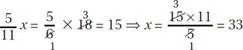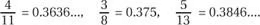Solved Examples: Fractions | Mathematics for Digital SAT PDF Download
What are Fractions?
Fractions represent the parts of a whole or collection of objects. A fraction has two parts. The number on the top of the line is called the numerator. It tells how many equal parts of the whole or collection are taken. The number below the line is called the denominator. It shows the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into or the total number of the same objects in a collection.
Solved Examples
Q1: Which of the following is greater than 1/2?
(a) 8/17
(b) 6/11
(c) 9/19
(d) 4/9
Ans: (b)
Sol: There are two ways to deal with fractions. One way is to convert them all to decimals (by using your calculator, divide the numerator by the denominator). Using this method, all you would need to do is to see which is greater than 0.5.
Otherwise, to see which is greater than 1/2, double the numerator and see if the result is greater than the denominator.
In B, the correct answer, doubling the numerator gives us 12, which is bigger than 11.
Q2: For how many integers, a, between 30 and 40 is it true that 5/a , 8/a ,13/a and are all in lowest terms?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans: (c)
Sol: If a is even, then 8/a is not in lowest terms, since both a and 8 are divisible by 2. The only possibilities are 31, 33, 35, 37, and 39, but 5/35 = 1/7 and 13/39 = 1/3 , so only 31, 33, and 37 (that is, 3 integers) remains.
Q3: Which of the following has the greatest value?
(a) 65%
(b) 5/8
(c) 4/7
(d) 52%
Ans: 65%
Sol: If all are converted to decimals, 0.65 is the biggest.
Hence, a is the correct option
Q4: If 3/11 of a number is 22, what is 6/11 of that number?
(a) 11
(b) 12
(c) 33
(d) 44
Ans: (d)
Sol: Don't bother writing an equation for this one; just think. You know that 3/11 of the number is 22, and 6/11 of a number is twice as much as 3/11 of it: 2 × 22 = 44.
Q5: What fractional part of a day is 12 minutes?
(a) 1/120
(b) 1/60
(d) 1/24
(d) 1/12
Ans: (a)
Sol: There are 60 minutes in an hour and 24 hours in a day, so there are 60 × 24 = 1440 minutes in a day: 12/1440 = 1/120.
Q6: 5/6 of 18 is equal to 5/11 of what number?
(a) 33
(b) 55
(c) 11/25
(d) 25/11
Ans: (a)
Sol:
Q7: Which of the following is less than 5/9?
(a) 5/6
(b) 21/36
(c) 25/45
(d) 55/100
Ans: (d)
Sol: Use your calculator: 5/9 = 0.555555…. Choice (C) is also equal to 0.555555…; choices (A) and (B) are both greater; only 55/100 = 0.55 is less.
Q8: Which of the following statements is true?
(a) 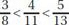
(b) 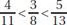 (c)
(c) 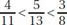
(d) None of these
Ans: (b)
Sol: Use your calculator to convert each fraction to a decimal:
This is the correct order
Q9: If a = 0.99, which of the following is (are) less than a?
I. √a
II. a2
III. 1/a
(a) None
(b) I only
(c) II only
(d) III only
Ans: (c)
Sol: Since a < 1, then √a > a. (I is false.)
Since a < 1, then a2 < a. (II is true.)
The reciprocal of a number less than 1 is greater than 1. (III is false.)
Q10: For the final step in a calculation, Paul accidentally divided by 1000 instead of multiplying by 1000. What should he do to his answer to correct it?
(a) Multiply it by 1000.
(b) Multiply it by 100,000.
(c) Multiply it by 1,000,000.
(d) Square it.
Ans: (c)
Sol: Multiplying the incorrect answer by 1000 would undo the final division Paul made-the point at which he should have multiplied by 1000. Then, to correct his error, he would have to multiply again by 1000. In all, he should multiply by 1000 × 1000 = 1,000,000.
|
204 videos|126 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Solved Examples: Fractions - Mathematics for Digital SAT
| 1. What are fractions and how are they used in mathematics? |  |
| 2. How do you add and subtract fractions with different denominators? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between proper fractions, improper fractions, and mixed numbers? |  |
| 4. How can I convert a fraction into a decimal? |  |
| 5. What are some common mistakes to avoid when working with fractions? |  |