Signs and Highway Capacity | Transportation Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Traffic Operations
Traffic Regulations Traffic regulations and laws cover the following four phases:
- Driver controls: include driving licenses, driver tests, financial responsibility and civil liability.
- Vehicle controls: Vehicle registration, requirements of vehicles, equipment and accessories, maximum dimensions and weight and inspection of vehicles.
- Flow Regulations: directions, turning and overtaking etc., signs and signals
- General controls: to report accidents and recording and disposing traffic violation cases
Total potential conflicts points on 2 lane roads: (Right Angled intersection)
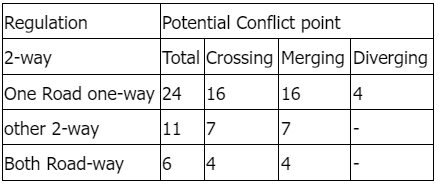
The potential conflicts an two-way operation and varying number of lanes are given in the following Table.


Traffic Control Devices
The most common devices are the following:
- Traffic signs
- Signals
- Markings
- Islands
Traffic Signs:
On the kerb roads, the edge of the sign adjacent to the road should not be less than 0.6 m away from the edge of the kerb. On roads without kerbs, the nearest edge may be 2.0 m to 3.0 m from the edge of the carriageway.
The signs should be mounted on sign posts painted alternately with 25 cm black and white bands.
Traffic signs have been divided into 3 categories: (a) Regulatory signs (b) Warning signs and (c)
Informatory signs
(a) Regulatory Sings:
Regulatory or mandatory signs are meant to inform the road users of certain laws, regulations and prohibitions; the violation of these signs is a legal offense.
The regulatory signs are classified under the following sub heads:
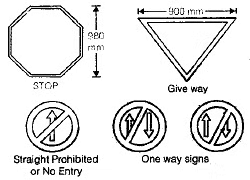
(i) Stop and Give Way Signs:
The stop sign is intended to stop the vehicles on a roadway. It is octagonal in shape and red in colour with a white border.
The give way sign is used to control the vehicles on a road so as to assign right of way to traffic on other roadways.
This sign is Triangular in shape with the apex downwards and white in colour with a red border.
(ii) Prohibitory Signs:
Prohibitory Signs are meant to prohibit certain traffic movements, use of horns or entry of certain vehicle class. Circular in shape and white in colour with a red border.
(iii) No parking and No stopping signs:
No parking and No stopping signs is meant to prohibit parking of vehicles at that place. circular in shape with a blue background a red border and an oblique red at an angle of 45°. No stopping/standing is meant to prohibit stopping of vehicles at that place.
Circular in shape with Blue background, Red border and two oblique red bars at 45° and right angle to each other.
(iv) Speed limit and vehicle control signs:
Speed limit signs are meant to restrict the speed of all or certain classes of vehicles on a particular stretch of a road. These signs are circular in shape and white background, red border and black numerals indicating the speed limit.
The vehicle control signs are circular in shape, red border and black symbols instead of numerals.
(v) Restriction Ends Sign:
Restriction Ends Sign indicates the point at which all prohibitions notified prohibitory sings for moving vehicles ceases to apply
Circular in shape with white back ground and broad diagonal black at 45°.


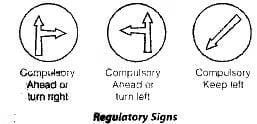
(vi) Compulsory Direction Control Signs:
It Indicate by arrows, the appropriate directions in which the vehicles are obliged to proceed. Circular in shape with a blue background and white direction arrows.

(b) Warning Signs:
Warning or cautionary signs are used to warn the road users of certain hazardous conditions that exist on or adjacent to the roadway.
The warning signs are in the shape of an equilateral triangle with its apex pointing upwards.
They have a white background, red border and black symbols.
These signs are to be located at sufficient distance in advance of the hazard warned against; these distances are: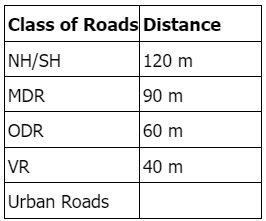

(c) Informatory Signs:
These signs are used to guide the road users along routes, inform them of destination and distance and provide with information to make travel easier, safe and pleasant.
The information signs are grouped under the following subheads:
(i) Direction and place Identification Signs are rectangular with white background , black border and black arrows and letters. include Destination signs, Direction signs, Route markers and Place identification signs.
(ii) The facility Information signs: Rectangular in shape with blue background and white/black letters symbols. Include Public Telephone, Petrol pump, Hospital, first aid post etc.
(iii) Parking Signs: Are set up parallel to the road using square sign board with blue background and white coloured letter 'P'.
(iv) Flood Gauge Sign Should be installed at all cause ways.
Traffic Signals Advantages Properly designed traffic signals have the following uses.
- They provide orderly movement of traffic handling capacity of most of the intersections at grade.
- They reduce certain types of accidents, notably the right angled collisions.
- When the signal system is properly coordinated, there is a reasonable speed along the major road traffic.
- Signals provide a chance to cross traffic of minor roads to cross the path of continuous flow of traffic stream at reasonable intervals of time.
- Automatic traffic signals may work out to be economical when compared to manual control.
Disadvantages
- The real-end collisions may increase.
- Improper design and location of signals may lead to violations of the control system.
- Failure of the signal due to electric power failure of any other defect may cause confusion to the road users.
Important terms related to traffic signals
- Cycle: The period of time required for one complete sequence of signal indications is called cycle.
- Phase: A part of the signal cycle allocated to a traffic movement or a combination of traffic movements is called phase.
- Interval: Any of the division of the signal cycle during which signal indications do not change is called the interval.
Type of Traffic Signals:
The signals are classified into the following types:
- Traffic control signal
- Fixed-time signal
- Manually operated signal
- traffic actuated (automatic) signal
- Pedestrian signal
- Special traffic Signal
Traffic Control Signals have three coloured light glows facing each direction of traffic flow. The red light is meant for “stop”, the green light indicates ‘Go’ and the amber light allows the clearance time for the vehicles which enter the intersection area by the end of green time, to clear off.
Fixed time Signal: The timing of each phase of the cycle is predetermined based on the traffic studies. The main drawback of the signal is that sometimes the traffic flow on one road may be almost nil and traffic on the cross road may be quite heavy yet as the signal operates with fixed timings, the traffic in the heavy stream will have to stop at red phase.
Traffic Actuated Signals are those in which the timings of the phase and cycle are changed according to traffic demand.
Type of Traffic Signal System
Simultaneous System
- All the signals show the same indication at the same time.
- As the division of cycle is also the same at all intersections, this system does not work satisfactorily.
Alternate System
- Alternate group of signals show opposite indications in a route at the same time. More satisfactory than simultaneous system
Simple Progressive Systems
- A time schedule is made to permit as nearly as possible a continuous operation of groups of vehicles along the main road at a reasonable speed.
Flexible Progressive System
- In this system it is possible to automatically vary the length of cycle, cycle division and the time schedule at each signalized intersection with the help of a computer.
Do you know?
This is the most efficient system of all the four types described above.
Flashing Beacons are meant to warn the traffic.
At flashing red signals, the drivers of vehicles shall stop before entering the nearest cross walk at an intersection or at a stop line.
When marked flashing yellow signals are caution signals meant to signify that drivers may proceed with caution
Design of Isolated Fixed Time Signal
- Stop time or red phase R, of a signal is the sum of go and clearance intervals or green and amber phases for the cross flow i.e. G2 + A2 at a two phase signal.
- Towards the end of red phase, there may be a short duration when the amber lights are put on along with red light signal in order to indicate 'get set' to go.
- This phase is the last part of red phase itself, and may be called ‘red-amber’ or ‘initial amber’.
Do you know?
The vehicles are not supposed to cross the stopline during the red amber period.
- Clearance time is provided just after the green phase before the red phase, to fulfill two requirements.
- Stopping time for approaching vehicle to stop at stop line after the signal changes from green to amber.
- Clearance time for app roaching vehicles. Usually 2 to 4 seconds would be suitable for the amber phase.
- Go time greentime is decided based on the approach volume during peak hour.
Design Procedures
IRC Guidelines
- The pedestrian green time required are calculated based on walking speed of 12 m/sec. and initial walking time of 7.0 sec.
- The cycle time is calculated after allowing amber time of 2 sec. each.
- The minimum green time required for vehicular traffic on any of the approaches is limited to 16 secs.
Road Marking:
Are made of lines, patterns, words, symbols or reflectors on the pavement, kerb side of islands or on the fixed objects within or near the roadway.
The various types of markings may be classified as,
- Pavement Markings
- Kerb Markings
- Object markings
- Reflector unit markings
Pavement Markings may be generally of white paint. yellow colour markings are used to indicate parking restrictions and for the continuous centre and barrier line markings.
The width of pedestrian crossing may be between 2.0 and 4.0 depending upon local requirements.
Kerb Markings:
The markings on the kerb are made with alternate black and white line.
Reflector Unit Markings:
Reflector markers are used as hazard markers and guide markers for safe driving during night. Hazard makers reflecting yellow light should be visible from distance of about 150 m.
Road Delineators:
Are devices to outline the roadway to provide visual assistance to drivers about the alignment of road ahead, especially at night.
Three types of delineators that may be used are:
- Roadway indicators
- Hazard Markers
- Object Markers
Roadway indicators are in the form of guide posts 0.08 to 1.0 m high and painted by black and white strips with or without reflectors and are intended to delineate the edges of the roadway.
Hazard markers are 12 m high plates on posts, either with three red reflectors or markers with black and yellow strips at 45° towards the side of the obstruction.
Object markers are circular red reflectors arranged on triangular or rectangular panels.
Traffic Islands:
Traffic islands are raised areas constructed within the roadway to establish physical channels through which the vehicular traffic may be guided.
Traffic islands may be classified based on the function as:
- Divisional islands
- Channelizing islands
- pedestrian loading islands
- Rotary
Divisional islands:
Are intended to separate opposing flow of traffic on a highway with four or more lanes. By dividing the highway into one way roadways, the head-on collisions are eliminated and other accidents are also reduced.
Channelizing islands:
Are used to guide the traffic into proper channel through the intersection area.
Pedestrian loading Islands:
Are provided at regular bus stops and similar places for the protection of passengers.
A pedestrian island at or near a cross walk to aid and protect pedestrian crossing the carriageway may be termed as pedestrian refuse islands.
Rotary:
Is the large central island of a rotary intersection; this islands is much larger than the central island of channelized intersection. The crossing maneuver is converted to wearing by providing sufficient wearing length.
|
26 videos|91 docs|58 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
















