Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Geography for Class 8 > Short Notes - Mineral and Power Resources
Class 8 Geography Notes - Mineral and Power Resources
Minerals
- A naturally occurring substance having a definite chemical composition is called a mineral. Minerals are found in certain areas only and not everywhere.
- Minerals are formed in different conditions and human activities do not play any role in their formation. Instead only natural processes are involved.
- Minerals can be identified on the basis of their physical properties like colour, density, hardness and chemical properties like solubility.
- On the basis of composition, we classify minerals as metallic and non-metallic.
 1. Metallic minerals contain metal. The metal is present in raw form, that is, it contains impurities and it needs to be processed in order to yield the pure metal.
1. Metallic minerals contain metal. The metal is present in raw form, that is, it contains impurities and it needs to be processed in order to yield the pure metal.
Ferrous minerals and non-ferrous minerals are a classification of metallic minerals. Ferrous minerals contain iron. Examples are iron ore, manganese ore and chromites. Non-ferrous minerals do not contain iron as a constituent. Examples include gold, silver, copper, lead.
2. Non-metallic minerals do not contain metals. Instead they contain impure compounds or mineral fuels. Examples: limestone, mica, coal and petroleum. - Metallic minerals are generally found in igneous rocks and metamorphic rocks in plateaus. Non-metallic minerals are usually found in sedimentary rock formation in plains and young-fold mountains.
- Extraction is the process of taking out minerals from under the earth’s surface so that useful materials can be derived from them.
- Mining is a process of extraction or taking out minerals from rocks under the earth’s surface.
- In open-cast mining, minerals lying at shallow depths are taken out by removing the surface layer. In shaft mining, deep bores (called shafts) are made to reach mineral deposits lying at large depths.
- Drilling is another method of extraction in which deep wells are bored to take out minerals.
- Quarrying refers to the process of extraction in which minerals lying very close to the surface are extracted just by digging them out.
- Major regions having large iron deposits are China and India in Asia; Russia, Ukraine, Sweden and France in Europe; the Canadian Shield region in North America; and Brazil in South America. Brazil is the largest producer of high grade iron ore.
- Asia produces over half the total tin production in the world. China leads in the production of lead, antimony, tin and tungsten.
- North America is divided into three zones to describe the presence of mineral deposits. These are Canadian region north of the Great Lakes, the Appalachian region and the mountain ranges in the western part of the continent.
- Chile and Peru in South America are leading producers of copper. Brazil and Bolivia are important producers of tin.
- Africa is the continent richest in mineral resources. South America, Zimbabwe and Zaire are the world’s most important producers of gold.
- Australia produces the largest quantity of bauxite. It also produces gold, diamond, iron, tin and nickel. The areas called Kalgoorlie and Coolgardie have large deposits of gold.
- In India, high grade iron ore is produced in Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Goa, Maharashtra and Karnataka. Bauxite is produced in Jharkhand, Orisha, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu. Mica deposits are found in Jharkhand, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh and Rajasthan. India is the largest producer and exporter of mica in the world.
- Kolar in Karnataka has large deposits of gold. India is a leading producer and exporter of salt.
- Minerals are non-renewable since their formation is a long process. Recycling of metals and reducing wastage are ways to conserve them.
Question for Short Notes - Mineral and Power ResourcesTry yourself: Which of the following minerals is a basic tool of the computer industry?
View Solution
Power Resources
- Power means energy. We require power for everything.
- Power resources are of two types: conventional and non-conventional.
1. Conventional power sources are those that have been in use for a long time. Fossil fuels and firewood are examples.
2. Non-conventional power sources are those power sources that have come into use recently due to the depleting conventional resources and growing awareness. - Firewood is widely used in India for cooking and heating. Fossil fuels are what the remains of plants and animals converted into after they remained buried under the earth for millions of years.
- Coal, petroleum and natural gas are important fossil fuels. Electricity from coal is called thermal power. Petroleum and its derivatives are called black gold because of their importance. Natural gas is found with petroleum deposits.
- Hydel power is the energy possessed by river water (stored in dams) or rain water falling from great heights. One-fourth of the world’s electricity is produced from hydel power.
- Solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, nuclear power and tidal energy are examples of non-conventional power sources.
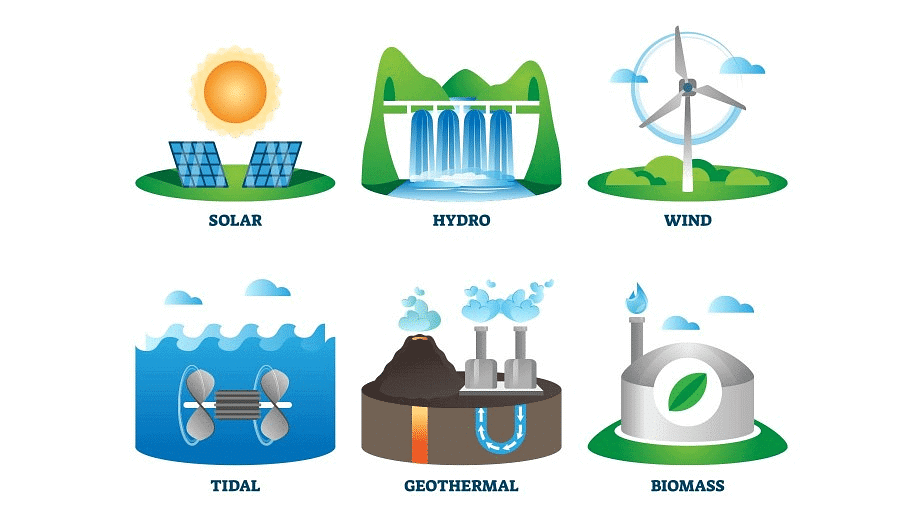 Non Conventional Power Sources
Non Conventional Power Sources - Solar energy is the heat and light energy captured from the sun. Solar cells help to convert this energy to electricity. Solar energy is used in solar heaters, solar cookers, solar dryers, etc.
- Wind energy is the energy possessed by moving air (wind). Windmills are used to convert wind energy to electricity. Wind farms having clusters of windmills are located in coastal regions and mountain passes.
- Nuclear power is energy possessed by the nuclei of atoms of naturally occurring radioactive elements like uranium, thorium, etc.
- Geothermal energy is the heat energy obtained from the inside of the earth. The temperature inside the earth increases as we go deeper. This heat is used to produce electricity. It is accessed in the form of hot springs.
- Tidal energy is the energy generated from tides. It is harnessed by building dams at narrow openings of the sea.
- Biogas is a gaseous fuel obtained from the decomposition of organic waste like dead plant and animal material or animal dung and kitchen waste. It is an excellent fuel for cooking and lighting, and is environment-friendly.
Words that Matter
- Mineral: A naturally occurring substance having a definite chemical composition is called a mineral.
- Rock: A rock is an aggregate of one or more minerals, without definite composition of constituent of minerals.
- Ore: An ore is a rock from which minerals are mined.
- Metallic Minerals: Metallic minerals are those containing metal. The metal is present in raw form, that is, it contains impurities and it needs to be processed in order to yield the pure metal.
- Ferrous Minerals: Ferrous minerals are the ones containing iron as a constituent.
- Non-ferrous Minerals: Non-ferrous minerals are the ones that do not contain iron as a constituent.
- Non-metallic Minerals: Non-metallic minerals are the ones that do not contain metals. Instead they contain impure compounds or mineral fuels.
- Extraction: Extraction is the process of taking out minerals from under the earth’s surface so that useful materials can be derived from them.
- Mining: Mining is a process of extraction or taking out minerals from rocks under the earth’s surface.
- Open-cast Mining: Open-cast mining is a method of extraction in which minerals lying at shallow depths are taken out by removing the surface layer.
- Shaft Mining: Shaft mining is a method of extraction in which deep bores (called shafts) are made to reach mineral deposits lying at large depths.
- Drilling: Drilling is another method of extraction in which deep wells are bored to take out minerals.
- Quarrying: Quarrying refers to the process of extraction in which minerals lying very close to the surface are extracted just by digging them out.
- Conventional Sources of Energy: Conventional power sources are those that have been in use for a long time.
- Non-conventional Power Sources: Non-conventional power sources are those power sources that have come into use recently due to the depleting conventional resources and growing awareness.
- Fossil Fuels: Fossil fuels are what the remains of plants and animals converted into after they remained buried under the earth for millions of years.
- Thermal Power: The electricity obtained from coal is called thermal power.
- Coal: Coal is a fossil fuel that was formed millions of years ago when giant ferns and swamps got buried under the layers of the earth.
- Petroleum: Petroleum is a thick black liquid fossil fuel found between layers of rocks and drilled from oil fields.
- Hydel Power: Hydel power is the energy possessed by river water (stored in dams) or rain water falling from great heights.
- Solar Energy: Solar energy is the heat and light energy captured from the sun.
- Solar Cell: Solar cells are devices to convert solar energy into electricity.
- Wind Energy: Wind energy is the energy possessed by moving air (wind).
- Nuclear Power: Nuclear power is energy possessed by the nuclei of atoms of naturally occurring radioactive elements like uranium, thorium, etc.
- Geothermal Energy: Geothermal energy is the heat energy obtained from the inside of the earth.
- Tidal Energy: Tidal energy is the energy generated from tides.
- Biogas: Biogas is a gaseous fuel obtained from the decomposition of organic waste like dead plant and animal material or animal dung and kitchen waste.
The document Class 8 Geography Notes - Mineral and Power Resources is a part of the Class 8 Course Geography for Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
24 videos|33 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Geography Notes - Mineral and Power Resources
| 1. What are minerals and why are they important? |  |
Ans. Minerals are naturally occurring solid substances found in the earth's crust. They have a definite chemical composition and crystal structure. Minerals are important because they are used in various industries, such as construction, manufacturing, and agriculture. They are also essential for our bodies as they provide necessary nutrients.
| 2. How are minerals formed? |  |
Ans. Minerals are formed through various geological processes. One common way is through cooling and solidification of molten rock, known as magma. This process creates minerals such as granite or basalt. Another way is through precipitation from hot water solutions, which leads to the formation of minerals like quartz or calcite. Minerals can also be formed by the alteration of pre-existing rocks under high pressure and temperature.
| 3. What are some examples of valuable minerals? |  |
Ans. Some examples of valuable minerals include gold, silver, copper, iron ore, diamond, and coal. These minerals have economic value and are extensively used in industries, jewelry, and energy production. They are also commonly traded in international markets.
| 4. How are power resources classified? |  |
Ans. Power resources are classified into two main categories: renewable and non-renewable. Renewable power resources are those that can be replenished naturally, such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy. Non-renewable power resources, on the other hand, cannot be replenished or take millions of years to form, such as fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas.
| 5. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using power resources? |  |
Ans. The advantages of using power resources are that they provide energy for various activities and industries, contribute to economic development, and can be harnessed to reduce dependency on fossil fuels. However, there are also disadvantages. Non-renewable power resources contribute to pollution, climate change, and resource depletion. Renewable power resources can be intermittent, require large initial investments, and may have limited availability in certain regions.
Related Searches

















