Short and Long Answer Questions: Exploring Forces | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Short Answer Questions
Q1. How does cycling uphill and downhill illustrate the role of different forces?
Answer: Uphill, gravity and friction oppose motion making it harder to pedal, while downhill gravity helps motion and friction is smaller, so the cycle speeds up easily.
Q2. Why do we say forces arise from interactions between two objects?
Answer: A force needs two partners, like a hand pushing a table or a bat hitting a ball, because one object acts on another to create the push or pull.
Q3. How can balanced and unbalanced forces explain why an object stays at rest or starts moving?
Answer: If forces are balanced, there is no change in motion and the object stays at rest or moves steadily; if they are unbalanced, the object speeds up, slows down, or changes direction.
Q4. How can you show in class that a force can change the shape of an object?
Answer: You can stretch a rubber band or squeeze clay to show that applying a force changes the object’s shape without necessarily moving it.
Q5. What everyday observations show that friction depends on the nature of surfaces?
Answer: A box slides farther on a smooth tile than on rough carpet because smooth surfaces have less friction and rough surfaces have more friction.
Q6. How does air or water resistance affect moving objects like cyclists or boats?
Answer: Air and water push back against motion as drag, so cyclists and boats go faster when they are streamlined to reduce this resisting force.
Q7. How can you identify the type of force acting in a given situation: contact or non-contact?
Answer: If objects touch, like pushing a door or rubbing hands, it is a contact force; if they act without touching, like magnets attracting or gravity pulling, it is a non-contact force.
Q8. How can a spring balance be used to compare the weights of two objects?
Answer: Hang each object on the hook one by one and read the scale in newtons; the object that stretches the spring more and gives a higher reading has greater weight.
Q9. Why is “10 kg” not a correct scientific way to report weight and what should we use instead?
Answer: Kilogram is a unit of mass, while weight is a force and should be reported in newtons; for example, a 10 kg mass weighs about 98–100 N on Earth.
Q10. What factors decide whether an object will float or sink in water?
Answer: If the buoyant force equals or exceeds the object’s weight, it floats; if the weight is greater than the buoyant force, it sinks.
Q11. How does Archimedes’ principle help explain floating?
Answer: It states that the upward buoyant force equals the weight of the displaced liquid, so an object floats when it displaces water weighing as much as the object itself.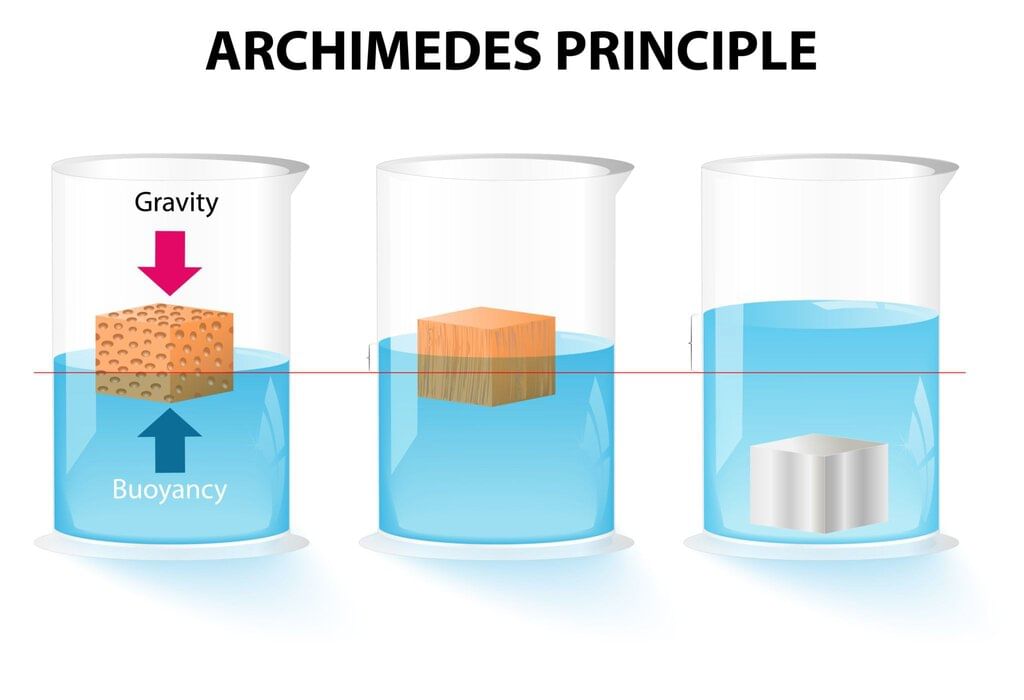
Q12. Why can some rocks like pumice float on water even though most rocks sink?
Answer: Pumice contains many air pockets that make it less dense than water, so the buoyant force balances its weight and it floats.
Long Answer Questions
Q1: Explain contact and non-contact forces. Give two examples for each.
Ans:
Contact forces: Forces that act only when there is physical contact between two interacting objects is known as Contact forces.
Example:
- Muscular force: This is the force we can exert with our bodies by using our muscles, e.g., pull etc.
- Frictional force: The force acting against the relative motion of surfaces in contact is called frictional force or friction.
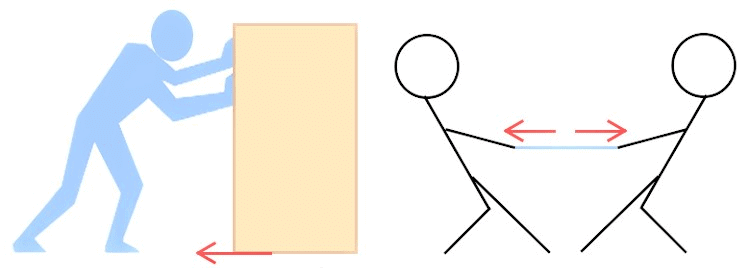 Friction Force and Tension Force
Friction Force and Tension Force
Non-contact forces: Forces that can act without physical contact between objects, i.e. those that can act from a distance, are called non-contact forces or field forces.
Example:
- Magnetic force: Magnets exert forces of attraction or repulsion on other magnets
- Electrostatic force: The force exerted by a charged body on another charged or uncharged body is known as electrostatic force.
 Gravitational Force and Electrostatic Force
Gravitational Force and Electrostatic Force
Q2: (a) How can friction be reduced?
(b) How can it be increased? Give examples.
Ans: Reducing Friction
- By using wheels and ball bearings. The use of wheels between surfaces moving over each other reduces friction. Ball bearings have small balls of steel between steel surfaces. Because of the balls, the steel surfaces can easily move over each other.
- By polishing the rubbing surfaces, they are smooth.
- Use a suitable lubricant, like oil (for light machinery) or grease (for heavy machinery). This helps because fluid friction is less than solid friction.
- Friction due to air (air resistance) or water is reduced by using streamlined shapes in airplanes or ships. A streamlined shape is narrow in front and broader at the back. Birds and aquatic animals have streamlined shapes that hold them in flying or swimming.
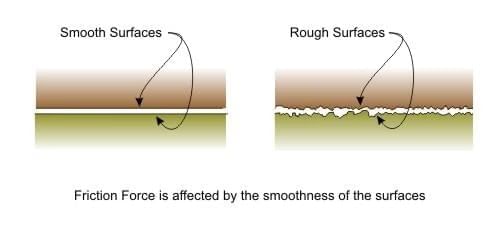
Increasing Friction
- Sand and gravel are strewn on slippery ground during the rainy season to increase friction. It is then easier to walk on the ground.
- By making the moving surfaces rough, e.g. tyres have designs and patterns with grooves on the surface to increase resistance with the road. This prevents the slipping of the tyres on a wet road.
- To increase friction, spikes are provided in the soles of shoes used by players and athletes.
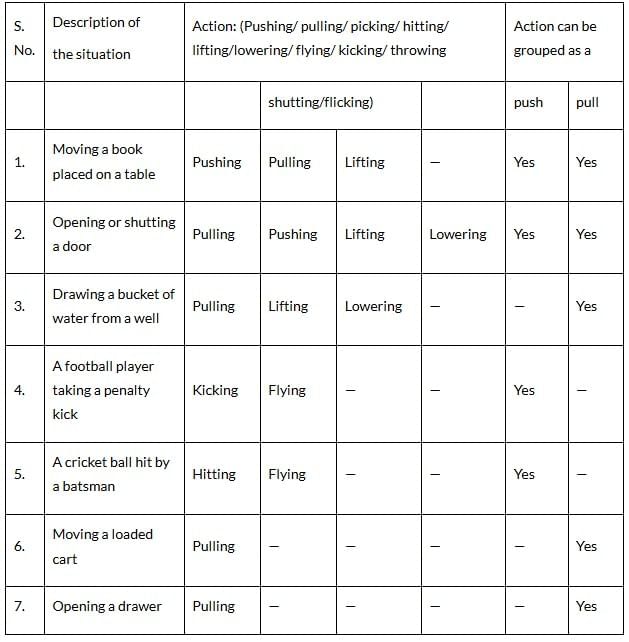
Q3: Read the Table and try to identify the action as push or pull. Ans:
Ans:
Q4. Read the Table and Complete it.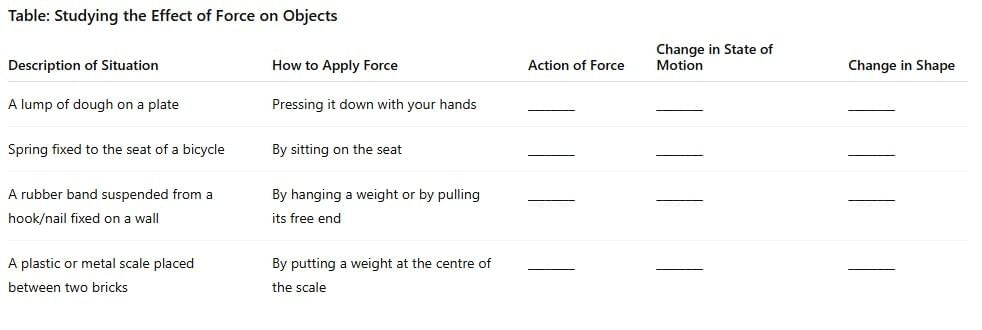 Answer:
Answer: 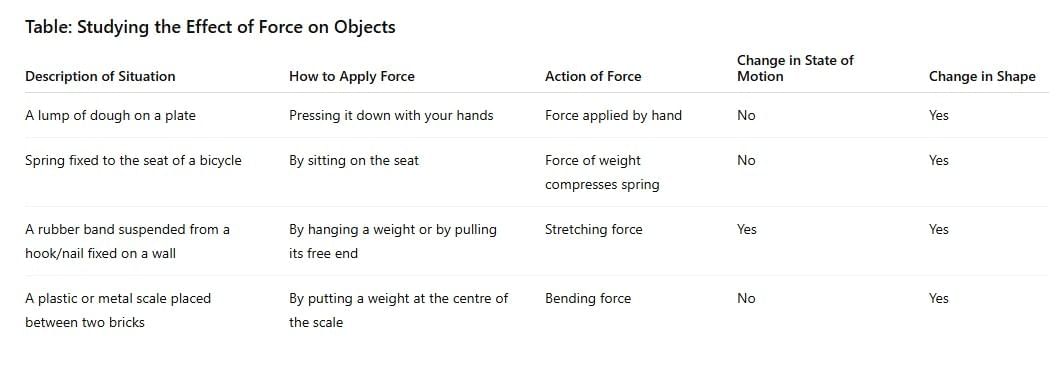
Q5. Explain how to read range and least count on a spring balance and why selecting the right range matters for accurate measurements.
Answer:
- The range is the maximum weight a spring balance can measure, such as 0–10 N, and using a load beyond it can damage the spring. The least count is the smallest division you can read; if 1 N is divided into 5 parts, the least count is 0.2 N.
- Choosing the right range ensures the pointer stays within the scale and improves accuracy. A balance with a smaller least count lets you measure small differences more precisely.
- Proper selection and reading help compare weights reliably in experiments.
Q6. Discuss how mass and weight differ and why the same object can have different weights on different planets while its mass remains unchanged.
Answer:
- Mass is the amount of matter in an object and does not change with location, while weight is the force due to gravity and depends on the planet’s gravitational pull.
- On Earth, a 1 kg mass weighs about 10 N, but on the Moon it weighs about 1.6 N because gravity is weaker there. On Jupiter, the same 1 kg mass would weigh much more due to stronger gravity.
- Scientists use kilograms (kg) for mass and newtons (N) for weight to avoid confusion. This distinction is important in scientific measurements and space exploration.
Q7. Describe the forces acting on an object floating in water and explain how changing the object’s shape can affect floating using the idea of displaced liquid.
Answer:
- A floating object experiences gravity downward and an upward buoyant force from the water; at float, these forces balance. Archimedes’ principle states the buoyant force equals the weight of the displaced water.
- By changing shape to increase volume without much change in mass, the object displaces more water and can float better, like a flat boat-shaped sheet versus a tight ball of the same material.
- This is why ships made of metal can float—they displace a lot of water due to their hollow shape. The balance of weight and displaced water decides floating.
Q8. Explain with examples how multiple forces can act simultaneously in motion, such as during cycling on a windy day, and how net force determines the outcome.
Answer:
- While cycling, the rider’s push provides a forward force, friction at the tires helps grip and move, air resistance opposes motion, and gravity acts downward with the road pushing upward.
- On a windy day, wind can add a backward or forward force depending on its direction. The combined effect of all these forces creates a net force, which decides if the cyclist speeds up, slows down, or maintains speed.
- If the rider’s push plus helpful wind is greater than resistive forces, speed increases; if not, the cycle slows. Understanding net force helps explain real-life motion in changing conditions.
|
54 videos|281 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Short and Long Answer Questions: Exploring Forces - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the key components of effective short answer questions for Class 8 exams? |  |
| 2. How can students prepare for long answer questions in their exams? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of understanding the marking scheme for short and long answer questions? |  |
| 4. What strategies can students use to improve their performance in written exams? |  |
| 5. How can teachers effectively assess students' understanding through short and long answer questions? |  |
















