Signed & Unsigned Binary Numbers | Digital Circuits - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
Introduction
The integer variables are represented in a signed and unsigned manner. The positive and negative values are differentiated by using the sign flag in signed numbers. The unsigned numbers do not use any flag for the sign, i.e., only positive numbers can be stored by the unsigned numbers.
- It is very easy to represent positive and negative numbers in our day to day life. We represent the positive numbers without adding any sign before them and the negative number with - (minus) sign before them. But in the digital system, it is not possible to use negative sign before them because the data is in binary form in digital computers. For representing the sign in binary numbers, we require a special notation.
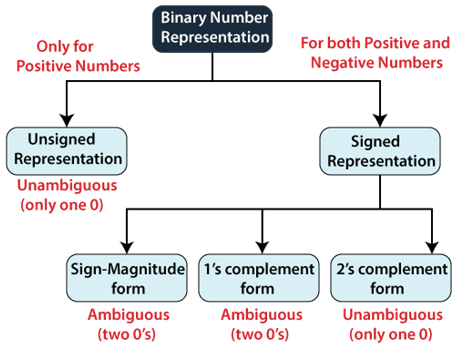
Binary Numbers Representation
Our computer can understand only (0, 1) language. The binary numbers are represented in both ways, i.e., signed and unsigned. The positive numbers are represented in both ways- signed and unsigned, but the negative numbers can only be described in a signed way. The difference between unsigned and signed numbers is that unsigned numbers do not use any sign bit for positive and negative numbers identification, but the signed number used.
Unsigned Numbers
- As we already know, the unsigned numbers don't have any sign for representing negative numbers. So the unsigned numbers are always positive. By default, the decimal number representation is positive. We always assume a positive sign in front of each decimal digit.
- There is no sign bit in unsigned binary numbers so it can only represent its magnitude. In zero and one, zero is an unsigned binary number. There is only one zero (0) in this representation, which is always positive. Because of one unique binary equivalent form of a number in unsigned number representation, it is known as unambiguous representation technique. The range of the unsigned binary numbers starts from 0 to (2n-1).
Example: Represent the decimal number 102 in unsigned binary numbers.
We will change this decimal number into binary, which has the only magnitude of the given name.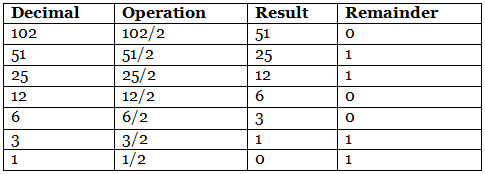 So the binary number of (102)10 is (1100110)2, a 7-bit magnitude of the decimal number 102.
So the binary number of (102)10 is (1100110)2, a 7-bit magnitude of the decimal number 102.
Signed Numbers
Signed numbers are numbers that can be positive or negative. They use a special "sign flag" to show whether the number is positive (+) or negative (-). This sign is combined with the size (magnitude) of the number. For example, in regular decimal numbers, we put a minus sign (-) in front of a number to show it’s negative, like -5.
Representation of Signed Binary Numbers
In computers, numbers are stored as binary (0s and 1s), and signed binary numbers also need a way to show if they are positive or negative. There are three main ways to do this: Sign-Magnitude, 1’s Complement, and 2’s Complement. These methods use an extra bit (called the sign bit) to indicate the sign. However, they handle the number zero (0) differently, which can cause confusion in some cases. Let’s break them down in simple terms:
(a) Sign-Magnitude Form
- In this method, we use one bit (usually the leftmost bit) to show the sign:
- 0 means positive (+).
- 1 means negative (-).
- The rest of the bits show the size of the number (its magnitude).
- For example, with 6 bits:
- 0 1010 = +10 (sign bit 0, magnitude 10).
- 1 1010 = -10 (sign bit 1, magnitude 10).
- Problem: Zero can be written in two ways: 0 00000 (+0) and 1 00000 (-0). This makes it confusing because there are two zeros.
- Range for 6 bits: From -31 (1 11111) to +31 (0 11111).
(b) 1’s Complement Form
- Here, positive numbers are written normally in binary with a sign bit of 0.
- For negative numbers:
- Take the positive version, flip all the bits (0 becomes 1, 1 becomes 0), and use a sign bit of 1.
- Example with 6 bits:
- +5 = 0 00101 (sign bit 0, binary 5).
- -5: Flip 00101 to 11010, so it’s 1 11010.
- Problem: Zero still has two forms:
- 0 00000 (+0).
- 1 11111 (-0, because flipping 00000 gives 11111).
- This makes it confusing too.
- Range for 6 bits: From -31 (1 00000) to +31 (0 11111).
(c) 2’s Complement Form
- This is the most common method in computers.
- Positive numbers are written normally with a sign bit of 0.
- For negative numbers:
- Take the positive version, flip all the bits (1’s complement), then add 1 to the result, and use a sign bit of 1.
- Example with 6 bits:
- +5 = 0 00101.
- -5: Flip 00101 to 11010, add 1 = 11011, so it’s 1 11011.
- Good news: Zero only has one form: 0 00000(+0).
- Negative zero doesn’t exist here because flipping and adding 1 wraps it back to a single zero.
- Range for 6 bits: From -32 (1 00000) to +31 (0 11111).
Key Differences Made Simple
- Sign-Magnitude: Uses a sign bit and keeps the number’s size the same. Two zeros (+0 and -0).
- 1’s Complement: Flips bits for negatives. Still has two zeros (+0 and -0).
- 2’s Complement: Flips bits and adds 1 for negatives. Only one zero, so no confusion. Computers love this one!
|
75 videos|188 docs|70 tests
|
FAQs on Signed & Unsigned Binary Numbers - Digital Circuits - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE)
| 1. What are signed and unsigned binary numbers? |  |
| 2. How do you convert a signed binary number to decimal? |  |
| 3. What is the range of values for an 8-bit signed and unsigned binary number? |  |
| 4. Why is the two's complement method used for signed binary numbers? |  |
| 5. How can I represent negative numbers in binary? |  |
















