Subjective Type Questions: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry- 3 | JEE Advanced | 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE PDF Download
Q. 29. Calculate the molality of 1 litre solution of 93% H2SO4 (weight/volume). The density of the solution is 1.84 g/ml. (1990 - 1 Marks)
Ans. Sol. TIPS/Formulae :
Molality = 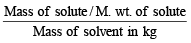
Mass of H2SO4 in 100 ml of 93% H2SO4 solution = 93 g
∴ Mass of H2SO4 in 1000 ml of the H2SO4 solution = 930 g
Mass of 1000 ml H2SO4 solution = 1000 × 1.84 = 1840 g
Mass of water in 1000 ml of solution = 1840 – 930 g = 910 g = 0.910 kg
Moles of H2SO4 = 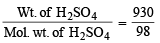
∴ Moles of H2SO4 in 1 kg of water
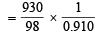 = 10.43 mol
= 10.43 mol
∴ Molality of solution = 10.43m
Q. 30. A solution of 0.2 g of a compound containing Cu2+ and C22- O4 ions on titration with 0.02 M KMnO4 in presence of H2SO4 consumes 22.6 ml. of the oxidant. The resultant solution is neutralized with Na2CO3, acidified with dil. acetic acid and treated with excess KI. The liberated iodine requires 11.3 ml of 0.05 M Na2S2O3 solution for complete reduction.
Find out the molar ratio of Cu2+ to C2O42- in the compound.
Write down the balanced redox reactions involved in the above titrations. (1991 - 5 Marks)
Ans. Sol. In th e given problem, a solution contain in g Cu2+ and C2O42- is titrated first with KMnO4 and then with Na2S2O3 in presence of KI. In titration with KMnO4, it is the C2O24- ions that react with the MnO-4 ions. The concerned balanced equation may be written as given below.
2MnO4- + 5 C2O24- + 16H+ → 2Mn2+ + 10CO2 + 8H2O
Thus according to the above reaction 2 mmol MnO-4 ≡ 5 mmol C2 O24-
However, No. of mmol of MnO-4 used in titration = Vol. in ml × M = 22.6 × 0.02 = 0.452 mmol MnO-4
Since 2 mmol MnO-4 ≡ 5 mmol C2O24-0.452 mmol MnO-4 ≡ 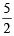 × 0.452 = 1.130 mmol C2 O24-
× 0.452 = 1.130 mmol C2 O24-
Titration with Na2S2O3 in the presence of KI.
Here Cu2+ react and the reactions involved during titrationare
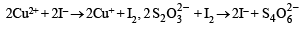
Thus 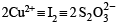
No. of m mol of S2O32- used in titration
= 0.05 × 11.3 = 0.565 mmol S2O32-
Now since 2 mmol S2O32- ≡ 2 mmol Cu2+ [From above equation]
0.565 mmol S2O32- =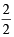 × 0.565 mmol Cu2+
× 0.565 mmol Cu2+
= 0.565 mmol Cu2+
∴ Molar ratio of Cu2+ to 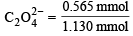 = 1 : 2
= 1 : 2
Balanced equations in two cases Case I. Mn+7 + 5e– → Mn+2
C2+3 → 2C+4 + 2e–
Case II. 2Cu+2 + 2e– → Cu2+ 2I– → I2 + 2e– and I2 + 2e– → 2I– 2S2+2 → S4+3/2 + 2e–
Q. 31. A 1.0 g sample of Fe2O3 solid of 55.2% purity is dissolved in acid and reduced by heating the solution with zinc dust.
The resultant solution is cooled and made upto 100.0 ml. An aliquot of 25.0 ml of this solution requires 17.0 ml of 0.0167 M solution of an oxidant for titration. Calculate the number of electrons taken up by the oxidant in the reaction of the above titration. (1991 - 4 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Mass of Fe2O3 in the sample = 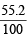 × 1 = 0.552 g
× 1 = 0.552 g
Number of moles of Fe2O3 = 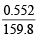 = 3.454 × 10–3
= 3.454 × 10–3
Number of moles of Fe3+ ions = 2 × 3.454 × 10–3
= 6.9 × 10–3 mol = 6.90 mmolSince its only 1 electron is exchanged in the conversion of Fe3+ to Fe2+, the molecular mass is the same as equivalent mass.
∴ Amount of Fe2+ ion in 100 ml. of sol. = 6.90 meq Volume of oxidant used for 100 ml of Fe2+ sol.
= 17 × 4 = 68 ml.
Amount of oxidant used = 68 × 0.0167 mmol
= 1.1356 mmolLet the number of electrons taken by the oxidant = n
∴ No. of meq. of oxidant used = 1.1356 × n
Thus 1.1356 × n = 6.90 ⇒ n = 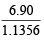 = 6
= 6
Q. 32. A 2.0 g sample of a mixture containing sodium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate and sodium sulphate is gently heated till the evolution of CO2 ceases. The volume of CO2 at 750 mm Hg pressure and at 298 K is measured to be 123.9 ml. A 1.5g of the same sample requires 150 ml. of (M/10) HCl for complete neutralisation. Calculate the % composition of the components of the mixture. (1992 - 5 Marks)
Ans. Sol. 1.5 g of sample require = 150 ml. of 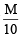 HCl
HCl
∴ 2 g of sample require =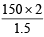 ml. of
ml. of 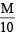 HCl
HCl
= 200 ml. of 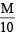 HCl
HCl
On heating, the sample, only NaHCO3 undergoes decomposition as given below.
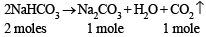
2 equ.
Neutralisation of the sample with HCl takes place as given below.
NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2
1 eq. 1 eq.
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
1 mole 2 mole
2 eq. 2 eq.
Hence, 2 g sample ≡ 200 ml. of M/10 HCl
= 200 ml. of N/10 HCl = 20 meq = 0.020 eq
Number of moles of CO2 formed, i.e.
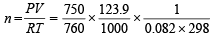 = 0.005
= 0.005
Moles of NaHCO3 in the sample (2 g) = 2× 0.005 = 0.01
Equivalent of NaHCO3 = 0.01
Wt. of NaHCO3 = 0.01 × 84 = 0.84 g
% of NaHCO3 = 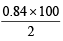 = 42%
= 42%
Equivalent of Na2CO3 = 0.02 – 0.01 = 0.01
Wt. of Na2CO3 = 0.01 × 53 = 0.53 g
∴ % of Na2CO3 = 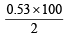 = 26.5%
= 26.5%
∴ % of Na2SO4 in the mixture = 100 – (42 + 26.5) = 31.5%
Q. 33. One gram of commercial AgNO3 is dissolved in 50 ml. of water. It is treated with 50 ml. of a KI solution. The silver iodide thus precipitated is filtered off. Excess of KI in the filterate is titrated with (M/10) KIO3 solution in presence of 6M HCl till all I– ions are converted into ICl. It requires 50 ml. of (M/10) KIO3 solution. 20 ml. of the same stock solution of KI requires 30 ml. of (M/10)KIO3 under similar conditions.
Calculate the percentage of AgNO3 in the sample.
(Reaction : KIO3 + 2KI + 6HCl → 3ICl + 3KCl + 3H2O) (1992 - 4 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Reaction involved titration is 1 mole 2 moles KIO3 + 2KI + 6HCl → 3ICl + 3KCl + 3H2O
20 ml. of stock KI solution ≡ 30 ml. of 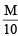 KIO3 solution
KIO3 solution
Molarity of KI solution = 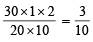
Millimoles in 50 ml. of KI solution = 50 ×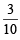 = 15
= 15
Millimoles of KI left unreacted with AgNO3 solution
= 2 × 50 × 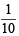 = 10
= 10
∴ Millimoles of KI reacted with AgNO3 = 15 – 10 = 5
Millimoles of AgNO3 present in AgNO3 solution = 5
Molecular weight of AgNO3 = 170
∴ Wt. of AgNO3 in the solution = 5 × 10–3 × 170 = 0.850 g
% AgNO3 in the sample =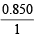 × 100 = 85%
× 100 = 85%
Q. 34. Upon mixing 45.0 ml. of 0.25 M lead nitrate solution with 25.0 ml of 0.10 M chromic sulphate solution, precipitation of lead sulphate takes place. How many moles of lead sulphate are formed? Also, calculate the molar concentrations of the species left behind in the final solution. Assume that lead sulphate is completely insoluble. (1993 - 3 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Calculation of number of moles in 45 ml. of 0.025 M Pb(NO3)2
Moles of Pb(NO3)2 = 0.25 × 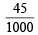 = 0.01125
= 0.01125
∴ Initial moles of Pb2+ = 0.01125
Moles of NO3- = 0.01125 × 2 = 0.02250 [1 mole Pb(NO3)2 ≡ 2 moles of NO3]
Calculation of number of moles in 25 ml. of 0.1 M chromic sulphate
Moles of chromic sulphate (Cr2(SO4)3
= 0.1 ×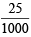 = 0.0025 moles
= 0.0025 moles
Moles of SO24- = 0.0025 × 3 = 0.0075 [1 Mole of chromic sulphate ≡ 3 moles of SO42–]
Moles of PbSO4 formed = 0.0075 [SO42– is totally consumed]
Moles of Pb2+ left = 0.01125 – 0.0075 = 0.00375
Moles of NO3- left = 0.02250 [NO3– remain unreacted]
Moles of chromium ions = 0.0025 × 2 = 0.005
Total volume of the solution = 45 + 25 = 70 ml.
∴ Molar concentration of the species left
(i) Pb2+ =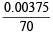 × 1000 = 0.05357 M
× 1000 = 0.05357 M
(ii) NO3- =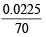 × 1000 = 0.3214 M
× 1000 = 0.3214 M
(iii) Cr3+ =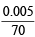 × 1000 = 0.0714 M
× 1000 = 0.0714 M
Q. 35. The composition of a sample of Wustite is Fe0.93O1.00 .
What percentage of the iron is present in the form of Fe (III)? (1994 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. In pure iron oxide (FeO), iron and oxygen are present in the ratio 1 : 1.
However, here number of Fe2+ present = 0.93 or No. of Fe2+ ions missing = 0.07 Since each Fe2+ ion has 2 positive charge, the total number of charge due to missing (0.07) Fe2+ ions = 0.07 × 2 = 0.14 To maintain electrical neutrality, 0.14 positive charge is compensated by the presence of Fe3+ ions. Now since, replacement of one Fe2+ ion by one Fe3+ ion increases one positive charge, 0.14 positive charge must be compensated by the presence of 0.14 Fe3+ ions.
In short, 0.93 Fe2+ ions have 0.14 Fe3+ ions 100 Fe2+ ions have = 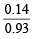 × 100 = 15.05%
× 100 = 15.05%
Q. 36. 8.0575 × 10–2 kg of Glauber ’s salt is dissolved in water to obtain 1 dm3 of a solution of density 1077.2 kg m–3. Calculate the molarity, molality and mole fraction of Na2SO4 in the solution. (1994 - 3 Marks)
Ans. Sol. The formula of Glauber’s salt is Na2SO4.10H2O Molecular mass of Na2SO4.10H2O
= [2 × 23 + 32.1 + 4 × 16] + 10 (1.01 × 2 + 16) = 322.3 g mol–1
Weight of the Glauber’s salt taken = 80.575 gm Out of 80.575 g of salt, weight of anhydrous Na2SO4
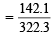 × 80.575 = 35.525 g
× 80.575 = 35.525 g
Number of moles of Na2SO4 per dm3 of the solution 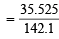 = 0.25
= 0.25
Molarity of the solution = 0.25 M
Density of solution = 1077.2 kgm–3
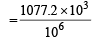 gm cm–3 = 1.0772 g cm–3
gm cm–3 = 1.0772 g cm–3
Total weight of sol = V × d = 1 dm3 × d
= 1000 cm3 × 1.0772 gcm–3 = 1077.2 g
Weight of water = 1077.2 – 35.525 = 1041.67 g
Molality of sol. = 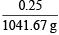 × 1000 g = 0.2399 = 0.24 m
× 1000 g = 0.2399 = 0.24 m
Number of moles of water in the solution = 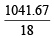 = 57.87
= 57.87
Mole fraction of Na2SO4
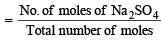
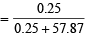
= 0.0043 = 4.3 × 10–3
Q. 37. A 3.00 g sample containing Fe3O4, Fe2O3 and an inert impure substance, is treated with excess of KI solution in presence of dilute H2SO4.The entire iron is converted into Fe2+ along with the liberation of iodine. The resulting solution is diluted to 100 ml. A 20 ml of the diluted solution requires 11.0 ml of 0.5 M Na2S2O3 solution to reduce the iodine present. A 50 ml of the diluted solution, after complete extraction of the iodine requires 12.80 ml of 0.25 M KMnO4 solution in dilute H2SO4 medium for the oxidation of Fe2+. Calculate the percentages of Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 in the original sample. (1996 - 5 Marks)
Ans. Sol. TIPS/Formulae : Find the milliequivalents and equate them as per data given in question.
For Fe3O4 → 3FeO
2e + Fe3(8/3)+ → 3Fe2+
Thus, valence factor for Fe3O4 is 2 and for FeO is 2/3.
For, Fe2O3 → 2FeO; 2e + Fe23+ → 2Fe2+ ...(1)
Thus valence factor for Fe2O3 is 2 and for FeO is 1.
Let Meq.of Fe3O4 and Fe2O3 be a and b respectively.
∴ Meq. of Fe3O4 + Meq. Fe2O3 = Meq. of I2 liberated
= Meq. of hypo used
a + b =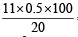 = 27.5
= 27.5
Now, the Fe2+ ions are again oxidised to Fe3+ by KMnO4.
Note that in the change Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e–; valence factor of Fe2+ is l.
Thus, Meq. of Fe2+ (from Fe3O4) + Meq. of Fe2+ (from Fe2O3) = Meq. of KMnO4 used .... (2)
If valence factor for Fe2+ is 2/3 from Eq. (1), then Meq. of Fe2+ (from Fe3O4) = a
If valence factor for Fe2+ is 1 then Meq. of Fe2+ (from Fe3O4) = 3a/2 … (3)
Similarly, from Eq. (2), Meq. of Fe2+ from (Fe2O3) = b.
∴ 3a/2 + b = 0.25 x 5 x 12.8 x 100/50 = 32 or 3a + 2b = 64 ....(4)
From Eqs. (3) and (4)
Meq. of Fe3O4 = a = 9 & Meq. of Fe2O3 = b = 18.5
∴ WFe3O4 = 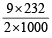 = 1.044g
= 1.044g
and WFe2O3 =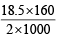 = 1.48g
= 1.48g
∴ % of Fe3O4 =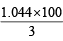 = 34.8
= 34.8
and % of Fe2O3 =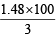 = 49.33
= 49.33
Q. 38. An aqueous solution containing 0.10 g KIO3 (formula weight = 214.0) was treated with an excess of KI solution. The solution was acidified with HCl. The liberated I2 consumed 45.0 mL of thiosulphate solution to decolourise the blue starch-iodine complex. Calculate the molarity of the sodium thiosulphate solution. (1998 - 5 Marks)
Ans. Sol. TIPS/Formulae : Write the reactions taking place, balance them and equate moles of I2 and Na2S2O3.
KIO3 + 5KI → 3K2O + 3I2 i.e., 2 I5+ + 10e– → I02
2I– → I02 + 2e–
Now liberated I2 reacts with Na2S2O3 I2 + 2e– → 2I–
2S2O32- → S4O62- + 2e–
∴ millimole ratio of I2 : S2O3 = 1 : 2
Thus, m mole of I2 liberated = m mole of Na2S4O6 used x 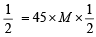
[M is molarity of thiosulphate]
Also m mole of KIO3 = 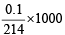
Now m mole ratio of KIO3 : I2 = 1 : 3
Thus, 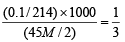
∴ M =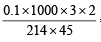 = 0.062
= 0.062
Q. 39. How many millilitres of 0.5 M H2SO4 are needed to dissolve 0.5 g of copper(II) carbonate? (1999 - 3 Marks)
Ans. Sol. TIPS/Formulae : Use molarity equation to find volume of H2SO4 solution.
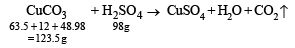
∴ For 123.5 gms of Cu(II) carbonate 98 g of H2SO4 are required.
For 0.5 gms of Cu(II) carbonate weight of H2SO4 reqd.
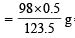 = 0.39676 g H2SO4
= 0.39676 g H2SO4
Weight of required H2SO4 = 0.39676 g
Weight of solute in grams
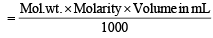
0.39676 = 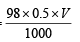 or
or 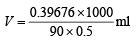
Volume of H2SO4 solution = 8.097 ml
Q. 40. A plant virus is found to consist of uniform cylindrical particles of 150 Å in diameter and 5000 Å long. The specific volume of the virus is 0.75 cm3/g. If the virus is considered to be a single particle, find its molar mass.(1999 - 3 Marks)
Ans. Sol. TIPS/Formulae : (i) Volume of virus = πr2ℓ (Volume of cylinder)
(ii) Mass of single virus = 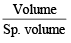
(iii) Molecular mass of virus = Mass of single virus × 6.02 × 1023
Volume of virus = πr2l
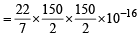 x 5000 x 10-8
x 5000 x 10-8
= 0.884 x 10–16 cm3
Weight of one virus = 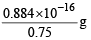
= 1.178 x 10-16 g
∴ Mol. wt. of virus = 1.178 x 10-16 x 6.02 x 1023 = 7.09 x 107
Q. 41. Hydrogen peroxide solution (20 ml) reacts quantitatively with a solution of KMnO4 (20 ml) acidified with dilute H2SO4.
The same volume of the KMnO4 solution is just decolourised by 10 ml of MnSO4 in neutral medium simultaneously forming a dark brown precipitate of hydrated MnO2. The brown precipitate is dissolved in 10 ml of 0.2 M sodium oxalate under boiling condition in the presence of dilute H2SO4. Write the balanced equations involved in the reactions and calculate the molarity of H2O2. (2001 - 5 Marks)
Ans. Sol. TIPS/Formulae : Write the balanced chemical reaction for change and apply mole concept.
The given reactions are MnO2 ↓ + Na 2C2 O4+ 2H2SO4
—→ MnSO4 + CO2 + Na 2SO4+ 2H2O
∴ Meq. of MnO2 ≡ Meq of Na2C2O4 = 10 × 0.2 × 2 = 4
∴ mM of MnO2 =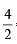 = 2
= 2 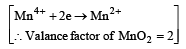
Now 2KMnO4 + 3MnSO4+ 2H2O
—→ 5MnO2 ↓ + K2SO4+ 2H2O
Since eq. wt. of MnO2 is derived from KMnO4 and MnSO4 both, thus it is better to proceed by mole concept
mM of KMnO4 ≡ mM of MnO2 × (2/5) = 4/5
Also 5H2O2 + 2KMnO4+ 3H2SO4
—→ 2MnSO4 + K2SO4 + 8H2O+ 5O2
∴ mM of H2O2 = mM of KMnO4 ×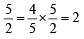
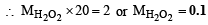
2KMnO4 + 5H2O2 + 3H2SO4 —→ K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 8H2O + 5O2
2KMnO4 + 3MnSO4 + 2H2O —→ 5MnO2 + 2H2SO4 + K2SO4
MnO2 + Na2C2O4 + 2H2SO4 —→MnSO4 + 2CO2 + Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Q. 42. Calculate the molarity of water if its density is 1000 kg/m3. (2003 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. 1 litre water = 1 kg i.e. 1000 g water (∵ d = 1000 kg/m3)
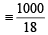 = 55.55 moles of water
= 55.55 moles of water
So, molarity of water = 55.55M
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
FAQs on Subjective Type Questions: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry- 3 - JEE Advanced - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE
| 1. What are some basic concepts of Chemistry? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare for the JEE Advanced Chemistry section? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of Chemistry in JEE Advanced exam? |  |
| 4. How can I improve my problem-solving skills in Chemistry for JEE Advanced? |  |
| 5. Are there any specific topics in Chemistry that are frequently asked in JEE Advanced? |  |
|
347 docs|185 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|

















