Gravitation Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 9
Universal Law of Gravitation
- Every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force which is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
- The force is along the line joining the centres of two objects.
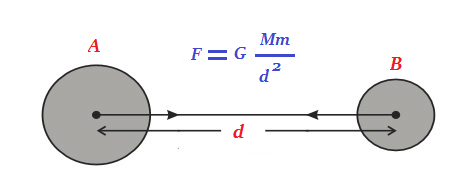
Gravitational Force between two uniform objects is directed along the line joining their centres.
- Let two objects A and B of masses M and m lie at a distance of d from each other as shown in the figure.
- Let F be the force of attraction between two objects. According to the universal law of gravitation
- G is called a universal constant because its value does not depend on the nature of the intervening medium temperature or any other physical variable.
- S.I. unit of G = Nm2/kg2
- Value of G = 6.673 × 10−11 Nm2/kg2 (Found by Henry Cavendish)
Importance of Universal Law of Gravitation
The universal law of gravitation successfully explained several phenomena:
(i) the force that binds us to the earth.
(ii) the motion of the moon around the earth.
(iii) the motion of planets around the Sun.
(iv) the tides due to the moon and the Sun.
Free fall
When an object falls towards the earth under the gravitational force alone, we say the object is in free fall.
The velocity of a freely falling body changes and is said to be accelerated.
This acceleration is called acceleration due to gravity, denoted by ‘g’. Unit is m/s2.
As F = ma (∵ a = g) ...(i)
F = mg ...(ii)
and
F = G(Mm/d2) (from Universal law of gravitation) ...(iii)
From (ii) and (iii)
∴ mg = G(Mm/d2)
∴ g= GM/d2
M = Mass of the earth
d = Distance between the object and the earth
G = Gravitational constant If the object is placed on the earth then
d = R (R = radius of the earth) ...(iv)
Earth is not a sphere, it is flattened at the poles.
Hence Rp − Radius at pole and Re − Radius at equator
∴ The value of ‘g’ is more at poles = (9.9 m/s2) and less at equator = (9.8 m/s2)
Calculation of value of g
g= G(M/R2
G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2
M = 6 × 1024 kg (Mass of the earth)
R = 6.4 × 106 m
On substituting the given values
- Motion of objects under the influence of gravity ‘g’ does not depend on the mass of the body. All objects small, big, heavy, light, hollow or solid fall at the same rate.
- The three equations of motion viz.
(i) v = u + at
(ii) s = ut + (1/2) at2
(iii) v2 – u2 = 2 as is true for the motion of objects under gravity. For free fall, the value of acceleration a = g = 9.8 ms–2. - If an object is just let fall from a height then in that case u = 0 and a = g = 9.8 m/s2.
- If an object is projected vertically upward with an initial velocity u, then a = – g = – 9.8 ms–2 and the object will go to a maximum height h where its final velocity becomes zero (i.e., v = 0).
Mass
The mass of an object is the measure of its inertia. It is the matter present in it. It remains the same everywhere in the universe.
Weight
The force of attraction of the earth on the object is known as the weight of the object. Its S.I. unit is Newton.
W = m × g
The weight of an object can change from one place to the other, from one planet to the other.
The weight of an object on the moon is given by the formula
Wm = weight of an object on the moon
Mm = Mass of the moon = 7.36 x 1022
Rm = radius of the moon = 1.74 x 106
G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2
Wm = 1.474 × 1010 G × m
and We = 1.474 × 1011 G × m
∴
∴ The weight of an object on the moon = (1/6) th the weight of an object on the earth.
Thrust
It is the net force applied in a particular direction. Its S.I. unit is N.
Pressure
- It is the force per unit area.
- Pressure = thrust / area , S.I unit = N/m2 = Pascal (pa)
 |
Download the notes
Short Notes - Gravitation
|
Download as PDF |
Pressure in fluids
- All liquids and gases are fluids, as they can flow.
- The pressure exerted by a fluid is transmitted in all directions.
Buoyancy
- The upward force exerted by water (fluid) on the body is known as upthrust or buoyancy.
- The magnitude of the buoyant force depends on the density of the fluid.
A − Wooden block
B1 − Beaker with tap water
B2 − Beaker with salty water
The buoyant force exerted in B2 is more as compared to B1. This is because the density of B2 water is higher.
The object may float, sink or remain half submerged and half above water, the density of the fluid and object decides this.- If the density of an object is less than the fluid, then it will float on the liquid.
- If the density of an object is more than the fluid, then it will sink in the liquid.
- If the density of an object is the same as the density of fluid, then it will half float and half sink.
Archimedes’ Principle
When a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid, it experiences an upward force that is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it.
Its applications are:
(i) Used in designing ships and submarines,
(ii) In lactometers to find the purity of milk.
(iii) In hydrometer to determine the density of the liquid.
Relative Density
- Relative density = density of substance/density of water
- It has no unit.
|
84 videos|384 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Gravitation Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 9
| 1. What is the law of universal gravitation? |  |
| 2. How does gravity affect the motion of planets? |  |
| 3. What is gravitational potential energy? |  |
| 4. What role does gravity play in the formation of stars and galaxies? |  |
| 5. How does gravity vary with altitude? |  |






















