Some Natural Phenomena Class 8 Worksheet Science Chapter 12
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
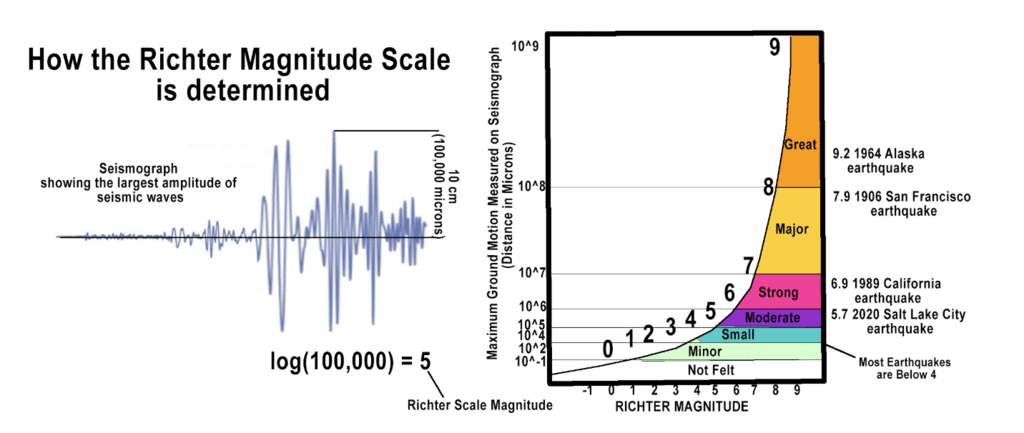
Q1: Which of the following measures the power (magnitude) of an earthquake?
A. Kelvin scale
B. Celsius scale
C. Richter scale
D. Decibel scale
Ans: C. Richter scale
Q2: Which device protects buildings from lightning by providing a direct path for electric charge to flow into the ground?
A. Electroscope
B. Lightning Conductor
C. Transformer
D. Fuse
Ans: B. Lightning Conductor
Q3: When a plastic scale is rubbed on dry hair and then it attracts tiny bits of paper, it demonstrates:
A. Magnetism
B. Static electricity
C. Gravitational force
D. Heat conduction
Ans: B. Static electricity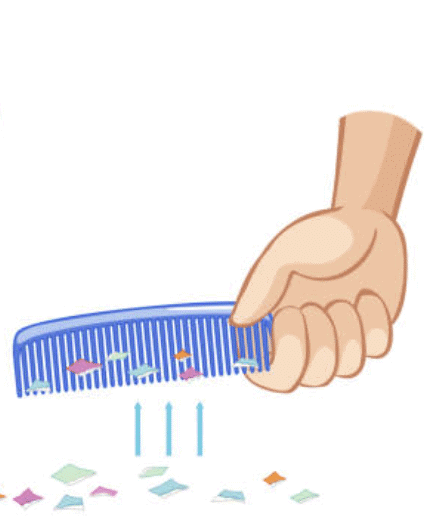
Q4: What is the primary cause of earthquakes according to modern science?
A. Strong winds
B. Tectonic plate movements
C. Lightning strikes
D. Climate change
Ans: B. Tectonic plate movements
Q5: Which of the following is the safest action if you are outdoors during an earthquake?
A. Run into a building quickly
B. Stand under a tall tree
C. Move to a clear, open area away from buildings and power lines
D. Lie flat on the ground immediately
Ans: C. Move to a clear, open area away from buildings and power lines
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The process of transferring excess charge from a charged object to the earth is known as Earthing.
Q2: The device used to detect the presence of electric charge is called an Electroscope.
Q3: When two objects are rubbed together, they become electrically charged due to the transfer of electrons.
Q4: The Earth’s outer layer is divided into fragments called plates, which constantly move and can cause earthquakes.
Q5: When a balloon made of rubber is rubbed with animal fur, the balloon gains extra electrons and becomes negatively charged.
True/False
Q1: Earthquakes can be accurately predicted by weather departments.
Ans: False
Q2: Objects with the same type of electric charge repel each other, while objects with different types of charges attract each other.
Ans: True
Q3: Lightning can never strike the same place more than once.
Ans: False 
Q4: During a thunderstorm, it is safer to be inside a car with the windows rolled up than to be out in the open.
Ans: True
Q5: Rubber that has been rubbed with fur becomes negatively charged, and the fur becomes positively charged.
Ans: True
Very Short Answer Questions
Q.1. What type of electric charge is acquired by a rubber balloon when rubbed with a woolen cloth?
Ans: When balloon is rubbed with a woolen cloth, it acquires negative electric charge.
Q.2. Sometime, a crackling sound is heard while taking off sweater during winters. Explain.
Ans: When we take off a woolen (or synthetic) sweater, it rubs against our shirt. Due to rubbing, opposite electric charges develop on them, which attract each other. The discharge of these electric charges produces tiny sparks of light as well as crackling sound.
Q.3. Explain why a charged balloon is repelled by another charged balloon whereas an uncharged balloon is attracted by another charged balloon?
Ans: A charged balloon is repelled by another charged balloon because both the balloons have same type of charges and like charges repel each other. Whereas an uncharged balloon is attracted by another charged balloon because charged balloon induces opposite charges in the nearer end of the uncharged balloon by electric induction and unlike charges attract each other.
Q.4. What causes lightning in the sky?
Ans: During the development of a thunderstorm, the air currents move upward while the water droplets move downward. These vigorous movements cause separation of charges. The positive charges collect near the upper edges of the clouds and the negative charges accumulate near the lower edges. There is accumulation of positive charges near the ground also. When the magnitude of the accumulated charges becomes very large, the air which is normally a poor conductor of electricity is no longer able to resist their flow. Negative and positive charges meet, producing streaks of bright light and sound. We see streaks as lightning. The process is called an electric discharge.
Q.5. List three states in India where earthquakes are more likely to strike.
Ans: Gujarat, Kashmir, Rajasthan
Q.6. The weather department has predicted that a thunderstorm is likely to occur on a certain day. Suppose you have to go out on that day. Would you carry an umbrella? Explain.
Ans:Carrying umbrella is not a good idea at all during thunderstorms because lightning may strike the top end of the metal rod of umbrella and harm us.
Q.7. What will you do to protect yourself from lightning if you are in an open field?
Ans: If no shelter is available and we are in an open field, we should stay far away from all trees. We should stay away from poles or other metal objects. We should not lie on the ground instead we should squat low on the ground. We should place our hands on our knees with our head between the hands. This position will make us the smallest target to be struck.
Q.8. What precautions would you take to protect yourself during an earthquake if you are at home?
Ans: In order to protect ourselves during an earthquake we must take following precautions:
(i) We should take shelter under a table and stay there till shaking stops.
(ii) We should stay away from tall and heavy objects that may fall on us.
(iii) If we are in bed then we should not get up and should protect our head with a pillow.
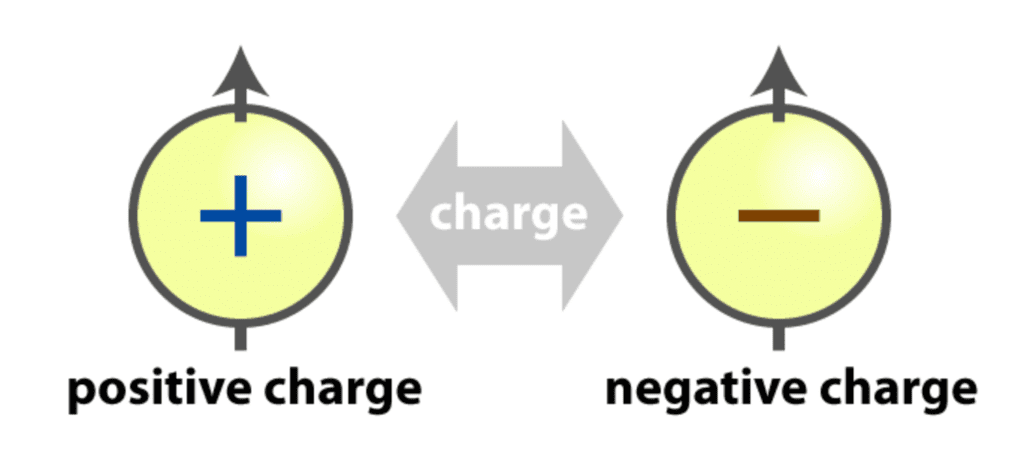
Q.9. What are the two kinds of electric charges?
Ans: There are two kinds of charges — positive charge and negative charge.
Q.10. What happens when plates brush past one another, or a plate goes under another due to collision?
Ans: When plates brush past one another, or a plate goes under another due to collision, they cause disturbance in the earth’s crust. It is this disturbance that shows up as an earthquake on the surface of the earth.
Q.11. When a charged refill is touched with the metal top of an electroscope, its aluminium leaves diverge. Give reason.
Ans: The aluminium foil strips receive the same charge from the charged refill through the paper clip. The strips carrying similar charges repel each other and they become wide open.
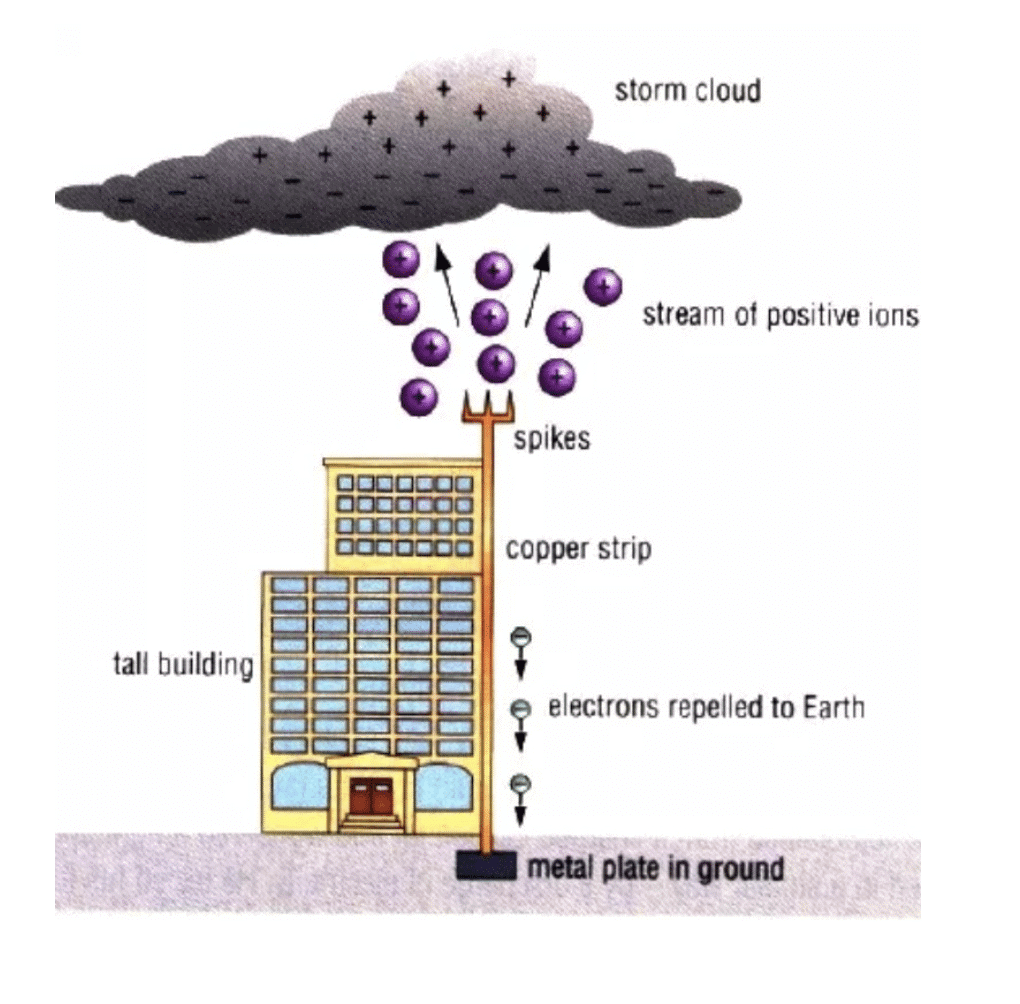
Q.12. What is lightning conductor? How does it work?
Ans: Lightning Conductor is a device used to protect buildings from the effect of lightning. A metallic rod, taller than the building, is installed in the walls of the building during its construction. One end of the rod is kept out in the air and the other is buried deep in the ground. The rod provides easy route for the transfer of electric charge to the ground.
Q.13. Name the scale on which the destructive energy of an earthquake is measured. An earthquake measures 3 on this scale. Would it be recorded by a seismograph? Is it likely to cause much damage?
Ans: The destructive energy of an earthquake is measured by Richter scale. An earthquake of 3 Richter can be recorded by a seismograph. An earthquake of magnitude 3 on Richter scale is often felt but not likely to cause much damage. Really destructive earthquakes have magnitudes higher than 7 on the Richter scale.
Q.14. How will you charge a glass rod by the method of friction?
Ans: A glass rod can be charged by rubbing it with silk cloth.
Q.15. Why is it not safe to stay under a tree during a thunderstorm?
Ans: During a thunderstorm, there is danger of lightning striking the tree and burning it up. This lightning can also pass through the body of the person standing under the tree and may kill him. Therefore, it is not wise to stand under a tree during a thunderstorm.
|
92 videos|282 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Some Natural Phenomena Class 8 Worksheet Science Chapter 12
| 1. What are some examples of natural phenomena? |  |
| 2. How do natural phenomena affect the environment? |  |
| 3. What causes earthquakes and how are they measured? |  |
| 4. Why do tornadoes form and what conditions are necessary for their development? |  |
| 5. What safety precautions should be taken during natural disasters? |  |