Sn1, Sn2, E1, E2 reactions | Organic Chemistry PDF Download
Substitution Reactions
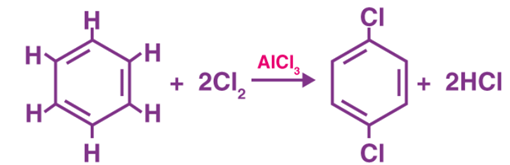
- The substitution reaction occurs when an atom or a functional group replaces another different atom or another different functional group of a compound.
- The presence of nucleophiles tend to favour substitution reactions.
What is a Nucleophile?
- Nucleophiles are nucleus loving. It is an electron-rich species tending to donate electron pairs to electron-deficient species.
- Nucleophile favours substitution reactions.
Types of Substitution Reactions
Based on reaction conditions, we can classify Substitution Reaction into two types:
- Nucleophilic Substitution Unimolecular Reaction
- Nucleophilic Substitution Bimolecular Reaction
Nucleophilic Substitution Unimolecular Reaction (SN1 Reaction)
- As the name suggests, it is a substitution reaction taking place in the presence of a nucleophile.
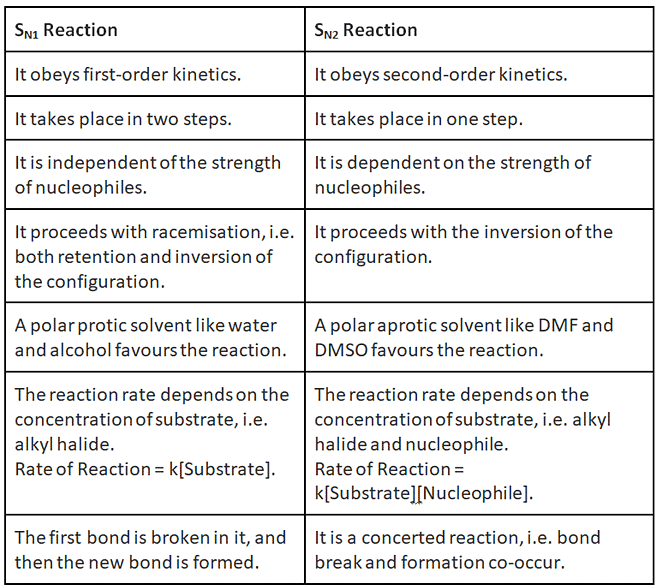
- Nucleophilic substitution unimolecular reaction (SN1) obeys first-order kinetics.
- Nucleophilic substitution unimolecular reaction (SN1) is independent of the strength of nucleophiles.
- Nucleophilic substitution unimolecular reaction (SN1) proceeds with racemisation, i.e. both retention and inversion of the configuration.
- A polar protic solvent like water and alcohol favours the reaction.
- The reaction rate depends on the concentration of substrate, i.e. alkyl halide.
Rate of Reaction = k[Substrate].
Step 1: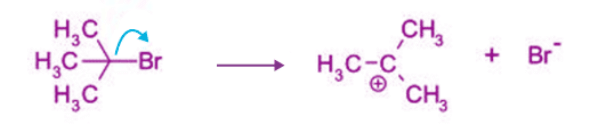 Step 2:
Step 2: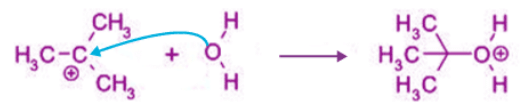 Step 3:
Step 3: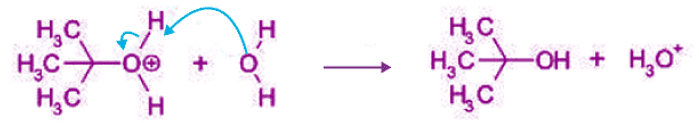
Nucleophilic Substitution Bimolecular Reaction (SN2 Reaction)
- As the name suggests, it is a substitution reaction taking place in the presence of a nucleophile.
- Nucleophilic substitution bimolecular reaction (SN2) obeys second-order kinetics.
- Nucleophilic substitution bimolecular reaction (SN2) is dependent on the strength of nucleophiles.
- Nucleophilic substitution bimolecular reaction (SN2) proceeds with the inversion of the configuration.
- A polar aprotic solvent like DMF and DMSO favours the reaction.
- The reaction rate depends on the concentration of substrate, i.e. alkyl halide and nucleophile.
Rate of Reaction = k[Substrate][Nucleophile].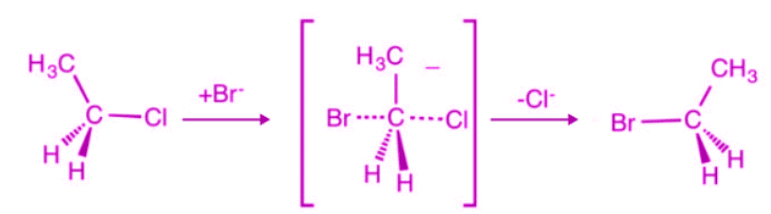
Difference between SN1 and SN2 Reaction
Elimination Reaction
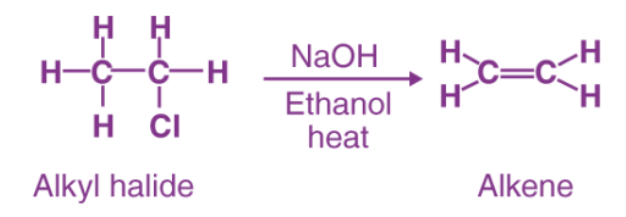
An elimination reaction is a type of reaction that is mainly used to transform saturated compounds (organic compounds which contain single carbon-carbon bonds) to unsaturated compounds (compounds that feature double or triple carbon-carbon bonds).
- It is a primary method for the preparation of alkenes.
- The presence of base tends to favour elimination reactions.
What is a Base?
- The base is electron-rich species tending to accept protons or donate a pair of electrons to electron-deficient species.
- Base favours elimination reactions.
Types of Elimination Reactions
Based on reaction conditions, we can classify Elimination Reaction into two types:
- Unimolecular Elimination Reaction
- Bimolecular Elimination Reaction
Unimolecular Elimination Reaction (E1 Reaction)
- Unimolecular elimination reaction (E1) follows first-order kinetics.
- Unimolecular elimination reaction (E1) occurs in two steps: ionisation and deprotonation.
- During the ionisation bond between carbon and halogen breaks, an intermediate carbocation is formed.
- During deprotonation, a proton is lost from carbocation.
- The base further forms a pi bond within the molecule.
- The reaction rate depends on the concentration of substrate, i.e. alkyl halide.
Rate of Reaction = k[Substrate].
- It is independent of the strength of the base.
- Unimolecular elimination reactions (E1) are similar to nucleophilic substitution unimolecular reactions (SN1).
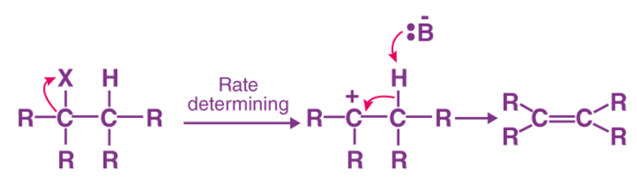
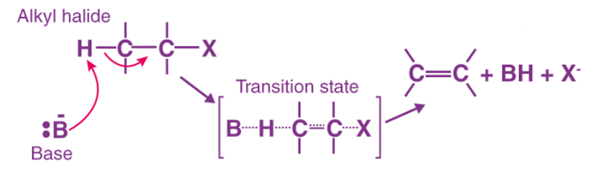
Bimolecular Elimination Reaction (E2 Reaction)
- Bimolecular elimination reaction (E2) occurs in the presence of a base.
- Bimolecular elimination reaction (E2) follows second-order kinetics.
- Bimolecular elimination reaction (E2) occurs in a single step.
- The reaction rate depends on the concentration of substrate, i.e. alkyl halide and a base.
Rate of Reaction = k[Substrate][Base].
- It is dependent on the strength of the base.
- Bimolecular elimination reactions (E2) are similar to nucleophilic substitution bimolecular reactions (SN2).
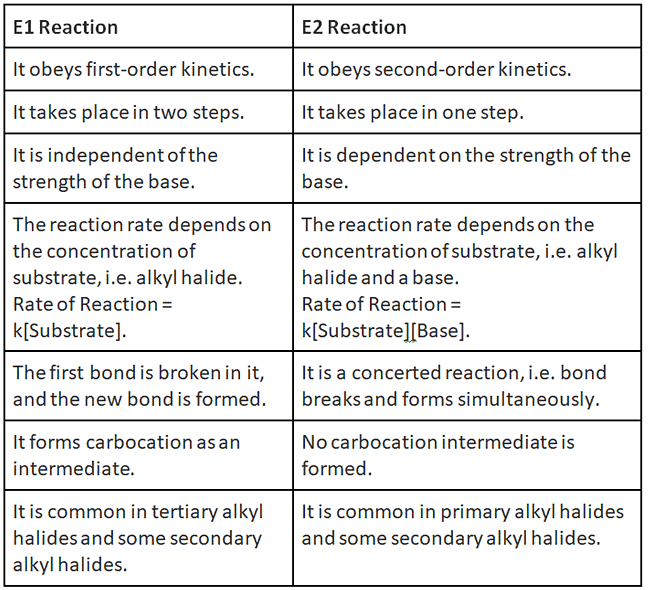
Difference between E1 and E2 Reaction
|
39 videos|92 docs|46 tests
|





















