Ratio and Proportion Class 6 Notes Maths Chapter 12
| Table of contents |

|
| Ratio |

|
| The unit must be same to compare two quantities |

|
| Equivalent Ratios |

|
| Simplifying a Ratio |

|
| Proportion |

|
| Extreme Terms and Middle Terms of Proportion |

|
| Unitary Method |

|
Ratio
- If we compare two quantities using division then it is called ratio.
- It compares quantities in terms of ‘How many times’.
- The symbol to represent ratio is “:”.

Example: If there are 35 boys and 25 girls in a class, then what is the ratio of
- Number of boys to total students
- Number of girls to total students.
Sol: In the ratio, we want the total number of students.
Total number of students = Number of boys + Number of girls
35 + 25 = 60
Ratio of number of boys to total number of students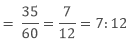
The ratio of the number of girls to the total number of students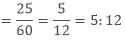
The unit must be same to compare two quantities
If we have to compare two quantities with different units then we need to convert them in the same unit .then only they can be compared using ratio.
 Example: What is the ratio of the height of Raman and Radha if the height of Raman is 175 cm and Radha is 1.35 m?
Example: What is the ratio of the height of Raman and Radha if the height of Raman is 175 cm and Radha is 1.35 m?
Sol: The unit of the height of Raman and Radha is not same so convert them in the same unit.
Height of Radha is 1.35 m = 1.35 × 100 cm = 135 cm
The ratio of the height of Raman and Radha
Equivalent Ratios
- If we multiply or divide both the numerator and denominator by the same number then we get the equivalent ratio. There could be so many equivalent ratios of the same ratio.
- In the case of equivalent ratios only their value changes but they represent the same portion of the quantity.
Example: Find two equivalent ratios of 2/4.
Sol: 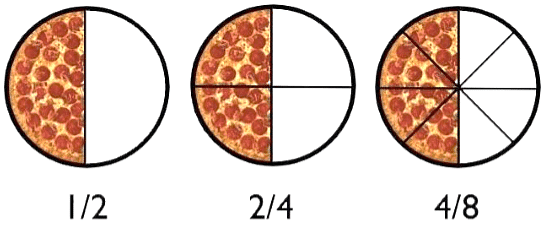 To get the equivalent ratio we multiply both the numerator and denominator with 2.
To get the equivalent ratio we multiply both the numerator and denominator with 2.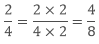
To get another equivalent ratio we divide both the numerator and denominator with 2.
From the above figure, we can see that in all the equivalent ratios only the number of equal parts is changing but all the ratios are representing the half part of the circle only.
Simplifying a Ratio
If there is no common factor of numerator and denominator except one then it is the lowest form of the ratio.
 Example: Find the lowest form of the ratio 25: 100.
Example: Find the lowest form of the ratio 25: 100.
Sol: The common factor of 25 and 100 is 25, so divide both the numerator and denominator with 25.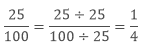
Hence the lowest ratio of 25: 100 is 1: 4.
Proportion
If we say that two ratios are equal then it is called Proportion.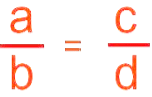 We write it as a: b : : c : d or a: b = c: d
We write it as a: b : : c : d or a: b = c: d
And reads as “a is to b as c is to d”.
Example: If a man runs at a speed of 20 km in 2 hours then with the same speed would he be able to cross 40 km in 4 hours?
Solution: Here the ratio of the distances given is 20/40 = 1/2 = 1: 2
And the ratio of the time taken by them is also 2/4 = 1/2 = 1: 2
Hence the four numbers are in proportion.
We can write them in proportion as 20: 40 : : 2: 4
And reads as “20 is to 40 as 2 is to 4”.
Extreme Terms and Middle Terms of Proportion
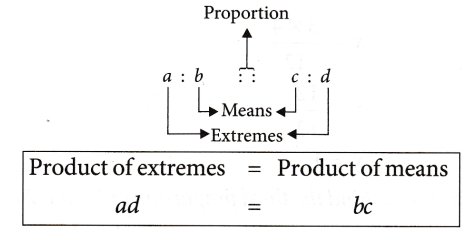
The first and the fourth term in the proportion are called extreme terms and the second and third terms are called the Middle or the Mean Terms.
In this statement of proportion, the four terms which we have written in order are called the Respective Terms.
If the two ratios are not equal then these are not in proportion.
Example 1: Check whether the terms 30,99,20,66 are in proportion or not.
Sol: To check the numbers are in proportion or not we have to equate the ratios.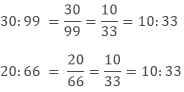
As both the ratios are equal so the four terms are in proportion.
30: 99 :: 20: 66
Unitary Method
If we find the value of one unit then calculate the value of the required number of units then this method is called the Unitary method.
Example : If the cost of 3 books is 320 Rs. then what will be the cost of 6 books?
Solution: Cost of 3 books = Rs. 320
Cost of 1 book = 320/3 Rs.
Cost of 6 books = (320/3) × 6 = 640 Rs.
Hence, the cost of 6 books is Rs. 640.
|
157 videos|229 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Ratio and Proportion Class 6 Notes Maths Chapter 12
| 1. What is a ratio and how is it used to compare two quantities? |  |
| 2. How can we simplify a ratio? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between equivalent ratios and simplifying ratios? |  |
| 4. What is a proportion and how do you identify extreme and middle terms in it? |  |
| 5. What is the unitary method and how is it applied in solving problems related to ratios and proportions? |  |
















