Telecommunication | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
Introduction
Telecommunications plays a crucial role in a country's economic and social development. Since the inception of the electric telegraph experiment in India in 1850, the telecommunications sector has evolved significantly. The industry has seen several milestones, including the establishment of regulatory frameworks, the introduction of advanced technologies, and the development of policies to enhance digital connectivity. This overview will explain key aspects of telecommunications, including policies, technologies, and regulatory bodies, in a simplified manner.
National Telecom Policy, 2012
 The Government of India approved the National Telecom Policy, 2012 on May 31, 2012. This policy introduced a unified licensing regime and aimed to enhance telecommunications development.
The Government of India approved the National Telecom Policy, 2012 on May 31, 2012. This policy introduced a unified licensing regime and aimed to enhance telecommunications development.
- Unified License: It authorized the creation of a new licensing framework to streamline and consolidate various telecommunications licenses.
National Digital Communications Policy-2018 (NDCP-2018)

The NDCP-2018 replaced the National Telecom Policy, 2012, aiming to modernize and expand digital communications in India.
- Universal Broadband Connectivity: The policy targets providing universal broadband connectivity at speeds of 50 Mbps to every citizen.
- Gram Panchayats Connectivity: It set goals for providing 1 Gbps connectivity to all Gram Panchayats by 2020 and 10 Gbps by 2022. Current average broadband speeds are around 5-6 Mbps.
- Investment and Skills: The policy aims to attract $100 billion in investments in the digital communications sector and train one million people in new-age skills.
- Internet of Things (IoT): It plans to expand the IoT ecosystem to 5 billion connected devices.
- Data Protection: The policy seeks to establish a comprehensive data protection regime to safeguard privacy, autonomy, and choice, ensuring secure digital communications.
- Telecom Commission Re-designation: The Telecom Commission will be renamed the "Digital Communications Commission" under this policy.
Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI)
TRAI was established on February 20, 1997, through the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India Act, 1997. Its role is to regulate telecom services and set tariffs, which were previously managed by the Central Government.
Telecommunication Dispute Settlement and Appellate Tribunal (TDSAT)
On May 29, 2000, an ordinance amended the TRAI Act to establish TDSAT. This tribunal handles adjudication and disputes related to telecommunications, which were previously under TRAI's jurisdiction.
Generations of Network Technology
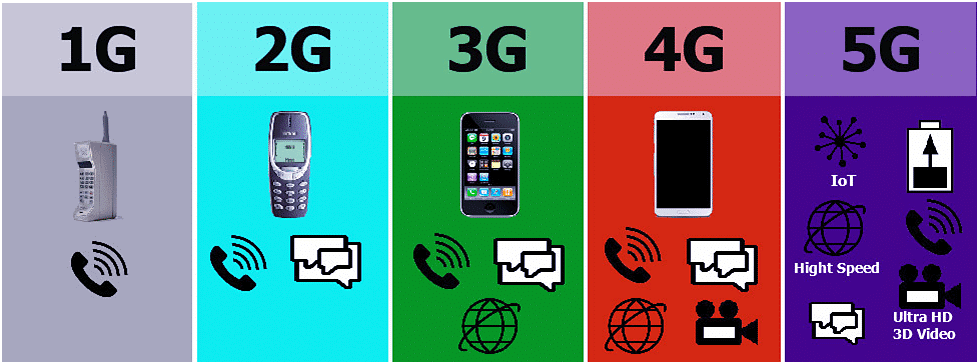
- 1G (First Generation): The initial wireless telephone technology introduced in the 1980s, characterized by analog communication standards.
- 2G (Second Generation): Introduced digital encryption for text messages, enhancing data security and allowing for data transfer.
- 3G (Third Generation): Enabled internet access on mobile phones, including web browsing, video calls, and music downloads.
- 4G (Fourth Generation): Provided high-speed mobile internet with applications such as mobile web access, IP telephony, gaming services, and cloud computing.
- 5G (Fifth Generation): Represents the next major phase in mobile telecommunications, promising even faster speeds and advanced capabilities beyond 4G.
NATGRID (National Intelligence Grid)
- Purpose: NATGRID is designed to integrate and link various government databases to provide comprehensive intelligence patterns. This facilitates better access and coordination for intelligence agencies.
Mobile Telephony
- Definition: Mobile telephony refers to phones that can move freely and connect to terrestrial cellular networks. Unlike satellite phones, which connect to orbiting satellites, mobile phones use base stations or cell sites.
Mobile Surveillance
- Definition: Mobile surveillance involves monitoring phone conversations, tracking locations, and data monitoring. Before mobile phones, similar monitoring was done via wiretapping of phone lines.
Cell Phone/Mobile Phone Jammer
- Definition: A mobile phone jammer is a device used to block cellular signals from reaching base stations, thereby preventing phones from receiving signals.
Bluetooth Technology
- Definition: Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard for short-range data exchange between devices, such as smartphones and computers, creating Personal Area Networks (PANs) with high security.
Channel Access Methods
- Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA): Divides frequency bands among different data streams.
- Wavelength Division Multiple Access (WDMA): Based on wavelength division multiplexing for channel access.
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA): A multi-user version of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) for efficient data transmission.
- Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA): Allocates different time slots to data streams in a repeating cycle.
- Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA): Uses unique codes to allow multiple users to share the same channel.
- Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM): A digital standard replacing the first-generation analog networks, optimized for voice telephony.
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL): A technology that enables digital data transmission over local telephone network wires.
Mobile Operating Systems

- Android: A Linux-based OS developed by the Open Handset Alliance, led by Google. It powers many smartphones and tablets. The latest stable version is Android 10, released on September 3, 2019.
- iOS: Developed by Apple Inc., iOS is a Unix-based operating system derived from OSX. It is designed for Apple's mobile devices.
- Windows Phone: Microsoft's mobile operating system, succeeding Windows Mobile. Windows Phone 8, also known as Apollo, is its second generation.
|
486 videos|1936 docs|395 tests
|
FAQs on Telecommunication - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What is the National Digital Communications Policy-2018 (NDCP-2018)? |  |
| 2. What is the role of the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI)? |  |
| 3. What are the different generations of network technology in telecommunications? |  |
| 4. What are channel access methods in telecommunication networks? |  |
| 5. What are some popular mobile operating systems used in the telecommunications industry? |  |
















