Solved Practice Questions on Sn1, Sn2, E1, E2 reactions | Organic Chemistry PDF Download
Q.1. How many number of pie e- is present in benzene?
(a) 6
(b) 7
(c) 8
(d) 9
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Pie electron are those which show de-localization of the electrons, in same plan or p orbitals and that there aren’t alternating double and single bonds. But the electron in one p-p overlapping is present perpendicular to the plane of ring.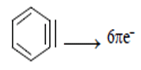
Q.2. Nitro group is meta-directing in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions?
(a) increases electron density at meta-position
(b) increases electrons density at ortho and para-positions
(c) decreases electron density at meta-position
(d) decreases electron density at ortho and para-positions
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Because nitro group decreases electron density at ortho and para-positions, which will leads to deactivation of ring.
Q.3. What will be the total number of isomers formed when 2-methyl butane is subjected to monochlorination?
(a) 5
(b) 4
(c) 3
(d) 6
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Monochlorination of 2 methyl butane gives two pairs of enantiomers. 1st pair of enantiomer is 1-chloro-2-methyl butane and 2nd pair of enantiomer is 2-chloro-3-methyl butane.
1-chloro-3-methyl butane and 2-chloro-2-methyl butane products are also formed.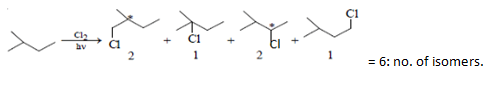
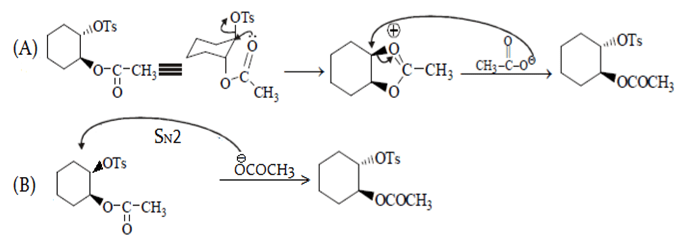
Q.4. What will be the decreasing order of electrophilic nitration of the following compounds?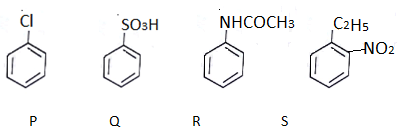 (a) S > R > P > Q
(a) S > R > P > Q
(b) R > S > P > Q
(c) R > P > S > Q
(d) P > S > R > Q
Correct Answer is Option (c)
In R electron donating group is present. In P, Cl will attract rings electron and donation will increase. In S there is electron donating group hence it is more reactive. If C2H5 is not there than this order reverses.
In Q electron pair will get into resonance.
Q.5. The number of substitution products formed when metabromo anisole is treated with KNH2/NH3?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Nucleophile (-NH2)will attack on Br and there will be three possibilities of bond formation and those are ortho, para and meta position as shown in the below structures number 2, 3 and 1 respectively.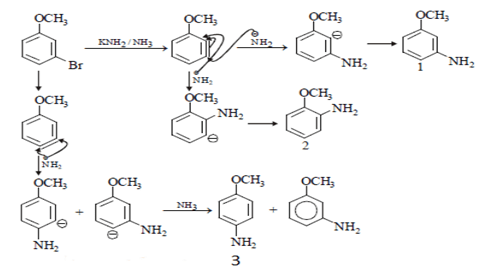
Q.6. Among the following, which one is not a meta directing group in an electrophilic attack?
(a) 
(b) 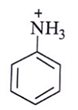
(c) 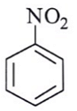
(d) 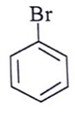
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Did not a meta directing group in electrophilic attack because halogen are ortho-para directing and ring deactivationg group.
Q.7. What is not true about below reaction?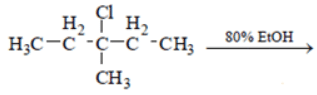 (a) Major product is given by SN1 reaction
(a) Major product is given by SN1 reaction
(b) Through E1 mechanism 3 alkenes are formed
(c) 3-Methylpentane-3-ol is also formed as one of the product
(d) Fractional distillation of elimination product will give two fractions
Correct Answer is Option (d)
As we see below mechanism major product is formed by SN1 mechanism and E1 mechanism forms 3 alkenes. 3-Methylpentane-3-ol is also formed in the reaction. Fractional distillation of elimination product will give three fractions. Hence statement d is false.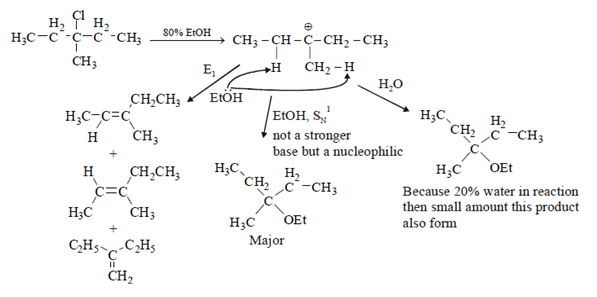
Q.8. Among the following compounds, what is the decreasing order of reactivity towards electrophilic substitution?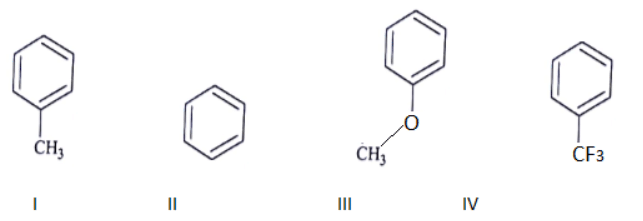 (a) III > I > II > IV
(a) III > I > II > IV
(b) IV > I > II > III
(c) II > III > II > IV
(d) I > III > II > IV
Correct Answer is Option (a)
This is a electrophilic substitution and more the electrodensity on the ring faster the reaction.
III > I > II > IV (Reactivity order towards E substitution)
Q.9. Which of the following is not true for SN1 reactions?
(a) They occur through a single step concerted reaction
(b) They are favoured by polar solvents
(c) Tertiary alkyl halides generally react through this mechanism
(d) Concentration of nucleophile does not affect the rate of such reactions
Correct Answer is Option (a)
SN1 reaction is a two-step reaction, step one is the leaving group leaves, and the second step is the substrate forms a carbocation intermediate. Formation of carbocation intermediate is the rate determining step. Since for the formation of stable intermediate carbocation, highly polar solvent is required. The bulky substituents prevent the nucleophiles from approaching the carbon, which is attached directly to the halogen. SN1is also more favorable as the neighboring alkyl groups are electron donating, which helps to stabilize the carbocation. SN1 reaction because the nucleophile is not a part of the rate-determining step.
Q.10. Benzyl chloride is reacted with different nucleophiles (HO–, CH3COO–, PhO–, CH3O–). Arrange them in the decreasing order of reactivity with Benzyl chloride.
(a) CH3O– > HO– > PhO– > CH3COO–
(b) HO– > CH3O– > PhO– > CH3COO–
(c) HO– > PhO– > CH3O– > CH3COO–
(d) CH3COO– > CH3O– > HO– > PhO–
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Here, CH3O– is most stable as the negative charge is distributed among two oxygen, followed by oxygen attach to phenyl group will share electron in resonance. And carbon is more electronegative than hydrogen attached to oxygen that’s why HO– is less stable than CH3O– and more nucleophilic.
Q.11. Which of the following structures represent the correct major product for the below reaction?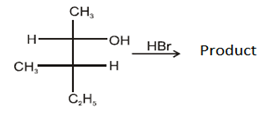 (a)
(a) 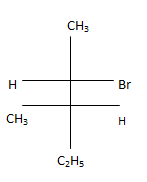
(b) 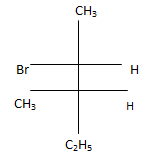
(c) 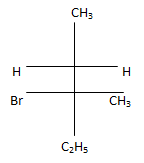
(d) 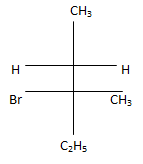
Correct Answer is Option (c)
According to following mechanism we can say that some are major products. As we can see protonation of hydroxyl group followed by dehydration will leads to hydride shift to the adjacent positively charged carbon for formation of more stable carbocation. This will unleash two possibility of attack by Br- at the new carbocation from upward and backward and two products will be formed that are shown below.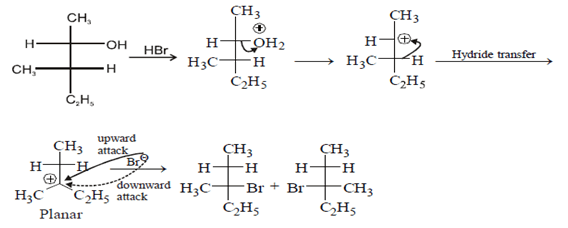
Q.12. Which of the following statement is true about the reaction given below?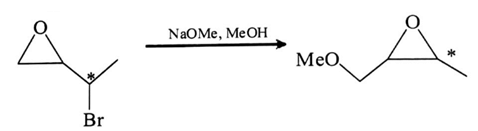 (a) It involves a carbocation intermediate
(a) It involves a carbocation intermediate
(b) The rearrangement is due to SN1 reaction mechanism
(c) It proceeds via a concerted SN2 pathway
(d) It proceeds via a concerted SN1 pathway
Correct Answer is Option (c)
In this reaction nucleophile (–OMe) will attack at carbon attach to oxygen and in this mechanism, one bond is broken and one bond is formed synchronously, i.e., in one step, so it will undergo SN2 pathway.
Q.13. What will be the final product in the below reaction?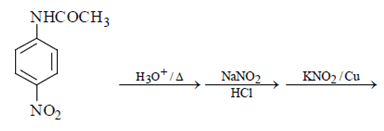 (a)
(a) 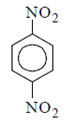
(b) 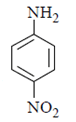
(c) 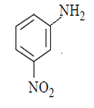
(d) 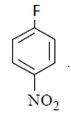
Correct Answer is Option (a)
As we can see hydrolysis is the first step which will form a amine group containing compound. This amino-compound undergoes diazotisation and a rapid reaction will take place between diazonium ion and KNO2 and the ‘a’ product will form.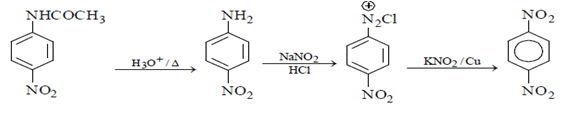
Q.14. What will be the starting material (I) in the given reaction?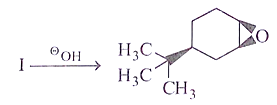 (a)
(a)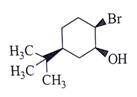
(b) 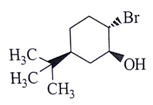
(c) 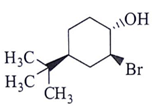
(d) 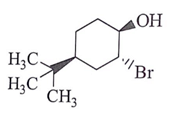
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Leaving group center should be anti to each other and nucleophilic.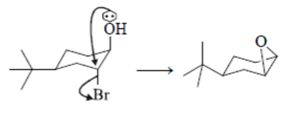
Q.15. In the following reaction sequence, what will be X?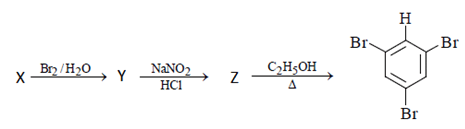 (a) Benzoic acid
(a) Benzoic acid
(b) Salicylic acid
(c) Phenol
(d) Aniline
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Aniline will be X as we can see below reaction. Free bromination will occur, and bromine will get add to ortho and para position followed diazotisation and a rapid reaction will take place between diazonium ion and C2H5OH and 1, 3, 5-tribromo benzene will form.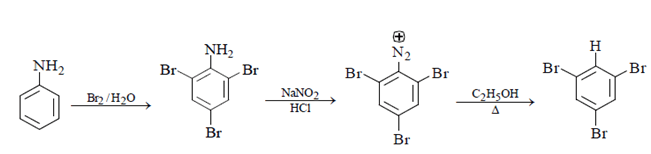
Q.16. Which of the following reaction is not possible?
(a) 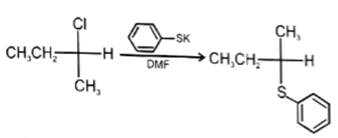
(b) 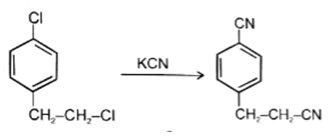
(c) 
(d) 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
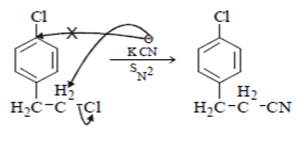
In reaction, the nucleophilic attack will be at aliphatic chlorine atom instead of aromatic chlorine because aromatic carbon SN2 is not possible.
Q.17. What will be the (X) in the below-mentioned reaction sequence?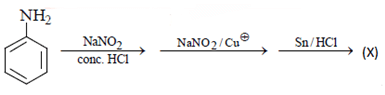 (a)
(a) 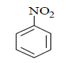
(b) 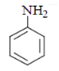
(c) 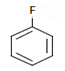
(d) 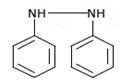
Correct Answer is Option (b)
As we can see in below reaction, that firstly diazotisation reaction will occur. This is followed by reaction of NaNO2 1 with diazonium ion forming nitro benzene, which will undergo reduction and form aniline.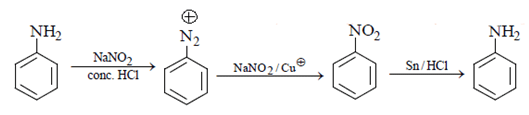
Q.18. The relative rates of nucleophilic substitution for the given substrates are as follows:
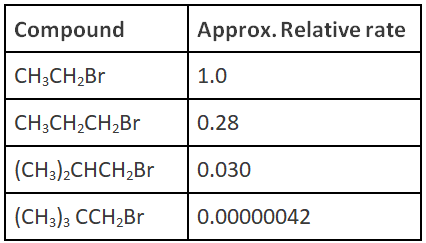 Which of the following statement is correct?
Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Each of the above reactions is likely to be SN2
(b) Each of the above reactions is likely to be SN1
(c) First two reactions follow SN2 and next two reactions follow SN1 pathway
(d) There is no role of “steric factor”
Correct Answer is Option (a)
As the steric hindrance increase, attack on carbon attached to Br decreases. It is possible only when reaction undergoes via SN2 reaction.
Q.19. Why are aryl halides less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions as compared to alkyl halides?
(a) The formation of a less stable carbanion
(b) Longer carbon halogen bond
(c) The inductive effect
(d) Sp2-hybridized carbon attached to the halogen
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Overlapping of sp2 orbital of carbon with p-orbital of halogen is one of the reasons. Due to conjugation double bond character in alkyl halide.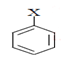
Q.20. Identify correct step representing SN1 mechanism for the cleavage of ether with HI.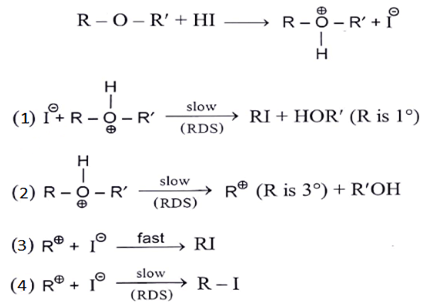 (a) 1 and 3
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 4
(d) 2 and 4
Correct Answer is Option (b)
As we can see in below reaction first step is a slow step in which carbocation is formed. And the second step is fast where nucleophile will attach carbocation.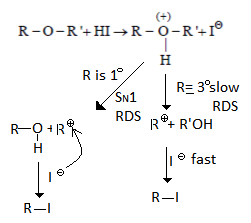
Q.21. Which of the following order is correct for the solvolysis in 50% aqueous ethanol at 44.6oC?
(a) 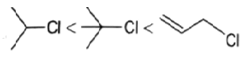
(b) 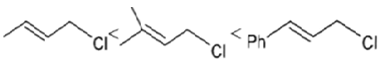
(c) 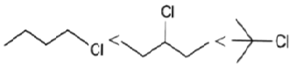
(d) 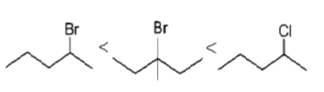
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Solvolysis is a nucleophilic substitution (SN1) or elimination, where the nucleophile is a solvent molecule. Solvolysis order CH3X < 1o halide < 2o halide < allylic halide < 3o halide.
Q.22. What is the correct order of nucleophilicity in the following options?
(a) (CH3)3CO– > CH3–
(b) CH3S– > CH3SH
(c) CH3CH2CH2O– < (CH3)3CO–
(d) (CH3CH2)3N > (CH3CH2)3P
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Alkoxides are weaker Nu– than carbanion because negative charge on oxygen is more stable than carbon. CH3CH2CH2O– is more nucleophilic, due to less steric hindrance. The negative charge is more nucleophilic than a stable compound.
Q.23. Which of the following statement is incorrect about nucleophiles?
(a) Nucleophiles have an unshared electron pair and can make use of this to react with an electron deficient species
(b) The nucleophilicity of an element (an electron donor) generally increases on going down a group in the periodic table
(c) A nucleophile is electron-deficient species
(d) All good nucleophiles are good bases when we deal across the period
Correct Answer is Option (c)
A nucleophile is a chemical species that donates an electron pair to an electrophile to form a chemical bond in relation to a reaction, it is an electron rich species.
Q.24. What is the correct statement for the given reactions?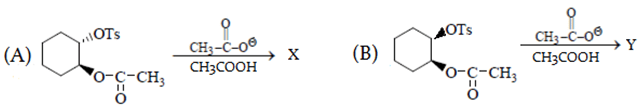 (a) B reacts faster than A
(a) B reacts faster than A
(b) Both give the same product
(c) A gives trans and B gives c is product
(d) A gives cis and B gives trans product
Correct Answer is Option (b)
In reaction A, groups attached to benzene are on opposite plane so SNGP mechanism will be followed and B will undergo SN2. Due to SNGP (A) reacts faster than B and both give same product.
|
39 videos|92 docs|46 tests
|