Steps to Solve Logical Reasoning Puzzles | Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Why Logical Reasoning Puzzles are Important for CAT |

|
| Steps to Solve Logical Reasoning Puzzles |

|
| Solved Example |

|
| Common Mistakes to Avoid |

|
- Logical reasoning puzzles are a common and challenging part of the Logical Reasoning and Data Interpretation (LRDI) section in the CAT exam.
- These puzzles test your ability to process complex information, apply logical rules, and arrive at structured conclusions. This provides a step-by-step approach to tackle such puzzles effectively.
Why Logical Reasoning Puzzles are Important for CAT
- They form a significant portion of the LRDI section.
- They require structured thinking , not just calculation skills.
- With practice, they become predictable and highly scoring.
- Puzzle-based sets often appear in high-difficulty slots , separating top scorers from the rest.
Steps to Solve Logical Reasoning Puzzles
Step 1: Read the Question Carefully
Start by reading the entire question without skipping any details . Understand:
- The number of people/objects involved.
- The type of puzzle: scheduling, grouping, sequencing, etc.
- Any constraints or conditions given (e.g., “A cannot be with B”, “C must come before D”).
EduRev Tip: Underline key constraints as you read to avoid missing them later.
Step 2: Identify and Categorise Constraints
Break down all clues into manageable parts:
- Direct Clues : Provide specific information (e.g., "A is sitting third to the left of B").
- Conditional Clues : Start with “if”, “either-or”, or “unless” (e.g., "If C is selected, then D must also be selected").
- Negative Clues : Indicate what cannot happen (e.g., "E does not sit next to F").
Organise these in a list or on paper for quick reference.
Step 3: Prioritise Fixed Information First
Focus on clues that fix positions or relationships:
- Example: "A sits at position 3" or "B and C must be together".
- Use this fixed data as a base to build the rest of the logic around.
Avoid working with vague or conditional clues until the structure starts forming.
Step 4: Visualize with Diagrams or Tables
Use rough sketches, grids, or tables to represent the setup:
- For seating arrangements , draw a circle or line and mark positions.
- For grouping puzzles , create two columns: one for selected and one for rejected.
- For scheduling , use a table with days/hours and assign tasks accordingly.
EduRev Tip: Keep your diagrams simple and update them as new info comes in.
Step 5: Create Logical Notation
Develop shorthand symbols or codes for faster processing:
- Use arrows like A → B to mean “A must be followed by B”.
- Use symbols like A ↔ B to indicate mutual dependency.
- Mark exclusions with X or “≠”: e.g., C ≠ D means C and D cannot be together.
This helps in reducing confusion and speeds up problem-solving.
Step 6: Build Scenarios for Conditional Clues
When faced with multiple possibilities due to conditional statements:
- Create separate scenarios for each valid case.
- Eliminate invalid ones as you progress.
For example:
- If the clue is “Either X is selected or Y is selected,” consider both cases separately and eliminate those that violate other constraints.
Step 7: Apply the Process of Elimination
Use the answer options to guide your deductions:
- Check which options contradict known facts.
- Eliminate impossible choices early to narrow down possibilities.
- Sometimes, you can deduce the correct option without solving the full puzzle.
Step 8: Track Dependencies and Conflicts
Be mindful of how selecting or rejecting an element affects others:
- Example: If “A requires B,” selecting A automatically includes B.
- If “C excludes D,” selecting C removes D from consideration.
Maintaining a dependency map helps manage complexity.
Step 9: Cross-Check After Each Step
After applying a clue or choosing an option:
- Re-check if it violates earlier constraints.
- Ensure consistency across all rules.
This prevents backtracking and saves time.
Step 10: Review All Options Before Finalizing
Even if you think you’ve found the right answer, always:
- Review all options.
- Re-verify against the original constraints.
Sometimes, multiple options seem correct, but only one will satisfy all the given conditions.
Solved Example
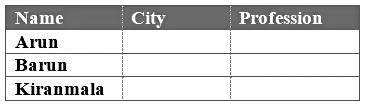
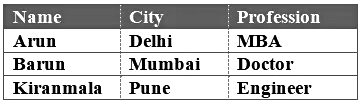
Q1: Arun Barun and Kiranmala are three friends who are from three different cities: Mumbai, Delhi, and Pune, not necessarily in that order. Arun is an MBA, while the other two have one of the professions – a doctor and an engineer. The engineer is from Pune, Barun is from Mumbai.
Sol:
In this case, the three objects are the three friends- Arun Barun and Kiranmala. And there are two parameters- city and profession.
Our task is to associate these parameters which belong to each of these friends. The best way to solve this puzzle is to organize these data in a table of three column. The first column is for the friends. The rest of the two columns are for the city and the profession respectively.Now let us analyse the clues.
1. Arun is an MBA is a direct clue. We can write MBA in the cell corresponding to the profession of Arun. We can also deduce that the other two friends, i.e., Barun and kiranmala are not MBA.2. The engineer is from Pune: Here we can see that both ‘engineer‘ and ‘Pune‘ are the two parameters and they are related to each other. From this clue, it is quite evident that Arun cannot be from Pune as he is an MBA. We can also symbolically write this piece of information as Engg –> Pune
3. Barun is from Mumbai: This information relates the object with a parameter. On combining this with the clue #2, we can deduce that Barun CANNOT be an engineer. And from clue #1, he cannot be an MBA. Hence, we can conclude that Barun is a doctor.
Also, Arun being an MBA cannot be from Pune. Neither he can be from Mumbai as Barun is from Mumbai. Therefore, he must be from Delhi. Which also concludes that Kiranmala is an engineer and she is from Pune.
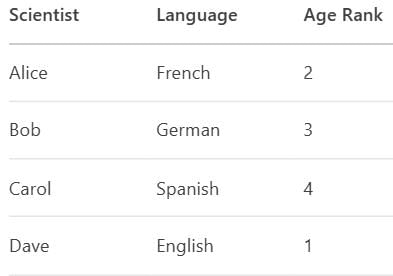
Q2: Four scientists—Alice, Bob, Carol, and Dave—speak English, French, German, and Spanish, each fluent in a different language. Alice does not speak English or German. The French speaker is older than Bob but younger than Dave. Carol and the Spanish speaker are the same age.
Assign the correct language to each scientist and determine their age order (oldest to youngest).
Sol:
Clue 1: Alice ≠ English, German → Alice speaks French or Spanish.
Clue 2: French speaker’s age: Dave > French > Bob → Dave is older than French speaker, who is older than Bob.
Thus, French speaker cannot be Dave (he’s older) or Bob (he’s younger).
So, French speaker = Alice or Carol.
Clue 3: Carol and Spanish speaker are same age → Carol must be the Spanish speaker (since no two scientists share an age rank).
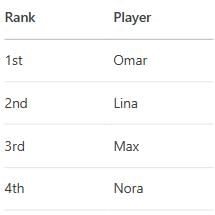
Q3: Four chess players—Lina, Max, Nora, and Omar—have rankings 1st to 4th (no ties). Max is ranked higher than Nora but lower than Omar. Lina is not last. The 2nd-place player has never lost to Omar. Determine the final standings.
Ans:
Step 1: Rank ConstraintsClue 1: Omar > Max > Nora.
Clue 2: Lina ≠ 4th.
Clue 3: 2nd-place player never lost to Omar → Omar cannot be 1st (since 2nd must have beaten him, implying Omar is lower).
Step 2: Deduce Omar’s Position
If Omar ≠ 1st, and Omar > Max > Nora, possible ranks:
Omar = 2nd → Max = 3rd, Nora = 4th.
Then 2nd-place (Omar) never lost to himself → Contradiction.
Omar = 1st → But violates Clue 4.
Only possibility: Omar = 3rd → Max = 4th (but contradicts Omar > Max).
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring Negative Clues : Missing statements like “X is not next to Y” leads to incorrect setups.
- Assuming Extra Info : Don’t add rules not mentioned in the question.
- Overcomplicating Diagrams : Keep visuals clean and updated.
- Rushing Through : Take time to understand the full set before jumping into solving.
- Not Using Options : Options can help validate assumptions and reduce effort.
|
88 videos|187 docs|96 tests
|
FAQs on Steps to Solve Logical Reasoning Puzzles - Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT
| 1. What are some typical characteristics of logical reasoning puzzles? |  |
| 2. What are the steps to solve logical reasoning puzzles? |  |
| 3. How can logical reasoning puzzles be helpful for exams like CAT? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific strategies or techniques to solve logical reasoning puzzles effectively? |  |
| 5. Can solving logical reasoning puzzles help in improving overall cognitive abilities? |  |