Class 11 Economics Short Questions with Answers - Collection of Data
Short Answer Questions
Q1. What do you mean by data?
Ans: Data refers to facts or information collected for analysis. It can be understood as follows:
- Plural of 'datum': The term originates from the Latin word 'datum', meaning a single piece of information.
- Types of data: Data can be classified into primary (collected firsthand) and secondary (collected by others).
- Purpose: Data is essential for understanding and solving problems by providing necessary information.
For example, if you survey students about a film star's popularity, the responses you gather are considered primary data.
Q2. What is the purpose of data collection?
Ans: The purpose of data collection is to:
- Gather evidence for analysis.
- Understand and explain economic problems.
- Identify effective solutions to these issues.
Data collection helps in making informed decisions based on accurate information.
Q3. What is primary data?
Ans: Primary data is information that is collected directly from the source by the researcher. It is known as first-hand data.
- Examples include surveys, interviews, and observations.
- It is often gathered to answer specific research questions.
- Primary data is valuable because it is original and tailored to the study's needs.
For instance, if you want to assess the popularity of a film star among school students, you would ask the students directly. The feedback you receive is considered primary data.
Q4. Define secondary data.
Ans: Secondary data refers to information that has already been collected by someone else. It is used by researchers for their own studies. Key points include:
- Data is gathered from published sources like reports, books, and websites.
- It saves time and costs compared to collecting new data.
- For example, if a researcher uses data from a previous study on film star popularity, that data is considered secondary.
Q5. Who is an investigator?
Ans: An investigator is someone who:
- Plans investigations to gather information.
- Executes the investigation process.
- Collects and analyses data to draw conclusions.
They play a crucial role in research and problem-solving.
Q6. Who is a respondent?
Ans: A respondent is an individual who provides information or data in response to questions during a survey or research study.
Q7. Who is an enumerator?
Ans: An enumerator is a person responsible for the actual collection of data during surveys or censuses.
- They gather information directly from respondents.
- Enumerators may conduct face-to-face interviews or use questionnaires.
- They play a crucial role in ensuring accurate and reliable data collection.
Q8. Write one internal and one external source of data.
Ans: Internal Source: An annual report of a company provides detailed information about its financial performance and operations.
External Source: Data from the National Sample Survey Organisation (NSSO) offers insights into various socio-economic factors affecting the population.
Q9. Name any two published sources of data.
Ans: The World Bank and the International Monetary Fund are two examples of published sources of data.
Q10. Name any two unpublished sources of data.
Ans: Private institutions and individual researchers are examples of unpublished sources of data.
Q11. Write any two methods of data collection.
Ans: The methods of data collection are:
- Direct personal investigation: This involves face-to-face interviews with respondents, allowing for clarification and deeper understanding.
- Indirect oral investigation: This method gathers information through conversations without direct questioning.
- Investigation through local correspondents: Utilises local contacts to gather relevant data.
- Questionnaires: Surveys are conducted via written questions sent to respondents.
Q12. What are the types of the questionnaire method?
Ans: There are two main types of questionnaire methods:
- Enumeration Questionnaire: This method involves collecting data through direct interaction, typically face-to-face.
- Mail Questionnaire: This method sends questionnaires to individuals via post, allowing them to complete and return them by a specified date.
Q13. List the types of questions that may be asked in the questionnaire.
Ans: The questionnaire may include:
- Closed-ended questions:
- Two-way questions: These offer only two options, such as 'yes' or 'no'.
- Multiple choice questions: These provide several options for respondents to choose from.
- Open-ended questions: These allow respondents to provide their own answers in detail.
Q14. What are close-ended questions?
Ans: Closed-ended questions can be classified into two types:
- Two-way questions: These offer only two possible answers, typically 'yes' or 'no'.
- Multiple choice questions: These provide several options for respondents to choose from.
However, they can be challenging to write, as the options must clearly represent the issue. There is also a risk that a respondent's true feelings may not be included in the options provided. To address this, an 'Any Other' option allows for additional responses.
Q15. List any two demerits of mailing questionnaires.
Ans: The demerits of mailing questionnaires include:
- Misinterpretation of questions is possible, as respondents may not fully understand them without clarification.
- Mail surveys often result in low response rates due to factors like incomplete returns or loss in transit.
Q16. When is it suggested to undertake an indirect oral investigation?
Ans: Indirect oral investigation is recommended when:
- Respondents are hesitant to answer questions directly.
- Sensitive topics may cause discomfort in personal interviews.
- There is a need for more honest or candid responses.
This method helps gather information while respecting the respondents' feelings.
Q17. What may be the impact of the presence of the researcher in a personal interview?
Ans: The presence of the researcher during a personal interview can have several impacts:
- The researcher may unintentionally inhibit respondents from expressing their true thoughts.
- Respondents might feel pressured to provide socially acceptable answers.
- Some individuals may withhold their opinions due to fear of judgment.
- The dynamic of the interview can change based on the researcher's behaviour and reactions.
Q18. What are the benefits of conducting a pilot survey?
Ans: The benefits of conducting a pilot survey include:
- Preliminary insights: It provides a prior idea about the overall survey.
- Identifying issues: It helps to uncover any shortcomings or drawbacks in the questions.
- Question suitability: It assesses the suitability and clarity of the questions.
Q19. What is data? Explain the sources of data.
Ans: Data refers to facts or information, derived from the Latin word 'datum'. It can be classified into two main sources:
- Internal Source of Data: This type of data comes from within an organisation. For example, a bank's report on its deposits and loans serves as an internal source for that bank.
- External Source of Data: This data is collected from outside an organisation. For instance, an economist may use data published by the Indian government to analyse an economic issue.
External data can be further divided into:
- Primary Data: This is first-hand information collected directly from individuals. For example, to gauge the popularity of a film star among school students, one would survey a large group of students.
- Secondary Data: This data is processed and compiled by another entity. It can be sourced from published materials like government reports, newspapers, or academic books. For instance, if someone uses the popularity data collected from students for their own study, it becomes secondary data.
In summary, data is essential for understanding and analysing various issues, and its sources can significantly impact the conclusions drawn from it.
Q20. Explain the questionnaire method of investigation.
Ans: The questionnaire method involves the investigator creating a series of questions tailored to the investigation's objectives. This method allows data collection in two primary ways:
- Enumerator: A trained individual administers the questionnaire directly to respondents.
- Mail: Questionnaires are sent to respondents, who complete and return them by a specified date.
This method is cost-effective and can reach individuals in remote areas. It also allows respondents to answer at their convenience, leading to more thoughtful responses.
Q21. What is the difference between enumerator’s and mail questionnaire method?
Ans: Enumerator's Method:
- The questionnaire is delivered by enumerators directly to respondents.
- Data is collected in person, allowing for immediate clarification of questions.
- This method can lead to better understanding and engagement from respondents.
Mail Questionnaire Method:
- The questionnaire is sent via mail to respondents.
- Respondents complete and return the questionnaire by a specified date.
- This method is generally less expensive and can reach people in remote areas.
- It allows respondents to take their time when answering, reducing pressure.
Q22. Differentiate between a schedule and a questionnaire.
Ans: A questionnaire is a set of questions designed for respondents to answer independently. In contrast, a schedule is a tool used by an enumerator or researcher to ask questions directly to respondents.
Questionnaire:
- Self-administered by respondents.
- Allows for personal reflection and thought.
Schedule:
- Administered by an enumerator.
- Facilitates direct interaction and clarification.
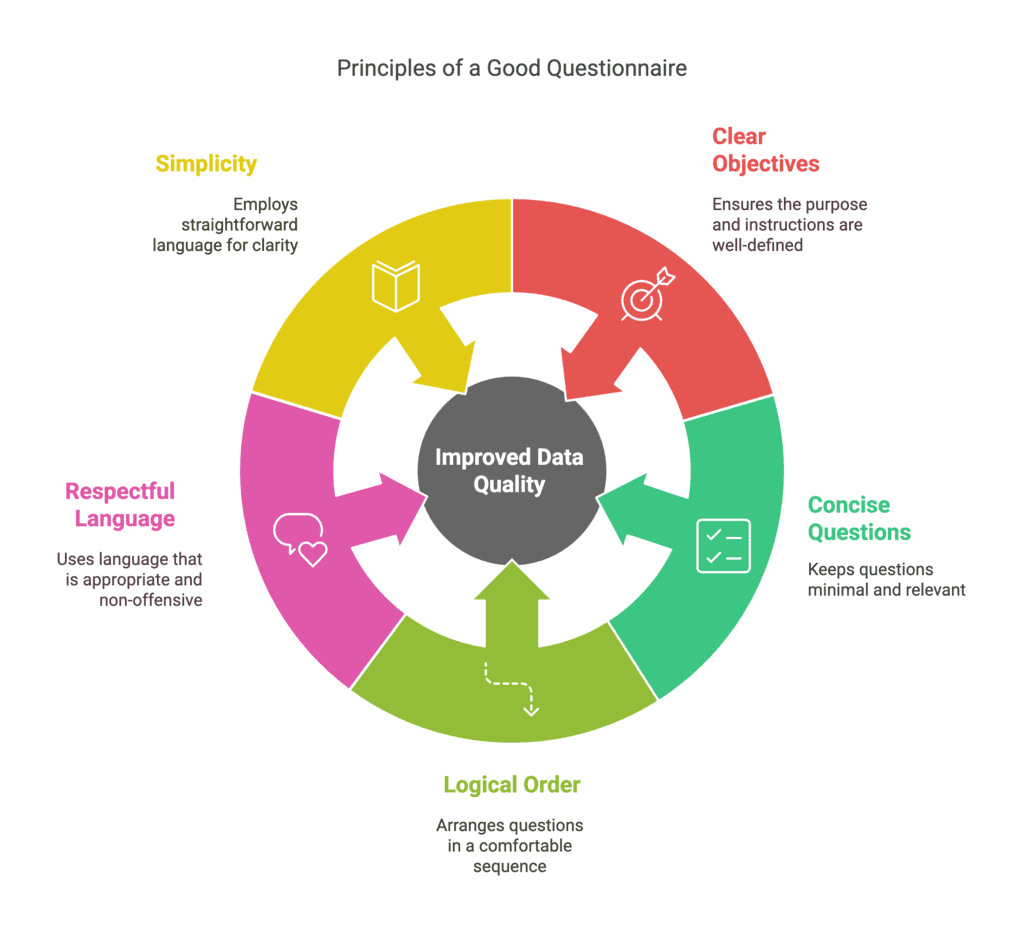
Q23. What are the features of a good questionnaire?
Ans: A good questionnaire is essential for collecting accurate and original data. It should possess the following features:
- Clear Objectives: The purpose of the investigation and instructions for completing the questionnaire should be clearly stated.
- Concise Questions: The number of questions should be minimal and relevant to the investigation.
- Logical Order: Questions should be arranged in a logical sequence to ensure comfort for the respondent.
- Respectful Language: Questions must not be irritating, inappropriate, or offensive to any group.
- Simplicity: The language used should be straightforward to understand for all respondents.
By adhering to these principles, the quality of the data collected can be significantly improved.
Q24. Define pilot survey. List its uses.
Ans: A pilot survey is a preliminary study conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of a research methodology before the main survey begins. Its purpose is to identify any unforeseen challenges that may arise during the actual survey. The pilot survey helps assess:
- Performance of enumerators
- Quality of questions
- Suitability of questions
- Cost involved in the final survey
- Time required for the final survey
|
59 videos|222 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on Class 11 Economics Short Questions with Answers - Collection of Data
| 1. What is data collection? |  |
| 2. Why is data collection important? |  |
| 3. What are some common methods of data collection? |  |
| 4. What are the challenges of data collection? |  |
| 5. How can data collection be improved? |  |

















