Getting to Know Plants Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 4
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Plants? |

|
| How are Plants Classified? |

|
| Structure of a Plant and its Parts |

|
| Leaf |

|
| Root |

|
| Flower |

|
| Important Questions |

|
What are Plants?
Plants are all around us. They help sustain life on earth by creating food and giving out oxygen that we breathe in.
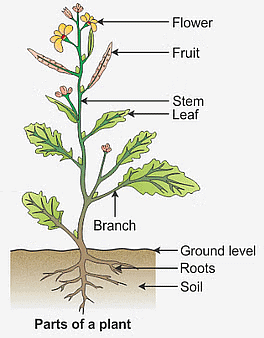 Parts of a Plant
Parts of a Plant
- Plants are the immovable living organisms all around us. They are the primary producers.
- They are mostly green in colour and use the sun as a source of energy to make food.
- In our garden, we have seen different varieties of plants. Few are herbs, shrubs, flowering plants, and tall coconut trees.
How are Plants Classified?
Plants can be classified on the basis of their height, stem, and branches. On these parameters, plants can be of three types, viz. herbs, shrubs and trees.
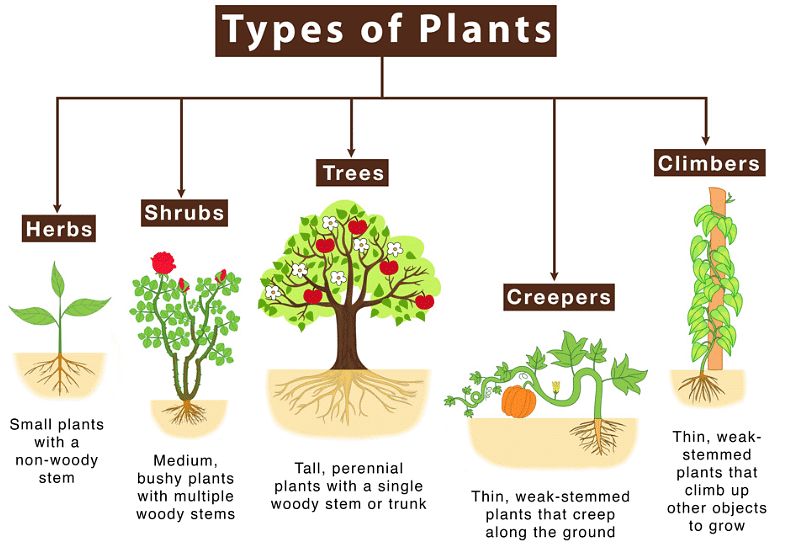 Types of Plants
Types of Plants
- Herbs: Herbs are small plants which have soft stems. Examples: Wheat, paddy, cabbage, grass, coriander, etc.
- Shrubs: These are bushy and medium-sized plants that are somewhat bigger than herbs. Their branches start from just above the ground. Examples: Lemon, Henna, Rose, etc.
- Tree: These are tall and large plants with hard and woody stems. A single main stem arises from the ground. The main stem is called the trunk. The trunk gives out many branches at a certain height. The branches carry leaves, flowers and fruits. Examples: Mango, banyan, acacia, coconut, poplar, willow, etc.
Creepers and Climbers
Creepers and Climbers are types of plants, which need support to grow.
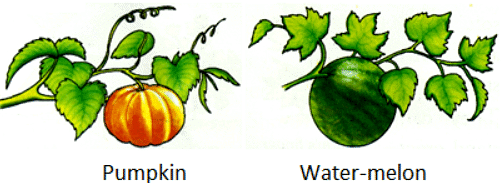
- Creepers: As the name suggests, these are plants that creep on the ground. They have very fragile, long, thin stems that can neither stand erect nor support all their weight. Examples: watermelon, strawberry, pumpkin and sweet potatoes.
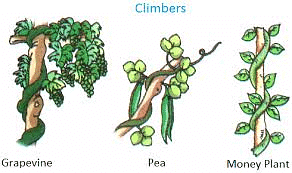
- Climber: Climbers are much more advanced than creepers. Climbers have very thin, long and weak stems which cannot stand upright, but they can use external support to grow vertically and carry their weight. These types of plants use special structures called tendrils to climb.
Examples: A few climbers’ plant names include pea plant, grapevine, sweet gourd, money plant, jasmine, runner beans, green peas, etc.
Structure of a Plant and its Parts
A typical plant contains two main parts, viz. roots and stem. The stem bears leaves, flowers and fruits.
Stem
Stem usually grows above the ground. The stem makes the main structural framework of the plant. The stem bears leaves, branches, buds, flowers and fruits.
- The point from where branches or leaves grow is called a node.
- The portion of a stem between two consecutive nodes is called the internode.
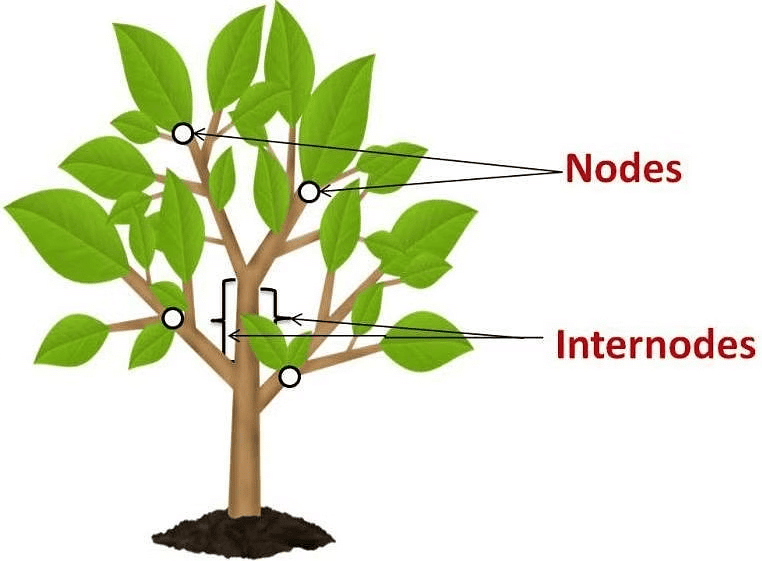 Nodes and Internodes in Stem
Nodes and Internodes in Stem
Functions of the stem
- The stem gives structural support to the plant.
- It bears branches, leaves, flowers and fruits.
- The stem carries water and minerals from the roots to different parts of the plant.
- Stems have nodes from which leaves arise. The space between two nodes is called an internode.
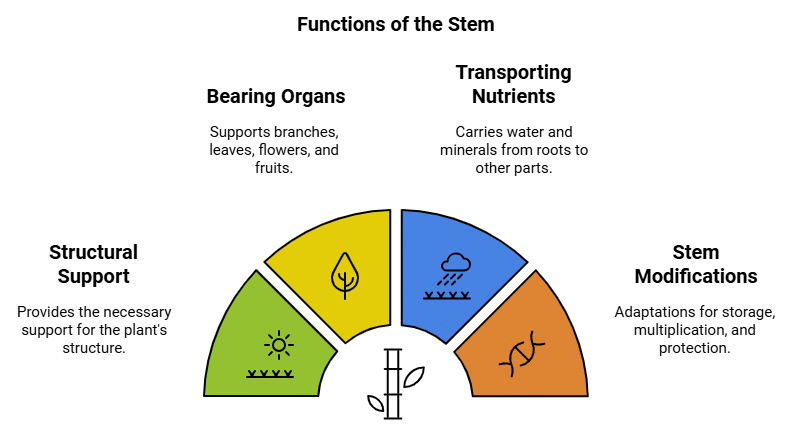
- Stem Modifications: Stems of certain plants are modified to perform special functions.
- For storage of water: Stems of plants such as cactus and jade swell up to store water in them.
- For storage of food: Potato, onion, and ginger are modified stems that store food. There are three kinds of underground stems: tubers (e.g., potato), rhizomes (e.g., ginger), and bulbs (e.g., onion and garlic).
 Underground Stems
Underground Stems - Multiplication of the plant: Rhizomes, bulbs, and tubers also help in the multiplication of the plant. Some plants, like rose, jasmine, and hibiscus, can grow new plants from their stem cuttings.
 Rose and hibiscus
Rose and hibiscus - For protection: Stems may be modified as thorns, like in bougainvillaea or hard and sharp prickles, as in rose, to protect the plant from being eaten by animals.
 Prickles of rose stem
Prickles of rose stem
Leaf
The leaf is a thin, flat, and green structure which arises from the node of the stem. The green colour of leaves is due to the presence of chlorophyll.
A leaf consists of two parts, namely the leaf lamina and the petiole. Below is the diagram for the parts of the leaf:
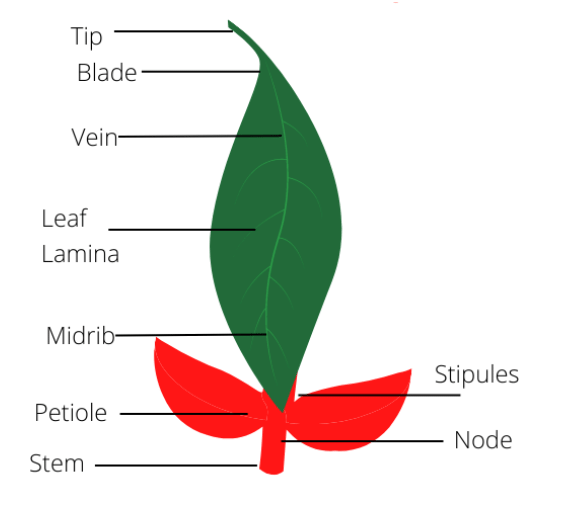 Parts of a Leaf
Parts of a Leaf
Leaf has different parts:
- A petiole is a narrow, stalk-like structure that connects the leaf to the stem.
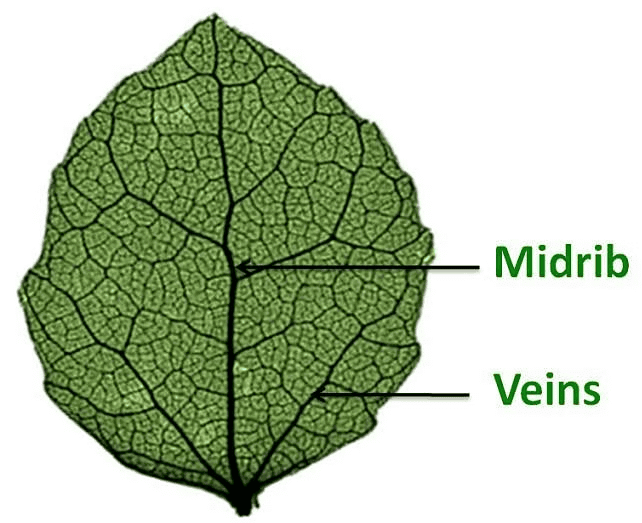
- The midrib: Midrib, a continuation of the petiole, is the central vein of the leaf. Smaller veins grow from the midrib.
- The veins: A network of branching veins forms a supporting framework and also serves to transport raw material and manufactured food into and out of the lamina.
- The leaf blade/lamina: The flat, green portion of the leaf is called the leaf blade or lamina.
Some Important Terms Regarding Leaves
- Chlorophyll: Chlorophyll is a green-coloured pigment. The flat green portion of the leaf is called leaf-blade or lamina.
- Petiole: The leaf is attached to the stem by a short stalk called petiole.
- Venation: The arrangement of veins in a leaf is called venation.

- Parallel venation: If the veins run parallel to one another from the base to the tip of the leaf, the leaf is said to have parallel venation, e.g., banana and onion.
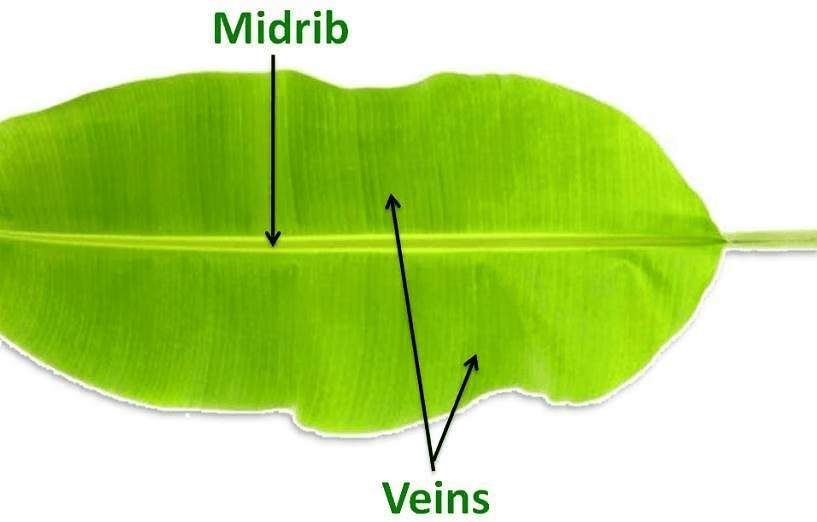 Parallel Venation
Parallel Venation - Reticulate venation: Leaves of some plants have veins arranged in a net-like pattern on both sides of the midrib. This kind of venation is called reticulate venation, e.g., Peepal (Bodhi) and Mango.
 Reticulate Venation
Reticulate Venation
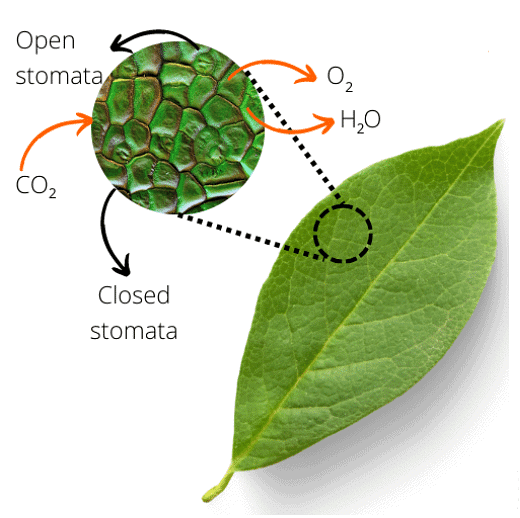
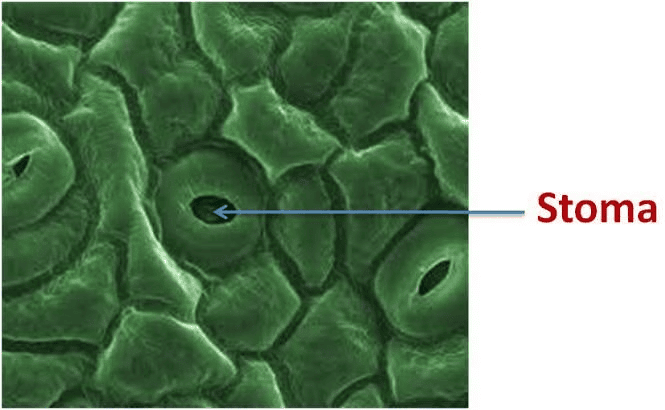
- Stomata: There are many small openings on the lower surface of a leaf. These are called stomata. Stomata allow gases to enter or exit the leaf. Unwanted water is also removed through stomata in the form of water vapour.
 Stomata
Stomata
- Transpiration: Loss of water vapour from plants through stomata and lenticels is called transpiration. A major portion of transpiration occurs through stomata.
Functions of Leaves
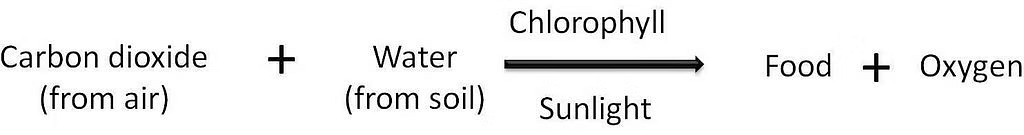
- Photosynthesis: This is the main function of a leaf. Plants prepare food from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of chlorophyll and sunlight. This process is called Photosynthesis.
- Exchange of gases: Stomata help in the exchange of gases, which are important for respiration and photosynthesis.
- Transpiration: Evaporation of excess water in vapour form and exchange of carbon dioxide takes place through stomata.
- Modifications for special functions: In certain plants, leaves perform functions like providing support and protection, Vegetative reproduction, and Trapping insects.
Root
The underground part of a plant is called root.
- Roots hold the plant firmly in the soil and thus provide anchorage to the plant.
- Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
- It is usually pale in colour.
 Roots of a Plant
Roots of a Plant
The root system consists of two types of roots:
- Taproot: This is composed of a main root which grows from the base of the stem. Many branches and sub-branches come out of the main root (tap root).
Examples: Peas, radishes, carrots, mangoes, marigolds, mustard, etc.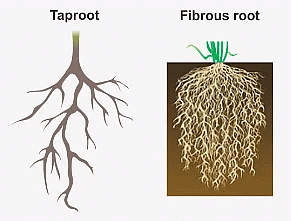 Tap and Fibrous Roots
Tap and Fibrous Roots - Fibrous root: In this type, a cluster of thin fibre-like roots arise from the base of the stem. These roots spread out in the soil.
Examples: Maize, grass, wheat, millet, etc.
Flower
Flower is the most beautiful and colourful part of a flowering plant. It is the reproductive part of a plant.
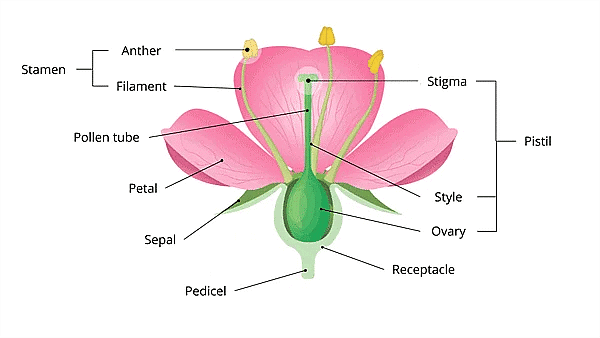 Parts of Flower
Parts of Flower
Different parts of flowers and their function
- Sepal: The outer green leafy structure in a flower is called sepal. Sepal makes the first whorl of a flower. This whorl is called calyx. It protects the flower at the bud stage.
- Petals: The coloured leaf-like structures next to the sepals are called petals. The bright colours of the petals attract insects. This helps the plants in reproduction. The whorl formed by the petals is called the corolla.
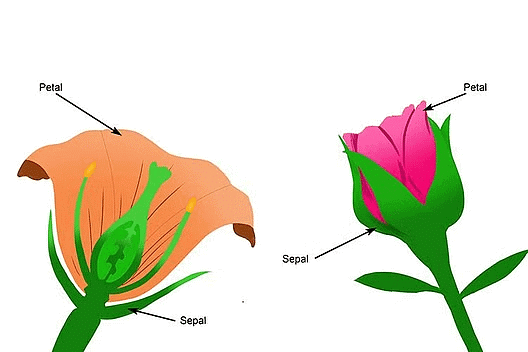 Petals and Sepals
Petals and Sepals - Stamens: Around the centre of the flower, there are many little stalks with swollen tops. These are called Stamen. It is the male part of the flower.
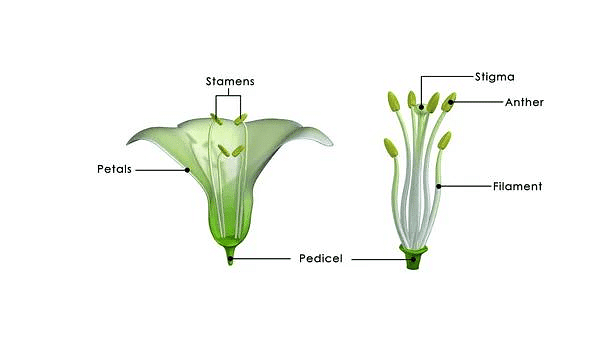 Parts of Stamens1. Filament: Each stamen consists of a stalk called filament.
Parts of Stamens1. Filament: Each stamen consists of a stalk called filament.
2. Anther: A capsule-like structure called anther is at the top of the stamen. The anther produces pollen grains. Pollen grains are powder-like particles that take part in reproduction. - Pistil: It is the female part of the flower. It is a flask-shaped structure in the middle of the flower. It is divided into three parts.
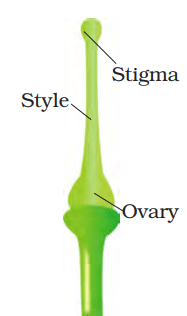 Parts of a Pistil1. Ovary: The lower broader portion of the pistil is called the ovary. It contains the ovules that become seeds after fertilization.
Parts of a Pistil1. Ovary: The lower broader portion of the pistil is called the ovary. It contains the ovules that become seeds after fertilization.
2. Style: The narrow middle portion of the pistil is called style.
3. Stigma: The sticky end at the top of the style is called stigma.
Important Questions
Q.1. What are the different types of plants?
There are several types of plants based on their characteristics and features. The main types include:
- Herbs: These are small plants with a soft, non-woody stem. Examples include mint, basil, and parsley.
- Shrubs: Shrubs are larger than herbs and have a woody stem. They are shorter than trees and often have multiple stems. Examples include lilacs and azaleas.
- Trees: Trees are large plants with a single main stem or trunk, supporting branches and leaves. Examples include oak trees, pine trees, and maple trees.
- Climbers: Climbing plants have specialized structures like tendrils or twining stems that help them climb. Examples include ivy and grapes.
- Creepers: Creeping plants spread horizontally along the ground. They often produce roots at nodes along the stems. Examples include strawberries and ground cover plants.
Q.2. What are the main parts of plants?
The main parts of most land plants include:
- Roots: They anchor the plant in the soil and absorb water and nutrients.
- Stems: These provide structural support and transport water, nutrients, and sugars between the roots and leaves.
- Leaves: Responsible for photosynthesis, where plants convert sunlight into energy.
- Flowers: Reproductive structures that produce seeds.
- Fruits: Develop from flowers and contain seeds. They protect and help disperse seeds.
- Seeds: Contain the embryo and serve as a means of reproduction for the plant.
Q.3. What are the parts of a leaf?
Leaf has different parts:
- Petiole is a narrow, stalk-like structure that connects the leaf to the stem.
- The midrib: Midrib, a continuation of the petiole, is the central vein of the leaf. Smaller veins grow from the midrib.
- The veins: A network of branching veins forms a supporting framework and also serves to transport raw material and manufactured food into and out of the lamina.
- The leaf blade/lamina: The flat, green portion of the leaf is called leaf blade or lamina.
Q.4. What are the parts of a flower?
(a) Sepals: Protective outermost layer of the flower.
(b) Petals: Attractive, often colorful structures that surround the reproductive organs.
(c) Stamens: Male reproductive organs that produce pollen.
(d) Pistil: Female reproductive organ that includes the stigma, style, and ovary.
Q.5. Name the part of a plant that produces food. Name the process.
Leaves produce food through a process called Photosynthesis. In this process, plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose (sugar) and oxygen. Chlorophyll, a pigment in the chloroplasts of plant cells, plays a crucial role in capturing sunlight and converting it into chemical energy.
|
74 videos|147 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Getting to Know Plants Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 4
| 1. What are plants? |  |
| 2. How are plants classified? |  |
| 3. What are the main parts of a plant? |  |
| 4. What is the function of a stem in a plant? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of flowers in a plant? |  |
















