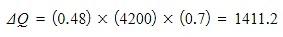Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Physics for Grade 10 > Specific Heat Capacity
Specific Heat Capacity | Physics for Grade 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Internal Energy |

|
| Average Kinetic Energy |

|
| Specific Heat Capacity |

|
| Calculating Specific Heat Capacity |

|
| Tips |

|
Internal Energy
- A rise in the temperature of an object increases its internal energy
- This can be thought of as due to an increase in the average speed of the particles
- Increasing speed increases kinetic energy
- Internal energy is defined as:
- The total energy stored inside a system by the particles that make up the system due to their motion and positions
- Motion of the particles affects their kinetic energy
- Positions of the particles relative to each other affects their potential energy
- Together, these two make up the internal energy of the system
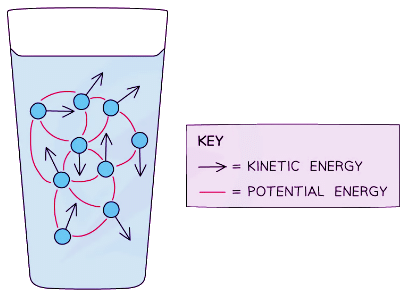 Substances have internal energy due to the motion of the particles and their positions relative to each other
Substances have internal energy due to the motion of the particles and their positions relative to each other
- Together, these two make up the internal energy of the system
Average Kinetic Energy
- Heating a system changes a substance's internal energy by increasing the kinetic energy of its particles
- The temperature of the material, therefore, is related to the average kinetic energy of the molecules
- This increase in kinetic energy (and therefore internal energy) can:
- Cause the temperature of the system to increase
- Or, produce a change of state (solid to liquid or liquid to gas)
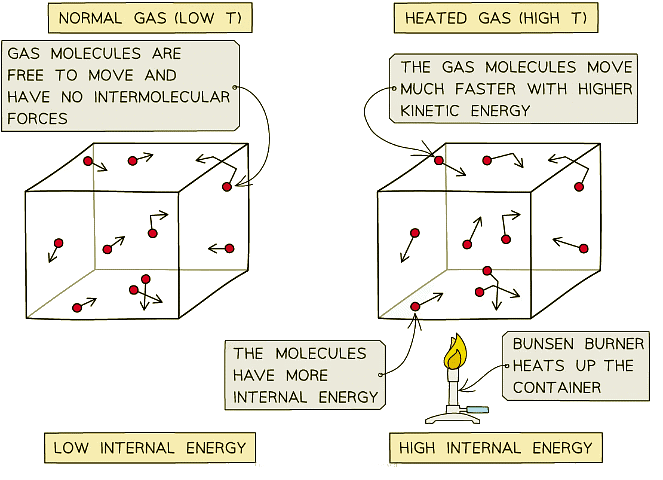
Note:
(i) As the container heats up, the gas molecules move faster
(ii) Faster motion causes higher kinetic energy and therefore higher internal energy
Specific Heat Capacity
- How much the temperature of a system increases depends on:
- The mass of the substance heated
- The type of material
- The amount of thermal energy transferred in to the system
- The specific heat capacity, c, of a substance is defined as:
- The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the substance by 1 °C
- Different substances have different specific heat capacities
- If a substance has a low specific heat capacity, it heats up and cools down quickly (ie. it takes less energy to change its temperature)
- If a substance has a high specific heat capacity, it heats up and cools down slowly (ie. it takes more energy to change its temperature)
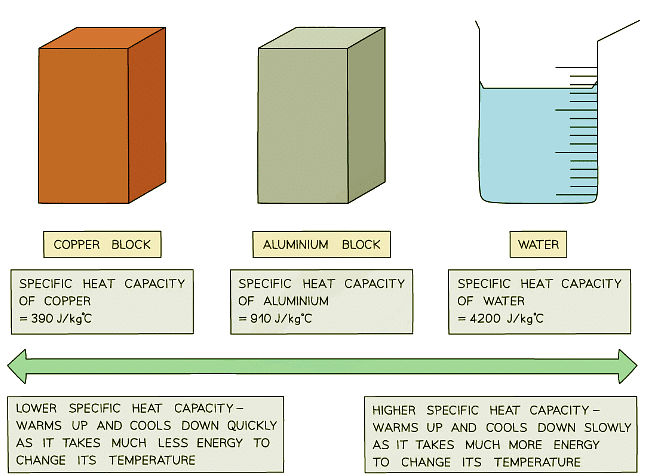 Low vs high specific heat capacity
Low vs high specific heat capacity
Calculating Specific Heat Capacity
- The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a given mass by a given amount can be calculated using the equation:
ΔQ = mcΔT - Where:
- ΔQ = change in thermal energy, in joules (J)
- m = mass, in kilograms (kg)
- c = specific heat capacity, in joules per kilogram per degree Celsius (J/kg °C)
- ΔT = change in temperature, in degrees Celsius (°C)
Example: Water of mass 0.48 kg is increased in temperature by 0.7 °C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J / kg °C.
Calculate the amount of thermal energy transferred to the water.
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
- Mass, m = 0.48 kg
- Change in temperature, ΔT = 0.7 °C
- Specific heat capacity, c = 4200 J/kg °C
Step 2: Write down the relevant equation
ΔQ = mcΔT
Step 3: Calculate the thermal energy transferred by substituting in the values
Step 4: Round the answer to 2 significant figures and include the units
ΔQ = 1400 J
Tips
- You will always be given the specific heat capacity of a substance, so you do not need to memorise any values.
- However, it's useful to have the general idea that, the larger the number, the less the substance will increase in temperature for a given amount of heat.
- You can see this for yourself in your own kitchen at home. Metal pans, which have a relatively low specific heat capacity get very hot, very quickly when put on the hob. Add water to the pan, which has a relatively high specific heat capacity and the water will take much longer to heat up.
- Notice the units of specific heat capacity:
- joules per kilogram per degree Celsius : J / kg °C
- 'per' means 'divided by'. We say 'per' in front of every value that is being divided by, hence 'per kilogram per degree Celsius'
The document Specific Heat Capacity | Physics for Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Physics for Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
122 videos|150 docs|40 tests
|
Related Searches