Solved Examples: Volume, Surface Area & Solid Figures | Quantitative Aptitude for SSC CGL PDF Download
Perimeter
Perimeter refers to the distance around the enclosed space of a shape or a closed curve, like a circle. The formula for calculating perimeters differs depending on the type of shape.
Area
Area can be defined as the extent of space within the boundaries of a shape. Area is commonly measured in square units. Similarly, the formula for calculating area varies based on the type of shape.
Volume
Volume is specifically calculated for solid 3D shapes, such as cylinders, cubes, spheres, and others. It represents the amount of space or mass encompassed within an object of any shape and size.
Formulas
Rectangle
Area = Length * Width
Perimeter = 2 [Lengths + Widths]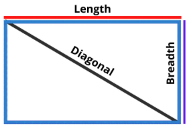
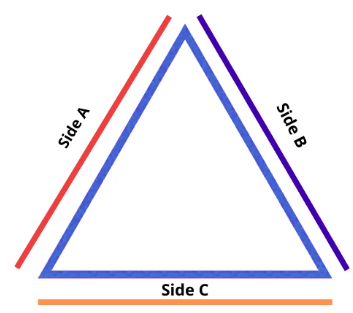
Triangle
- Area = 1/2 * base * height
- Perimeter = a + b + c (add the length of the three sides)
- Area using Heron’s formula =
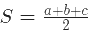
then,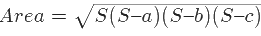
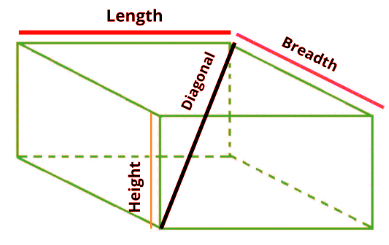
Cuboid
- Volume = Length * Width * Height
- Surface = 2lw + 2lh + 2wh
- Curved Surface Area = 2h(l + b)
Cylinder
Volume = πr2 × height
Surface area = 2πrh + 2πr2
Curved Surface Area = 2πrh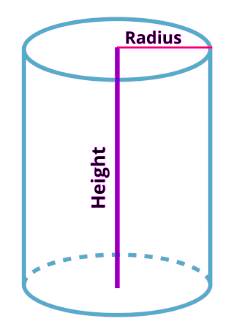
Sphere
- Volume =
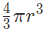
- Surface = 4πr2

Examples
Example 1: A cube of 5 cm was cut into as many 1 cm cubes as possible. Find out the ratio of the surface area of the larger cube to that of the surface areas of the smaller cubes?
(a) 1:2
(b) 2:3
(c) 1:5
(d) 1:3
Ans: (c)
Volume of the original cube = 53 = 125 cm3.
Volume of each smaller cubes = 1 cm3. It means there are 125 smaller cubes.
Surface area of the cube = 6a2
Surface area of the larger cube = 6a2 = 6 * 52 = 6 * 25 = 150
Surface area of one smaller cubes = 6 (12) = 6
Now, surface area of all 125 cubes = 125 * 6 = 750
Therefore,
Required ratio = Surface area of the larger cube: Surface area of smaller cubes
= 150: 750
= 1: 5
Example 2: The volumes of two cones are in the ratio 1:10. The radius of the cones are in the ratio of 1: 2. What is the ratio of the height of the cone?
(a) 3:4
(b) 3:5
(c) 2:5
(d) 1:3
Ans: (c)
Volume of cone = 
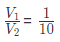
Now the ratio of the radius of both the cone = 1: 2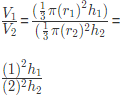
On solving we get 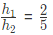
Therefore, the ratio of the height of the cone = 2:5
Example 3: The curved surface area of a cylindrical pillar is 264 m2 and its volume is 924m3. Find the ratio of its diameter to its height.
(a) 7:4
(b) 3:4
(c) 6:5
(d) 7:3
Ans: (d)
Volume of cylinder = πr2h
Curved Surface area of cylinder = 2 πrh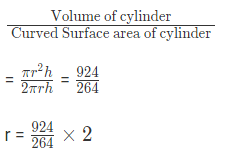
r = 7
Curved Surface area of cylinder = 2πrh = 264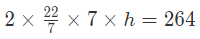
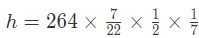
h = 6
Now, required ratio = 2r/h = 2 *7/6 = 14/6 = 7/3 = 7:3
Example 4: A rectangular piece of cloth when soaked in water, was found to have lost 20% of its length and 10% of its breadth. Calculate the total percentage of decrease in the area of rectangular piece of cloth?
(a) 75% decrease
(b) 28 % increase
(c) 28 % decrease
(d) 20% decrease
Ans: (c)
Let the original length = l
Let the original breadth = b
Original Area = l * b
New length 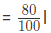
New breadth 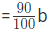
Decrease in the area 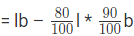
Decrease in the area 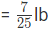
Decrease percentage 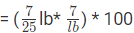
Decrease percentage 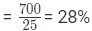
Example 5: If the length of a rectangle is increased by 25% and the width is decreased by 20%, then find the area of the rectangle?
(a) 25% increase
(b) 50 % decrease
(c) remains unchanged
(d) 10 % increase
Ans: (c)
Let the original length = l
Let the original breadth = b
Original Area = l * b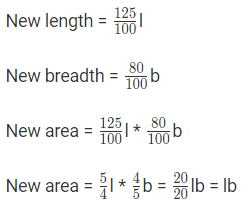
Therefore, original and new area are same. It means the area remains unchanged.
|
315 videos|295 docs|185 tests
|
















