Short and Long Answer Questions: Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Short Answer Questions
Q1. How can you tell that an electric current is flowing even without a bulb in the circuit?
Answer: You can place a magnetic compass near the wire and look for a needle deflection, or feel gentle warming of a high-resistance wire, showing current flow.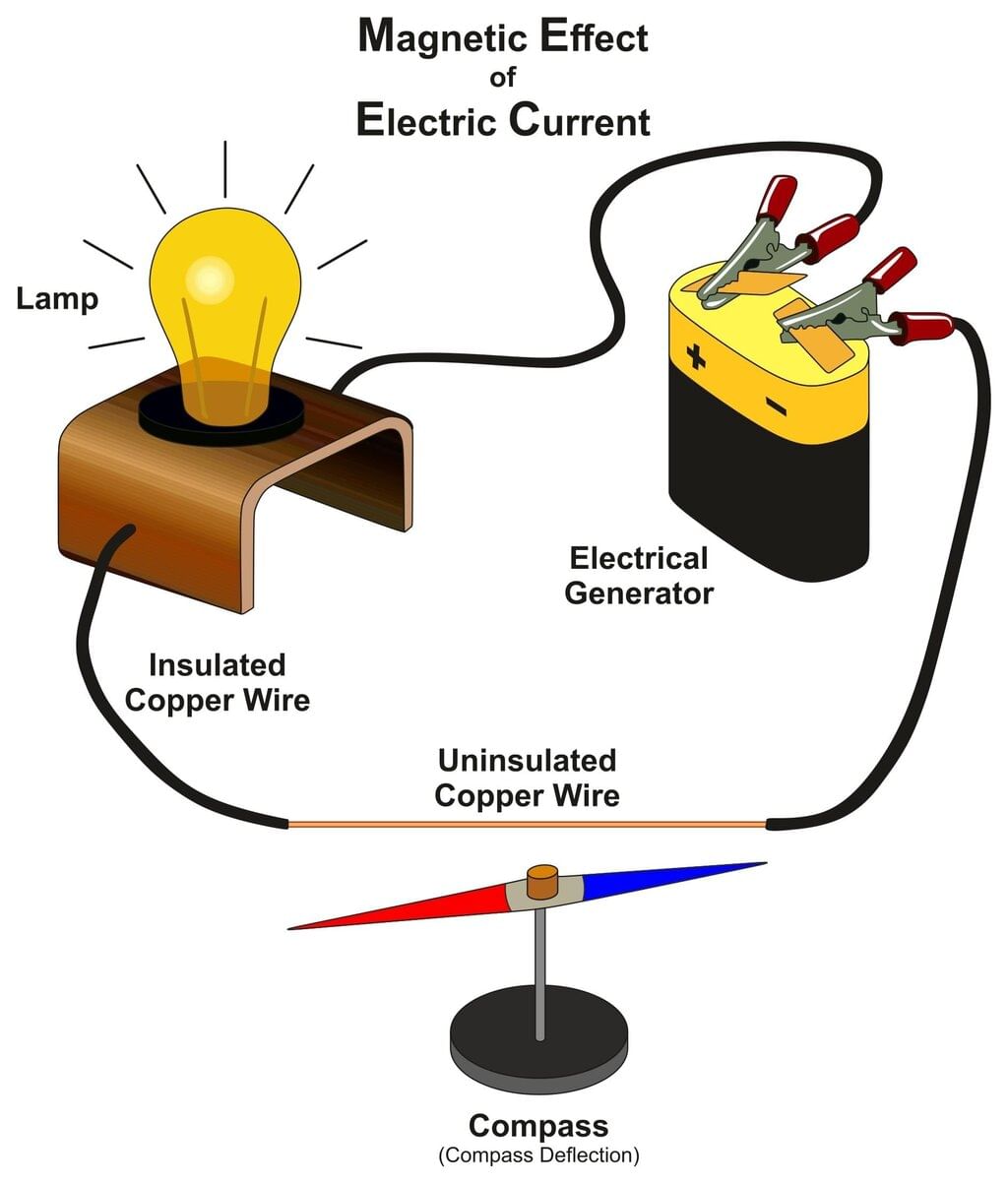
Q2. What does a magnetic field around a current-carrying wire mean in practical terms?
Answer: It means the wire behaves like a weak magnet, which can influence a nearby compass or interact with other magnetic materials.
Q3. How did Oersted’s experiment change our understanding of science?
Answer: Oersted showed that electricity and magnetism are connected, which led to new technologies like electromagnets and electric motors.
Q4. Why is soft iron used as the core in an electromagnet instead of steel?
Answer: Soft iron magnetizes and demagnetizes quickly, so the magnet turns on and off easily with current, while steel tends to stay magnetized.
Q5. How can you safely test the polarity (north and south poles) of an electromagnet you built?
Answer: Bring a compass near each end of the coil and observe which way the needle points, then reverse the battery connections to see the poles swap.
Q6. Why are more turns of wire in a coil better for making a strong electromagnet?
Answer: More turns concentrate the magnetic effect, increasing the field strength for the same current.
Q7. Why are lifting electromagnets preferred over permanent magnets in scrap yards?
Answer: They can be switched on to pick up metal and switched off to drop it, making sorting and moving heavy metal easy and controlled.
Q8. What everyday signs show the heating effect of electric current?
Answer: Devices like irons, kettles, and heaters become hot when switched on because their elements convert electrical energy into heat.
Q9. Why do longer and thinner wires get hotter than shorter and thicker ones with the same current?
Answer: Longer and thinner wires have higher resistance, so more electrical energy is converted to heat in them.
Q10. What are two safety steps to prevent overheating in home circuits?
Answer: Use wires and plugs with correct current ratings and install protective devices like fuses or circuit breakers.
Q11. How does a simple lemon cell demonstrate the idea of chemical energy changing to electrical energy?
Answer: The lemon’s acid acts as an electrolyte and the two metals act as electrodes, creating a chemical reaction that pushes electrons through a circuit.
Q12. Why are lithium-ion batteries widely used in phones and laptops instead of ordinary dry cells?
Answer: Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable, store more energy for their size, and provide steady power over many cycles, reducing waste.
Q13: Why the filament of bulb does not get heated sometimes in a circuit?
Ans: This is because current through the circuit is too weak so the filament of the bulb does not get heated sufficiently and it does not glow.
Q14: Is it possible for an electric tester to detect weak current also, if no how can we detect weak current flowing in a circuit?
Ans: If weak current flows through the circuit then bulb in it will not glow. In order to detect weak current we use LED or may use another effect of electric current that is it produces magnetic effect also so we can use this property of electric current to detect weak current.
Q15: What do you mean by electric current?
Ans. The continuous and directional flow of charges (electrons) is called electric current. It is denoted by I and its unit is ampere.
Q16: What is LED? Why is it most important source of light?
Ans. The device which is used in the tester in place of bulb is called LED. It glows even at very small current. There are two wires called leads attached to the LED. One lead is longer than the other. A long wire is connected with the positive terminal and shorter lead is connected to the negative terminal of battery.
Q17: What do you mean by magnetic effect of electricity?
Ans. When electric current is passed through a coil or wire, then it behaves like a magnet. This is called magnetic effect of current. The strength of magnetic field depends on the amount of current passing through a coil or wire. The coil or wire shows magnetism till current is passed.
Q18: Why do we need magnetic compass to test the conduction of electric current?
Ans. Sometimes the bulb does not glow on passing electric current. This is because the electric current flowing through a conductor is so small, that the filament of the bulb does not get heated up to the temperature where it starts glowing. So, in case of small current we need magnetic compass to test the conduction.
Long Answer Questions
Q1. Explain how a magnetic compass can be used to map the shape and direction of the magnetic field around a straight current-carrying wire.
Answer:
- Place a board with a straight wire passing through its center and sprinkle small compass needles or iron filings around it. When current flows, observe that the compass needles align in circular paths around the wire, showing the field’s shape.
- Reverse the current and note that all needles flip direction, proving field direction depends on current direction. Mark the needle directions to draw concentric circles indicating magnetic lines of force. This activity shows both the pattern and the direction of the magnetic field created by current.
Q2. Describe how the magnetic field changes around a coil (solenoid) compared to a straight wire, and what this tells us about making stronger electromagnets.
Answer:
- A straight wire makes circular fields around it, but a coil (solenoid) concentrates the field inside, making it stronger and more uniform. The coil’s field resembles a bar magnet with a clear north and south pole.
- Inserting a soft iron core inside the coil further increases the field strength by channeling the magnetic lines. Increasing the number of turns or the current also strengthens the field. This shows why solenoids with iron cores are used to make powerful electromagnets.
Q3. Explain the role of materials in heating elements and why nichrome is preferred over copper for appliances like irons and heaters.
Answer: 
- Heating elements need materials with high electrical resistance so that more electrical energy converts into heat. Nichrome has higher resistance than copper and can tolerate high temperatures without melting or oxidizing quickly. It also maintains a stable resistance over time, giving steady heating performance.
- Copper, though an excellent conductor, produces little heat and can overheat dangerously at high currents. Therefore, nichrome provides safe, efficient, and durable heating in appliances.
Q4. Discuss the balance between useful heating and energy loss in electric circuits, and suggest ways to reduce unwanted heating at home.
Answer:
- Heating is useful in devices like heaters and kettles, but in regular wires it wastes energy and can be risky. Unwanted heating comes from resistance in wires, loose connections, and overloading circuits.
- Using proper wire thickness and high-quality plugs reduces resistance and heat buildup. Keeping connections tight and clean lowers energy loss. Distributing heavy appliances across circuits and using circuit breakers helps prevent overheating and improves safety.
Q5. Describe a classroom investigation to compare how wire length and thickness affect heating, including the steps, variables, and observations.
Answer:
- Set up a simple circuit with a cell, switch, and replaceable test wires of the same material but different lengths and thicknesses. Keep the cell and time constant, and change only one factor at a time (length first, then thickness).
- After switching on for a fixed time, feel carefully or use a thermometer/IR sensor to note temperature rise. Record results to compare which wire heats more. You will observe that longer and thinner wires heat more due to higher resistance.
Q6. Explain how connecting cells in series or parallel changes the performance of an electromagnet or a small motor, and why.
Answer:
- Cells in series add their voltages, increasing the current in the circuit for the same resistance, which strengthens an electromagnet or speeds a motor. Cells in parallel keep the same voltage but provide more total charge, allowing the device to run longer at the same power. For quick, strong magnetic pull, series connection is helpful.
- For longer operation without frequent cell changes, parallel connection helps. Choosing series or parallel depends on whether you need more strength or more duration.
Q7. Describe the working differences between a dry cell and a rechargeable battery in terms of chemistry and practical use.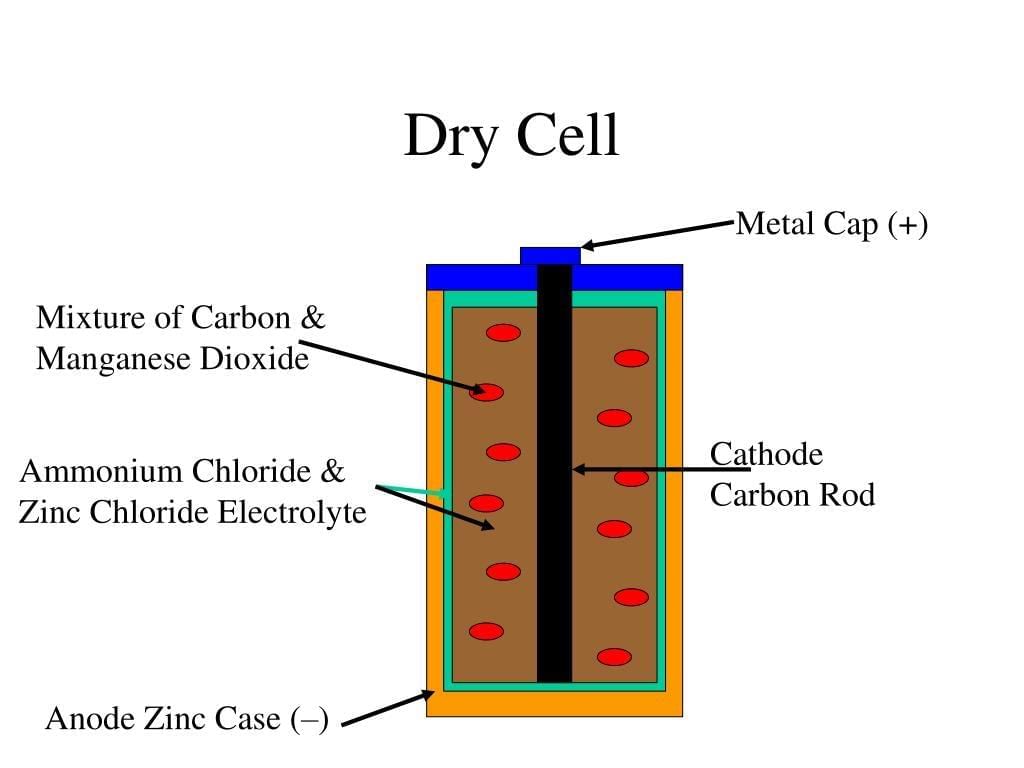 Answer:
Answer:
- A dry cell uses a chemical reaction that is mostly one-way, so when its reactants are used up, it becomes a dead cell and must be discarded. A rechargeable battery uses reversible chemical reactions, so applying an external current restores the original chemicals for reuse.
- In daily life, dry cells are simple and cheap for low-power devices, while rechargeables reduce waste and cost over time for frequent use. Rechargeables also provide steadier voltage over many cycles. Their design supports repeated charging and discharging without quick damage.
Q8. Explain how the Earth’s magnetic field interacts with currents and magnets, and describe one real-life use of this knowledge.
Answer:
- The Earth’s magnetic field surrounds us and sets a preferred direction for compass needles. When a current flows near a compass, the local magnetic field from the wire competes with Earth’s field, causing needle deflection.
- Engineers design instruments considering Earth’s field to avoid false readings, placing sensitive circuits away from strong currents or magnets. One real-life use is in navigation tools and smartphone compasses, which calibrate sensors to subtract Earth’s field and nearby magnetic interference. This ensures accurate direction finding for maps and travel.
|
54 videos|234 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Short and Long Answer Questions: Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the magnetic effects of electricity? |  |
| 2. How does the heating effect of electricity work? |  |
| 3. What are some applications of magnetic effects in daily life? |  |
| 4. What safety precautions should be taken when working with electricity? |  |
| 5. Who discovered the principle of electromagnetism, and why is it significant? |  |
















