Stability of Slopes | Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Stability Analysis of Slopes
The quantitative determination of the stability of slopes is necessary in a number of engineering activities, such as:
- the design of earth dams and embankments,
- the analysis of stability of natural slopes,
- analysis of the stability of excavated slopes,
- analysis of the deepseated failure of foundations and retaining walls.
Quite a number of techniques are available for these analyses
Factor of Safety
The factor of safety is commonly thought of as the ratio of the maximum load or stress that a soil can sustain to the actual load or stress that is applied. Referring to Fig. given below the factor of safety F, with respect to strength, may be expressed as follows:
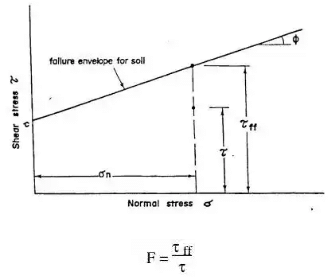
where τff is the maximum shear stress that the soil can sustain at the value of normal stress of σn, τ is the actual shear stress applied to the soil.
Above equation may be expressed in a slightly different form as follows: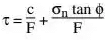
Two other factors of safety which are occasionally used are the factor of safety with respect to cohesion, Fc, and the factor of safety with respect to friction, Fφ.
The factor of safety with respect to cohesion may be defined as the ratio between the actual cohesion and the cohesion required for stability when the frictional component of strength is fully mobilised. This may be expressed as follows: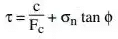
The factor of safety with respect to friction, Fφ, may be defined as the ratio of the tangent of the angle of shearing resistance of the soil to the tangent of the mobilised angle of shearing resistance of the soil when the cohesive component of strength is fully mobilised.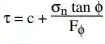
A further factor of safety which is sometimes used is FH, the factor of safety with respect to height. This is defined as the ratio between the maximum height of a slope to the actual height of a slope and may be expressed as follows: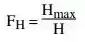
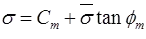
where, Cm = Mobilized Cohesion
∅m = Mobilized Friction Angle
Cm = C / Fs and tan∅m = tan∅ / Fs
Factor of Safety w.r.t. Cohesion (fc)
and Fc = C / Cm
where, Hc = Critical depth
H = Actual depth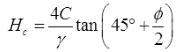
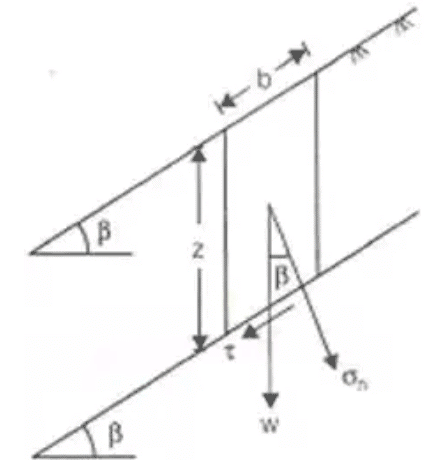
Stability Analysis of Infinite Slopes
- Cohesionless dry soil/dry sand
W = yz cosβ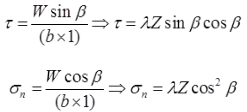
 where,
where,
τ = Developed shear stress or mobilized shear stress
σn = Normal stress.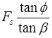
where,
Fs = Factor of safety against sliding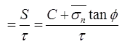
For safety of Slopes
β < φ
↓
Fs > 1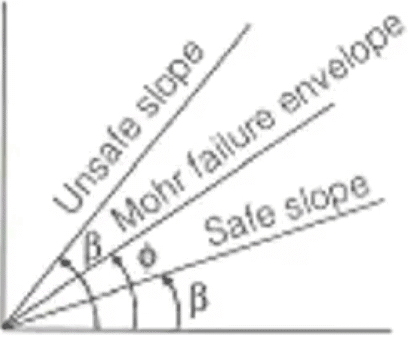
- Seepage taking place and the water table is parallel to the slope in Cohesionless Soil
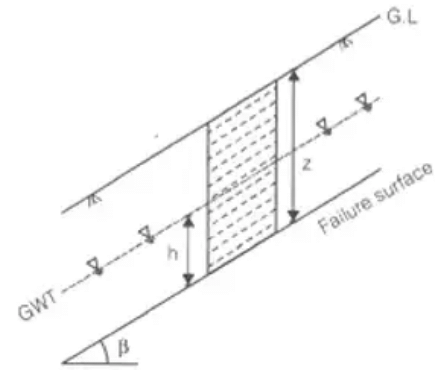 h = Height of water table above the failure surface.
h = Height of water table above the failure surface.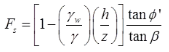
φ’ is effective friction angle
γ-avg. total unit weight of soil above the slip surface upto ground level.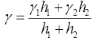
- If water table is at ground level: i.e.,
h = z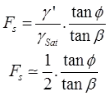
- Infinite Slope of Purely Cohesive Soil
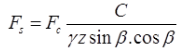
Fc = Hc/H
Here H = z = depth of slice/cut.
At Critical Stage Fc = 1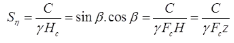
where, Sη = Stability Number. - C-∅ Soil in Infinite Slope
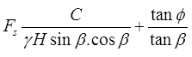
- Taylor's stability no.
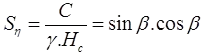
(for cohesive soil)
Max. theoretical value of stability no. = 0.5
Max. practical value is = 0.261
Sη = [tanβ - tan∅]cos2β (for C-∅ soils)
Stability Analysis of Finite Slopes
- Fellinious Method
(For Purely Cohesive Soil)
(i) (F = Cr2θ / we) where, F = Factor of safety
r = Radius of rupture curve
I = Length of rupture curve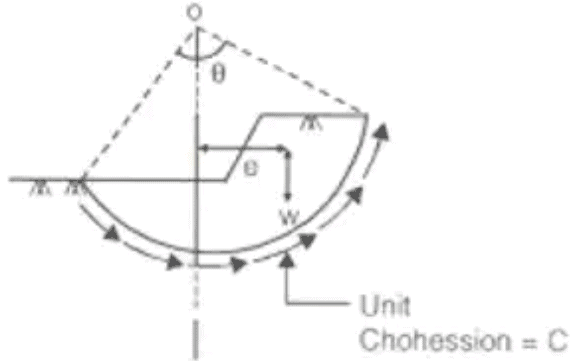 (ii) F = Cr2θ1/ we
(ii) F = Cr2θ1/ we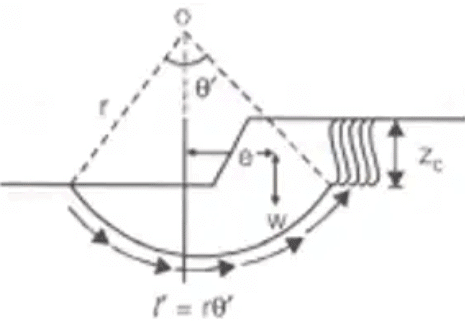 F = Factor of safety it tension cracks has developed.
F = Factor of safety it tension cracks has developed.
zc = 2C / γ - Swedish Circle Method
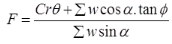
where, F = Factor of safety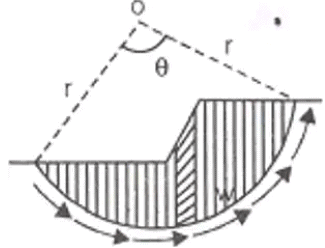
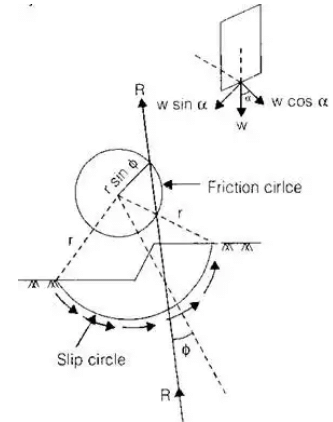
- Friction Circle Method
Fc = C / Cm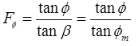
- Taylor's Stability Method (C-∅ soil)
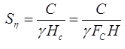
In case of submerged slope γ should be used instead of γ and if slope is saturated by capillary flow they γsat should be used instead of γ.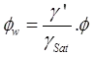
where ∅w = weight friction angle.
|
30 videos|77 docs|74 tests
|






















