Subjective Type Questions: Analytical Chemistry- 1 | JEE Advanced | 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE PDF Download
Q.1. Account for the following. Limit your an swer to two sentences: The precipitation of second group sulphides in qualitative analysis is carried out with hydrogen sulphide in presence of hydrochloric acid and not nitric acid. (1979)
Ans. Sol. HNO3 is strong oxidising agent and it oxidises H2S to S. So HNO3 cannot be used to precipitate second group elements.
Q.2. Compound A is a light green crystalline solid. It gives the following tests: (1980) (i) It dissolves in dilute sulphuric acid. No gas is produced. (ii) A drop of KMnO4 is added to the above solution. The pink colour disappears. (iii) Compound A is heated strongly. Gases B and C, with pungent smell, come out. A brown residue D is left behind. (iv) The gas mixture (B) and (C) is passed into a dichromate solution. The solution turns green. (v) The gr een solution from step (iv) g ives a white precipitate E with a solution of barium nitrate. (vi) Residue D from step (iii) is heated on charcoal in a reducing flame. It gives a magnetic substance.
Name the compounds A, B, C, D and E
Ans. Sol. (i) (A) is FeSO4.7H2O because it is light green crystalline solid. Which dissolves in water containing H2SO4
(ii) On strong heating FeSO4 both SO2 (B) and SO3 (C) are evolved. The colour of KMnO4 disappears due to the formation of MnSO4.
(iii) SO2 being a reducing agent turns a dichromate solution green and forms H2SO4 in the solution. SO3 dissolves in water to give H2SO4. Therefore, white ppt of BaSO4 is formed with a solution of Ba(NO3)2
(iv) The brown residue left behind (D) is Fe2O3 which is reduced to Fe on heating in charcoal cavity. Fe is magnetic substance.
Q.3. When 16.8 g of white solid X were heated, 4.4 g of acid gas A that turned lime water milky was driven off together with 1.8 g of a gas B which condensed to a colourless liquid. The solid that remained, Y, dissolved in water to give an alkaline solution, which with excess barium chloride solution gave a white precipitate Z. The precipitate effervesced with acid giving off carbon dioxide. Identify A, B and Y and write down the equation for the thermal decomposition of X. (1984 - 4 Marks)
Ans. Sol.
Representing the given facts in the form of equation.
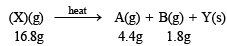
The above equation leads to the following facts : (i) Since the gas A turned lime water milky, it must be CO2.
(ii) NOTE : The compound Y gives alkaline solution in water which when treated with BaCl2 forms a white precipitate of Z. Since the compound Z when treated with acid gives effervescenes of CO2, Z and hence Y must be metal carbonate, CO32- . Hence Y may be written as metal carbonate MCO3 or M2CO3.
(iii) When X is heated, it yields a carbonate (Y) along with the evolution of CO2 (A) and another gas (B), it must be a bicarbonate.
(iv) The above facts point out that B may be water vapour Thus the above reaction can be written as below.
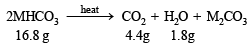
Calculation of molecular weight of MHCO3 4.4.g of CO2 is given by 16.8 g of MHCO3
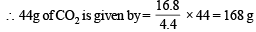
Since two molecules of MHCO3 are taking part in the reaction, the molecular weight of
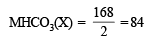
Calculation of atomic weight of metal M MHCO3 = 84; M + 1 + 12 + 48 = 84
M + 61 = 84; M = 84 – 61 = 23
Thus the metal must be Na and hence the given salt X is NaHCO3. The above facts coincide with the given thermal decomposition.
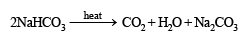
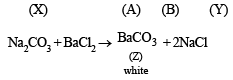
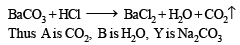
Q.4. A mixture of two salts was treated as follows : (1987 - 5 Marks)
(i) The mixture was heated with manganese dioxide and concentrated sulphuric acid when yellowish green gas was liberated.
(ii) The mixture on heating with sodium hydroxide solution gave a gas which turned red litmus blue.
(iii) Its solution in water gave blue precipitate with potassium ferricyanide and red colouration with ammonium thiocyanate.
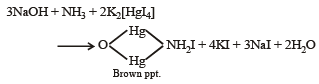
(iv) The mixture was boiled with potassium hydroxide and the liberated gas was bubbled through an alkaline solution of K2HgI4 to give brown precipitate.
Identify the two salts. Give ionic equations for reactions involved in the tests (i), (ii) and (iii).
Ans. Sol. (A) Test (i) of the problem indicates that the mixture contains Cl– ion which is liberated as Cl2 (yellowish green gas) when heated with MnO2 and conc. H2SO4. (B) Test (ii) indicates the presence of NH4+ ion in the mixture which gives ammonia when heated with NaOH solution.
Since ammonia is basic in nature, it turns red litmus blue. Presence of NH4+ in the mixture is further confirmed by the given test (iv) according to which the gas (NH3) gives brown precipitate with Nessler’s reagent (alkaline solution of K2[HgI4]. (C) Test (iii) indicates Fe2+ ion in the mixture which gives blue precipitate with potassium ferricyanide (note that potassium ferricyanide gives brown ppt. with Fe3+ ions). (D) Red colouration with ammonium thiocynate indicates that the mixture also contains Fe3+ ions which are believed to be formed by the oxidation of Fe2+ ions by air.
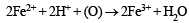
Thus the mixture contains FeCl2 and NH4Cl.
Ionic reactions :
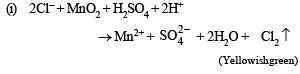
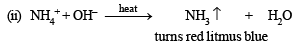
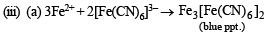
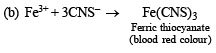
Q.5. A hydrated metallic salt A, light green in colour, on careful heating gives a white anhydrous residue B. B is soluble in water and its aqueous solution reacts with NO to give a dark brown compound C. B on strong heating gives a brown residue D and a mixture of two gases E and F. The gaseous mixture when passed through acidified permanganate, discharges the pink colour and when passed through acidified BaCl2 solution gave a white precipitate. Identify A, B, C, D, E and F. (1988 - 3 Marks)
Ans. Sol. (i) (A) on heating loses water of crystallization and thus it is a hydrated salt.
(ii) Anhydrous salt (B) on heating gives two gases and brown residue and so (B) is FeSO4. Thus (A) is
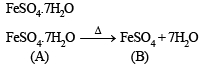
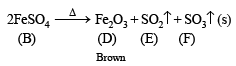
(iii) (B) is soluble in water and reacts with NO to give brown compound.
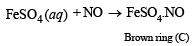
(iv) Gaseous mixture decolorizes acidified KMnO4. 5SO2 + 2KMnO4 + 2H2O → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 2H2SO4
(v) Gaseous mixture on passing through BaCl2, gives white ppt. of BaSO4.
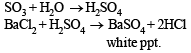
Q.6. When 20.02 g of a white solid X is heated 4.4 g of an acid gas A and 1.8 g of a neutral gas B are evolved, leaving behind a solid residue Y of weight 13.8 g. A turns lime water milky and B condenses into a liquid which changes anhydrous copper sulphate blue. The aqueous solution of Y is alkaline to litmus and gives 19.7 g of white precipitate Z with barium chloride solution. Z gives carbon dioxide with an acid. Identify A, B, X, Y and Z. (1989 - 5 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Representing the given facts in the form of equation, we get
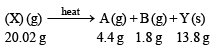
The above equation leads to the following facts : (i) Since the gas A turned lime water milky, it must be CO2.
(ii) NOTE : The compound Y is alkaline to litmus and when treated with BaCl2 forms a white precipitate of Z. Since the compound Z when treated with acid gives effervescenes of CO2, Z and hence Y must contain carbonate, CO32- . Hence Y may be written as metal carbonate MCO3 or M2CO3.
(iii) When X is heated, it yields a carbonate (Y) along with the evolution of CO2 (A) and a neutral gas (B), it must be a bicarbonate. (iv) B changes anhydrous CuSO4 blue, which point out that B is water.
Thus the above reaction can be written as below :
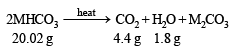
Calculation of molecular weight of MHCO3 4.4 g of CO2 is given by 20.02 g of MHCO3
44 g of CO2 is given by = 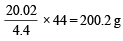
Since two molecules of MHCO3 are taking part in the reaction, the molecular weight of
MHCO3 (X) =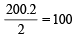
Calculation of atomic weight of Metal M MHCO3 = 100; M + 1 + 12 + 48 = 100
M + 61 = 100; M = 100 – 61 = 39
Thus the metal must be K and hence the given salt X is KHCO3.
The above facts coincide with the given thermal decomposition.
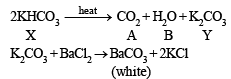
Hence, we have
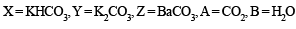
Q. 7. The gas liberated on heating a mixture of two salts with NaOH, gives a reddish brown precipitate with an alkaline solution of K2[HgI4]. The aqueous solution of the mixture on treatment with BaCl2 gives a white precipitate which is sparingly soluble in conc. HCl. On heating the mixture with K2Cr2O7 and conc. H2SO4, red vapours of A are produced.
The aqueous solution of the mixture gives a deep blue colouration B with potassium ferricyanide solution. Identify the radicals in the given mixture and write the balanced equations for the formation of A and B. (1991 - 4 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Let us summarise the given facts of the question.
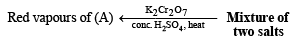
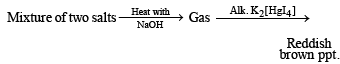
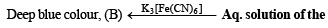
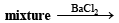 White ppt.sparingly soluble in conc.
White ppt.sparingly soluble in conc.
HCl.
The given reactions lead to the following conclusions.
(i) Formation of reddish brown precipitate on treatment with alk. K2[HgI4] indicates the evolution of NH3 gas and hence the presence of NH4+ in the mixture of salts.
(ii) Heating of mixture with K2Cr2O7 and conc. H2SO4 to give red vapours (of chromyl chloride) indicates the presence of Cl– ion in the mixture.
(iii) Reaction of aqueous solution of the mixture with barium chloride solution to give white ppt. (of BaSO4) sparingly soluble in conc. HCl indicates the presence of SO42-ions in the mixture.
(iv) NOTE : Reaction of aqueous solution of the mixture with potassium ferricyanide solution to give deep blue colour indicates the presence of Fe2+ ions in the mixture.
Hence the mixture contains following four ions :
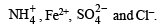
Equations for the formation of A and B.
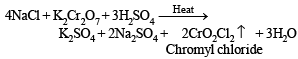
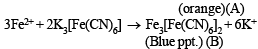
Q.8. A light bluish green crystalline compound responds to the following tests :
(i) Its aqueous solution gives a br own pr ecipitate or colour with alkaline K2[HgI4] solution.
(ii) Its aqueous solution gives a blue colour with K3[Fe(CN)6] solution.
(iii) Its solution in hydrochloric acid gives a white precipitate with BaCl2 solution.
Identify the ions present and suggest the formula of the compound. (1992 - 4 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Compound gives brown ppt. with alkaline K2[HgI4] and so contain NH+4 ions.’ ‘Compound gives blue colour with K3[Fe(CN)6] and so contains Fe2+ ions.’ ‘Solution of compound in HCl gives white ppt. with BaCl2 and so it contains SO42- ions.’ ‘Bluish green compound with NH+4 , Fe2+ and 2-
SO4 suggests that it is Mohr's salt i.e.’ FeSO4(NH4)2SO4.6H2O Reactions :
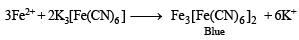
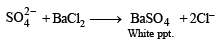
Q.9. An orange solid (A) on heating gave a green residuce (B), a colourless gas (C) and water vapour. The dry gas (C) on passing over heated Mg gave a white solid (D). (D) on reaction with water gave a gas (E) which formed dense white fumes with HCl. Identify (A) to (E) and give reactions involved. (1993 - 3 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Let us summarise the given facts
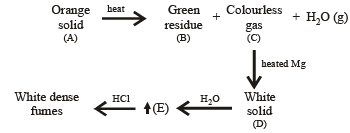
(i) Formation of white dense fumes by gas (E) with HCl indicates that the gas (E) is ammonia (NH3).
(ii) Formation of ammonia (E) by the hydrolysis of white solid (D) indicates that (D) should be magnesium nitride, Mg3N2.
(iii) Since compound (D) is formed by reaction of gas (C) with magnesium, the colourless gas (C) must be nitrogen.
(iv) Orange colour of the original compound (A) and green colour of the residue (B) indicates that compound (A) is ammonium dichromate, (NH4)2Cr2O7.
Reactions :
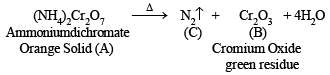
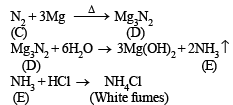
Q.10. A is a binary compound of a univalent metal, 1.422 g of A reacts completely with 0.321 g of sulphur in an evaccuated and sealed tube to give 1.743 g of a white crystalline solid B, that forms a hydrated double salt, C with Al2(SO4)3. Identify A, B and C (1994 - 5 Marks)
Ans. Sol. As the solid B forms a hydrated salt C with Al2(SO4)3; B should be sulphate of a monovalent cation, i.e. M2SO4.
Now since sulphate of a monovalent cation contains one sulphur atom per mol, weight of metal sulphate obtained by 32.1 g (at. wt. of S) should be the molecular weight of the metal sulphate. Thus, – 0.321 g of sulphur is present in 1.743 g of B
∴ 32.1 g of sulphur is present in = 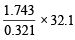 = 174.3 g
= 174.3 g
Thus mol. wt. of B (M2SO4) = 174.3 g mol–1
2x + 32.1 + 64 = 174.3 (at wt. of M = x] 2x = 78.2
⇒ x = 39.1
Atomic weight 39.1 corresponds to metal potassium, K.
Thus B is K2SO4, and C is K2SO4 . Al2(SO4)3 . 24H2O
Nature of compound A : Since A is a binary compound of potassium and it reacts with sulphur to form K2SO4, it must be oxide of potassium, probably potassium superoxide (KO2) which is supported by the given data.
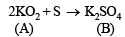
2 (39.1 + 32) = 142.2
32.1g of Sreacts with 142.2g of KO2 0.321g of Sreacts with = 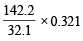 = 1.422 g
= 1.422 g
Similarly, 32.1 g of S gives 174.3 g of K2SO4
0.321 g of S gives = 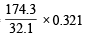 = 1.743 g
= 1.743 g
Both these datas are also given in the problem. Thus A is KO2.
Q.11. A scarlet compound A is treated with conc. HNO3 to give a chocolate brown precipitate B. The precipitate is filtered and the filtrate is neutralised with NaOH. Addition of KI to the resulting solution gives a yellow precipitate C. The precipitate B on warming with conc. HNO3 in the precence of Mn(NO3)2 produces a pink-coloured solution due to the formation of D. Identify A, B, C and D. Write the reaction sequence. (1995 - 4 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Summary of the given facts.

From the colour of the known compound and reaction involved, it is clear that (A) is red lead (Pb3O4) and its various reactions can be represented as below.
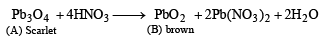
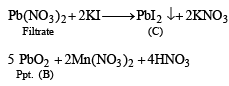
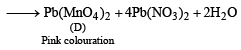
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
|
347 docs|185 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|

















