Statistics for Economics- Assertion-Reason & Case Based Questions | Economics Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Assertion and Reasoning
Directions: In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Question 1:
Assertion (A): Mohit gets a raise in his salary by 10% as he was a hard-working person and was an employee of the week for three months straight.
Reason (R): The raise in the salary is a part of the consumption for Mohit.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Ans: (c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
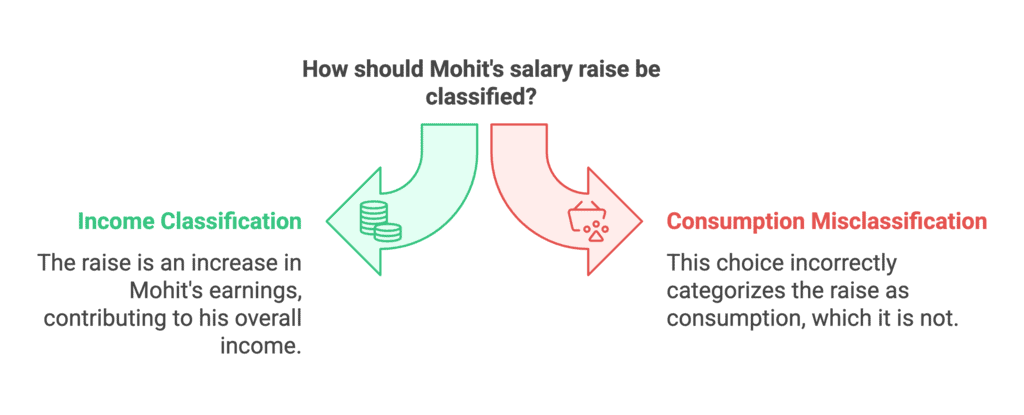
Assertion (A): Mohit gets a raise in his salary by 10% because he was hardworking and was the employee of the week for three months straight.
- This is true because it's clearly mentioned that Mohit received a raise due to his hard work and consistent recognition as the employee of the week.
Reason (R): The raise in the salary is a part of the consumption for Mohit.
- This is false because a salary raise is considered as income, not consumption. Consumption refers to the use of goods and services to satisfy needs, while income is what you earn (like salary, wages, etc.). Mohit's salary raise adds to his income, not his consumption.
Question 2:
Assertion (A): Housewife working in the house is termed as Non-economic activity.
Reason (R): There is no monetary gain or salary paid to the housewife for working in the house.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Ans: (a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A): Housewife working in the house is termed as Non-economic activity.
- This is true because non-economic activities are those performed out of love, affection, care, or duty, without expecting monetary gain. Household work done by a housewife is considered a non-economic activity.
Reason (R): There is no monetary gain or salary paid to the housewife for working in the house.
- This is true because a housewife does not receive any salary or payment for her household work.
The Reason (R) correctly explains why the activity is termed as a non-economic activity.
Question 3:
Assertion (A): Arun purchased a car from the Bharat Automobiles.
Reason (R): Arun is a consumer as he was the reason of the economic activity performed
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Ans. (b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A): Arun purchased a car from the Bharat Automobiles.
- This is true because it is a straightforward statement indicating that Arun bought a car.
Reason (R): Arun is a consumer as he was the reason for the economic activity performed.
- This is true, but not properly explained. Arun is a consumer because he purchased a good (car) for personal use. While he indirectly triggered the economic activity of selling the car, this is not the reason he is considered a consumer.
The Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). It should state that Arun is a consumer because he is using the car for his personal satisfaction or use.
Question 4:
Assertion (A): Statistics cannot calculate the qualitative aspects of economics.
Reason (R): Qualitative aspects are the aspects that influence the working of an economy, though cannot be expressed in terms of money.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Ans. (a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A): Statistics cannot calculate the qualitative aspects of economics.
- This is true. Statistics deals with numerical data, and qualitative aspects like motivation, honesty, or happiness cannot be measured directly by statistical tools.
Reason (R): Qualitative aspects are the aspects that influence the working of an economy, though cannot be expressed in terms of money.
- This is true. Qualitative aspects like social attitudes, culture, or ethics influence the economy but cannot be measured or expressed in monetary terms.
Reason (R) correctly explains Assertion (A) because it provides a valid reason why statistics cannot calculate qualitative aspects — they cannot be expressed in numerical terms.
Question 5:
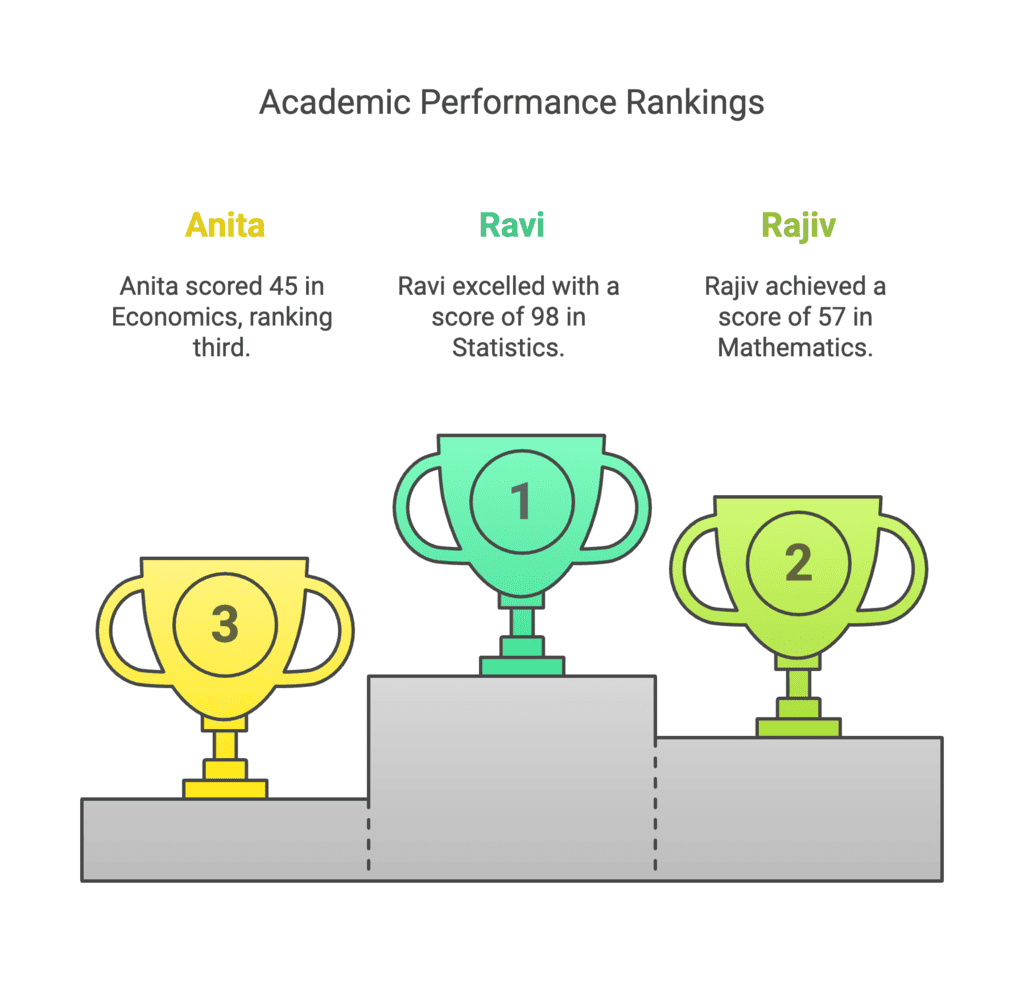
Assertion (A): Rajiv scored 57 in Mathematics, Ravi scored 98 in Statistics, Anita Scored 45 in Economics. The given data is statistical data.
Reason (R): The statistical data needs to be numerical in nature.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Ans: (a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A): Rajiv scored 57 in Mathematics, Ravi scored 98 in Statistics, Anita scored 45 in Economics. The given data is statistical data.
- This is true. The given data provides numerical scores related to individuals, making it statistical data.
Reason (R): The statistical data needs to be numerical in nature.
- This is true. Statistical data is often numerical because statistics primarily deals with quantifiable data for analysis.
Reason (R) correctly explains Assertion (A) because the scores provided are numerical, which is a fundamental requirement for statistical data.
Case-Based Questions
1. Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow:
Activities involved in production (manufacturing), distribution (transportation) and consumption (retail) are constantly seeking economies to improve their competitiveness and increase their market share. The consumption of goods and services is a primary component of economic well-being and, as such, a primary indicator of living standards. Wealth and income are available to support consumption, today and in the future. Production, in the market and at home, supports consumption.
Economies of transportation relate to the benefits that lower transport costs may grant to specific activity sectors and are derived from a locational choice. For production, it relates to a location that minimizes total transport costs and thus lowers production unit costs. Some are elements of transport costs in production while others are elements of transport costs in consumption.
Economies of scope relate to the benefits derived by expanding the range of goods and services. For production, they are commonly based on product diversification and flexible manufacturing systems able to produce a variety of products in view of changes in the demand and consumer preferences.
For distribution, economies of scope are very important and commonly achieved when a transporter is able to bundle several different loads into fewer loads. For consumption, activities offering a wider range of goods or services are usually able to attract more customers since they have more choices. Economies of scale and economies of scope are highly related.
Q1: Establishing a dairy for producing milk products for consumers which turns to be a method of earning wealth is an example of economic activity.
(a) True
(b) False
Ans: Option (a)
Establishing a dairy to produce milk products for consumers is an economic activity because it involves producing goods to sell for profit, which generates income.
Q2: Economics is a ..................... science which studies the economic behaviour of a man.
(a) social
(b) physical
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Ans: Option (a)
Economics is a social science that studies the economic behavior of individuals and societies. It focuses on how people make choices to allocate scarce resources to satisfy their needs and wants.
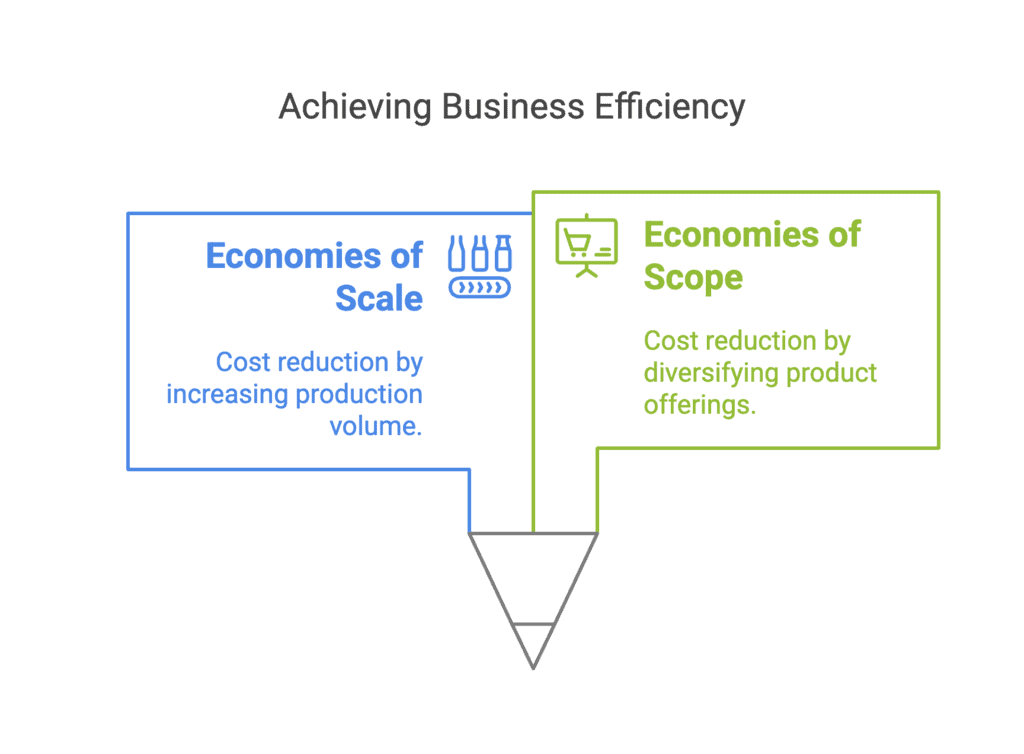
Q3: Assertion (A): Economies of scale and economies of scope are highly related.
Reason (R): Both economies of scale and economies of scope result in savings in cost.
Select the correct alternative from the following:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason ( R) are true.
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are false.
Ans: Option (a)
Economies of scale refer to the cost advantages that a business obtains due to expansion, which results in a reduction in per-unit cost as output increases. Economies of scope refer to the cost advantages that a business obtains due to a variety of products being produced together. Both result in cost savings, making the assertion and the reason true.
Q4. When we want to know how the consumer decides, given his income and many alternative goods to choose from, what to buy when he knows the prices. This is the study of ..................... .
(a) production
(b) consumption
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of above
Ans. Option (b)
When we want to know how the consumer decides, given his income and many alternative goods to choose from, what to buy when he knows the prices. This is the study of consumption .
2. Read the following passage and answer the question that follows:
Alok and Shyam went to their teacher and asked help for properly understanding statistics. While enquiring with them their teacher Mrs. Tiwari understood that she needed to start with the basics with them. She told them Statistics is a mathematical tool used by us to analyse any sort of data. For example, with the help of statistics we can calculate the average height of the students in your class, or average marks that the students might have got in statistics or any other subject. Shyam asked, “Can we calculate the interest of a person using statistics?” Mrs Tiwari said, “We can only calculate the things that can be expressed in quantitative form, that is in terms of numbers then we can use statistics, or else statistics is of no use.” Alok asked, “Can I find an average of my height and weight using statistics?” Mrs Tiwari smiled and then answered, “No Alok. The data needs to be homogeneous. You cannot find the relation between the data which is not related to each other.” Alok thought for a while and then again said, “But what is BMI Index then, ma’am? It is calculated with the help of height and weight of a person.” Mrs. Tiwari said, “That is an excellent question, Alok. Body Mass Index is the ratio between the two, but not an average. When we talk of statistics
it is not only related to only average, but we can also analyse trends, measure relations and see the depth of the data.” They both thanked their teacher and went back.
State whether the given statement is true or false:
Q1: In statistics, the data needs to be related to each other.
(a) True
(b) False
The correct answer is Option (a)
Yes, In statistics the data needs to be related to each other.
Q2. Which of the following is not the use of statistics?
(a) Calculating the average of the data
(b) Calculating the trend of the data
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
The correct answer is Option (d)
Statistics is used for calculating both the average of the data and the trend of the data. Therefore, neither of these options is not a use of statistics. Statistics involves collecting, analyzing, interpreting, presenting, and organizing data, which includes calculating averages and trends among other functions.
Q3: .................... it is not only related to only average, but we can also analyse trends.
(a) Statistics
(b) Economics
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Ans: Option (a)
Statistics is not only related to only average, but we can also analyse trends.
Q4: What can’t statistics be used for?
(a) Non-numerical data
(b) Quantifiable data
(c) Related data
(d) None of the above
Ans: Option (a)
Statistics cannot be used for non-numerical data because statistical methods are designed to handle numerical and quantifiable data. Non-numerical data does not fit into the mathematical framework that statistics operate within.
|
59 videos|222 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on Statistics for Economics- Assertion-Reason & Case Based Questions - Economics Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are some common statistical tools used in economics? |  |
| 2. How do statistics help in making economic decisions? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of data interpretation in economics? |  |
| 4. How is statistical analysis used in measuring economic indicators? |  |
| 5. How can econometric models be applied in economic research? |  |

















