class 7 Notes Maths Chapter 2
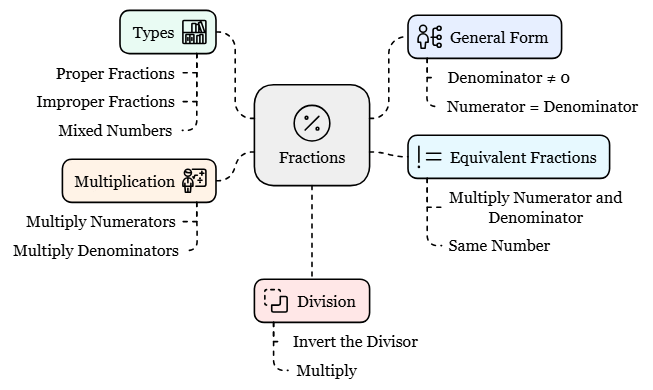
Fractions
Fractions tell about “a part of a whole”.
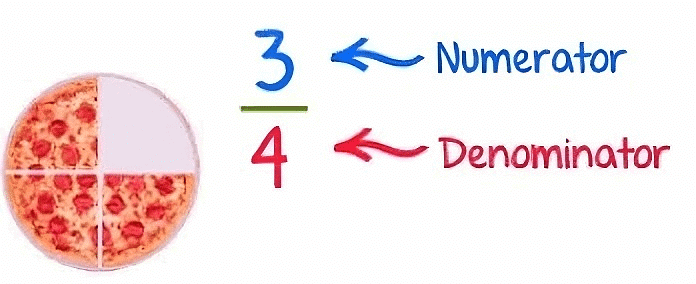
Here the pizza is divided into 4 equal parts and there are 3 parts left with us.
We will write it in a fraction as 3/4, in which 3 is numerator which tells the number of parts we have and 4 is denominator which tells the total parts in a whole.
The General form of a Fraction
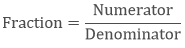
Where, denominator ≠ 0
If numerator = denominator then the fraction becomes a whole i.e. 1. This is called unity of fraction.
Types of Fraction
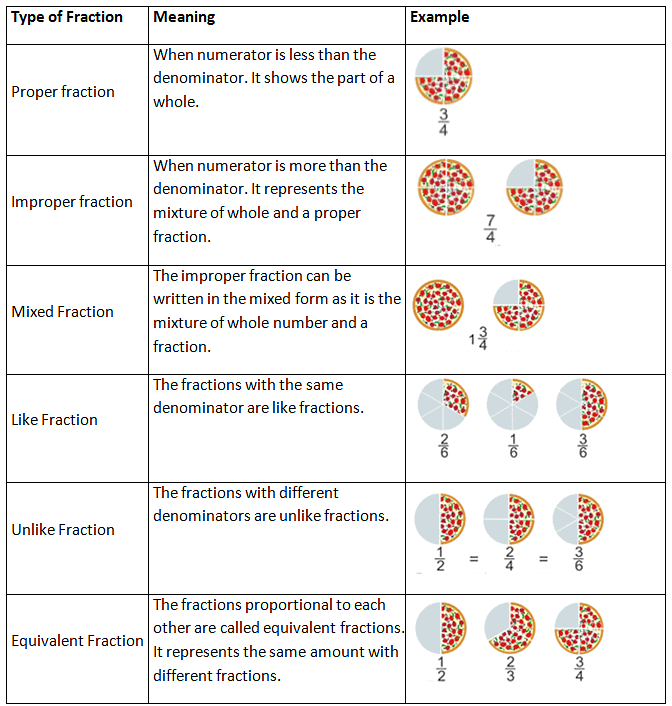
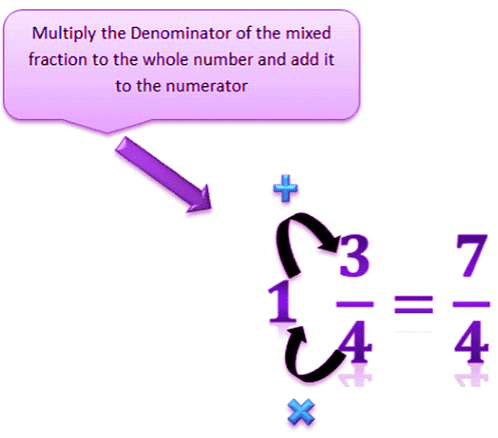
Converting a Mixed Fraction into an Improper Fraction
Converting an Improper Fraction into a Mixed Fraction
Divide the Numerator by the denominators that the quotient will be the whole number and remainder will be the numerator, while denominator will remain the same.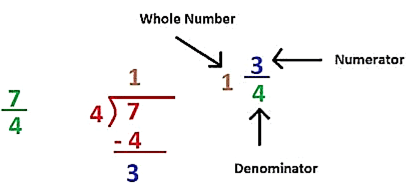
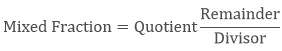
How to find the equivalent fractions?
To find the equivalent fraction of proper and improper fraction, we have the multiply both the numerator and denominator with the same number.
Example 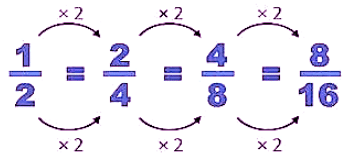
Reciprocal of a Fraction
If we have two non-zero numbers whose product is one then these numbers must be the reciprocals of each other.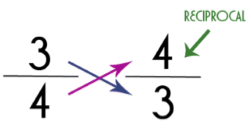
To find the reciprocal of any fraction, we just need to flip the numerator with the denominator.
Multiplication of Fractions
1. How to multiply a fraction with a whole number?
(a) If we have to multiply the proper or improper fraction with the whole number then we simply multiply the numerator with that whole number and the denominator will remain the same.
Example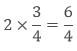
(b) If we have to multiply the mixed fraction with the whole number then first convert it in the form of improper fraction then multiply as above.
Example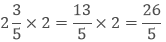
(c) Fraction as an operator “of”.
If it is written that find the 1/2 of 24 then what does ‘of’ means here?
Here ‘of’ represents the multiplication.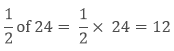
2. How to multiply a fraction with another fraction?
If we have to multiply the proper or improper fraction with another fraction then we simply multiply the numerator of both the fractions and the denominator of both the fractions separately and write them as the new fraction.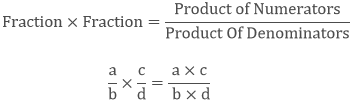
Example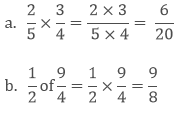
Value of the products of the fractions
Generally when we multiply two numbers then we got the result which is greater than the numbers.
5 × 6 = 30, where, 30 > 5 and 30 > 6
But in case of a fraction, it is not always like that.
(a) The product of two proper fractions
If we multiply two proper fractions then their product will be less than the given fractions.
Example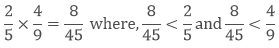
(b) The product of two improper fractions
If we multiply two improper fractions then their product will be greater than the given fractions.
Example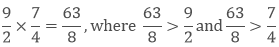
(c) The product of one proper and one improper fraction
If we multiply proper fraction with the improper fraction then the product will be less than the improper fraction and greater than the proper fraction.
Example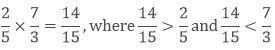
Division of Fractions
1. How to divide a whole number by a Fraction?
(a) If we have to divide the whole number with the proper or improper fraction then we will multiply that whole number with the reciprocal of the given fraction.
Example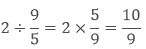
(b) If we have to divide the whole number with the mixed fraction then we will convert it into improper fraction then multiply it’s reciprocal with the whole number.
Example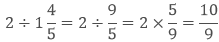
2. How to divide a Fraction with a whole number?
To divide the fraction with a whole number, we have to take the reciprocal of the whole number then divide it with the whole number as usual
Example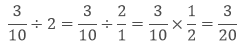
3. How to divide a fraction with another Fraction?
To divide a fraction with another fraction, we have to multiply the first fraction with the reciprocal of the second fraction.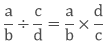
Example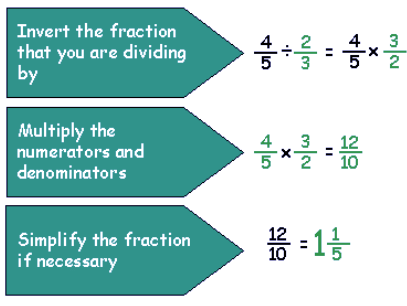
Decimal Numbers
Fractions which has denominator 10, 100, 1000 etc are called Decimal Fractions.
A decimal number is a number with a decimal point. Numbers left to the decimal are 10 greater and numbers to the right of the decimal are 10 smaller.
Multiplication of Decimal Numbers
1. How to multiply a decimal number with a whole number?
If we have to multiply the whole number with a decimal number then we will multiply them as normal numbers but the decimal place will remain the same as it was in the original decimal number.
Example
35 × 3.45 = 120.75
Here we have multiplied the number 35 with 345 as normal whole numbers and we put the decimal at the same place from the right as it was in 3.45.
2. How to multiply Decimal numbers by 10,100 and 1000?
(a) If we have to multiply a decimal number by 10 then we will transfer the decimal point to the right by one place.
Example
5.37 × 10 = 53.7
(b) If we have to multiply a decimal number by 100 then we will transfer the decimal point to the right by two places.
Example
5.37 × 100 = 537
(c) If we have to multiply a decimal number by 1000 then we will transfer the decimal point to the right by three places.
Example
5.37 × 1000 = 5370
3. How to multiply a decimal number by another decimal number?
To multiply a decimal number with another decimal number we have to multiply them as the normal whole numbers then put the decimal at such place so that the number of decimal place in the product is equal to the sum of the decimal places in the given decimal numbers.
Example
Division of Decimal Numbers
1. How to divide a decimal number with a whole number?
If we have to divide the whole number with a decimal number then we will divide them as whole numbers but the decimal place will remain the same as it was in the original decimal number.
Example
12.96 ÷ 4 = 3.24
Here we divide the number 1296 with 4 as normal whole numbers and we put the decimal at the same place from the right as it was in 12.96.
2. How to divide Decimal numbers by 10,100 and 1000?
(a) If we have to divide a decimal number by 10 then we will transfer the decimal point to the left by one place.
Example
5.37 ÷ 10 = 0.537
(b) If we have to divide a decimal number by 100 then we will transfer the decimal point to the left by two places.
Example
253.37 × 100 = 2.5337
(c) If we have to divide a decimal number by 1000 then we will transfer the decimal point to the left by three places.
Example
255.37 × 1000 = 0.25537
3. How to divide a decimal number by another decimal number?
To divide a decimal number with another decimal number
- First, we have to convert the denominator as the whole number by multiplying both the numerator and denominator by 10, 100 etc
- Now we can divide them as we had done before.
Example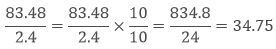
Here we had converted denominator 2.4 in the whole number by multiplying by 10. Then divide it as usual.
|
76 videos|344 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Fractions and Decimals Class 7 Notes Maths Chapter 2
| 1. What is the general form of a fraction? |  |
| 2. How do you convert a mixed fraction into an improper fraction? |  |
| 3. What is the process for finding equivalent fractions? |  |
| 4. How do you multiply fractions? |  |
| 5. What is the reciprocal of a fraction? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|


















