Class 8 Civics Chapter 1 Notes - The Indian Constitution
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Constitution? |

|
| Why Does a Country Need a Constitution? |

|
| The Indian Constitution: Key Features |

|
| Words that Matter |

|
What is Constitution?
A Constitution is a written document that contains a set of rules and principles for governing a country.
 Constitution of India
Constitution of India
- A society is bound to a certain set of rules, which makes it what it is and differentiates it from other kinds of society. These rules, in large societies in which different communities of people live together, are formulated through consensus.
- In modern countries, this consensus is usually available in written form. A written document in which we find such rules is known as a Constitution.
- A Constitution helps serve as a set of rules and principles that all persons in a country can agree upon as the basis of the way in which they want the country to be governed.
- This includes the type of government and also an agreement on certain ideals that they all believe the country should uphold.
Why Does a Country Need a Constitution?
A Constitution is is an essential document that guides the functioning of a country and helps create a just and democratic society. Constitution is important for a country because it serves several purposes, including:

- Defining our society: The Constitution tells us about the fundamental nature of our society. It outlines the values, ideals, and principles that we believe in as a country.
- Setting rules for the government: The Constitution acts as a rulebook for how our country should be governed. It provides a set of rules and principles that everyone agrees upon. It helps to ensure that those in power, such as political leaders, do not misuse their authority.
- Protecting our rights and principles: The Constitution helps to protect our rights and freedoms. In democratic societies, it lays down rules that guard against the misuse of power by our political leaders. It also safeguards us against decisions that could go against the larger principles and values that our country believes in.
- Ensuring fairness and equality: The Constitution ensures that a dominant group or individuals in power do not use their authority to oppress or harm less powerful people or groups. It promotes fairness and equality among all citizens.
In summary, a Constitution is necessary because it defines our society, sets rules for the government, protects our rights and principles, and ensures fairness and equality.
The Indian Constitution: Key Features
A group of 300 people became members of the Constituent Assembly in 1946 and had written India’s Constitution. While writing the Indian Constitution, these members kept in mind the different communities who speak different languages, belong to different religions, and have distinct cultures.
Listed below are the key features of the Indian Constitution.

1. Federalism
Federalism is the prime feature of our Constitution, which refers to the existence of more than one level of government in the country.
- In India, there are governments at the state and the centre. Panchayati Raj is the third tier of the government.
- While each state in India enjoys autonomy in exercising powers on certain issues, they are bound to follow the laws of the central government as a matter of national concern.
- The Constitution clearly defines the jurisdictions of powers of the government at the state and the at level.
2. Parliamentary form of Government
The people of India have a direct role in electing their representatives. Also, every citizen of the country, irrespective of his/her social background, can contest in elections.
3. Separation of powers
Separation of powers in the Constitution of India recommends three organs of the State: the legislature, the executive and the judiciary.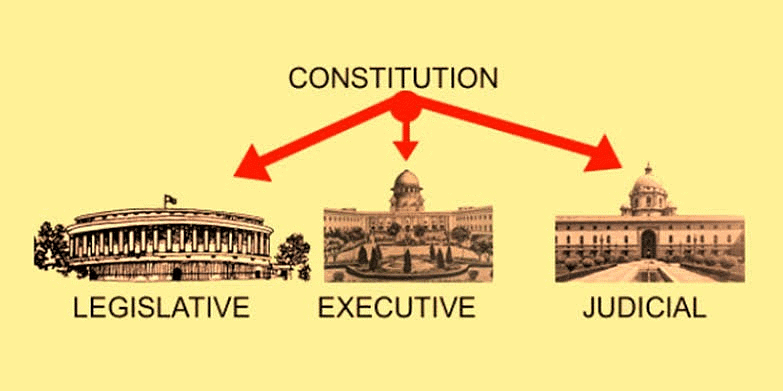 Separation of Powers
Separation of Powers- Legislature refers to our elected representatives.
- The executive refers to a smaller group of people who are responsible for implementing laws and running the government.
- Judiciary refers to the system of courts in the country for preventing the misuse of power by any branch of the State. It also ensures the balance of power between all three organs.
4. Fundamental Rights
Fundamental Rights are the ‘conscience’ of the Indian Constitution. These Rights protect citizens against the arbitrary and absolute exercise of power by the State. The Constitution, thus, guarantees the rights of individuals against the State as well as against other individuals.The Fundamental Rights in the Indian Constitution include: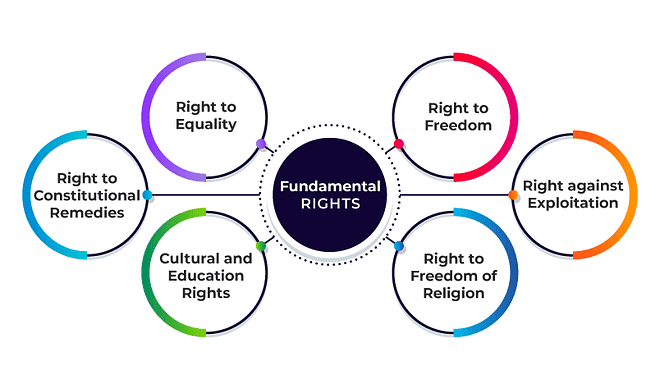 Fundamental Rights
Fundamental Rights
i. Right to Equality
ii. Right to Freedom
iii. Right against Exploitation
iv. Right to Freedom of Religion
v. Cultural and Educational Rights
vi. Right to Constitutional Remedies.
In addition to the Fundamental Rights, there is the provision of Directive Principles of State Policy, which ensure greater social and economic reform, and serve as a guide to the independent Indian State to institute laws and policies that help reduce the poverty of the masses.
5. Secularism:
The Indian Constitution defines that a secular state is one in which the state does not officially promote any one religion as the state religion.
The Constitution, thus, plays a crucial role in laying out the ideals that we would like all citizens of the country to adhere to, including the representatives that we elect to rule us.
Words that Matter
- Constitution: Usually a written document which contains the rules of governing a sovereign state.
- Consensus: Agreement of all the people on an issue.
- Democracy: A form of government in which people at large hold the ultimate power of governance. The representatives of the people constitute the government and undertake the Constitutional responsibilities to achieve the ideals of the Constitution.
- Fundamental Rights: The set of Rights which ensures the life of dignity, and honour of all who live in its jurisdiction.
- Equality: State of being equal in all respects.
- Majority: Maximum in number.
- Minority: Minimum in number.
- Federalism: The existence of more than one level of government in the country.
- Representative: The person who is elected by people through a general election to represent a constituency in the government.
- Secularism: A system under which a state does not officially promote any one religion as a state religion.
|
69 videos|431 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Civics Chapter 1 Notes - The Indian Constitution
| 1. What is the definition of a constitution? |  |
| 2. Why is a constitution important for a country? |  |
| 3. What are some key features of the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 4. How does the Indian Constitution protect the rights of citizens? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the directive principles of state policy in the Indian Constitution? |  |
















