Tenses (काल) | Basic English Grammar for Competitive Exams - Bank Exams PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Types of Tenses |

|
| Rules Related to Tenses |

|
| Functions of Tenses |

|
| Solved Exercises |

|
Introduction
Tenses are the forms that verbs take to indicate the time of an action as well as aspects like completion, continuity, or future intention. When a person speaks a sentence, the verb provides a sense of time, which is referred to as tense (काल).जब एक व्यक्ति कोई वाक्य (Sentence) बोलता है तो उस वाक्य में क्रिया (Verb) से हमें समय (Time) का बोध (Sense) होता है, इसी को काल (Tense) कहते हैं।
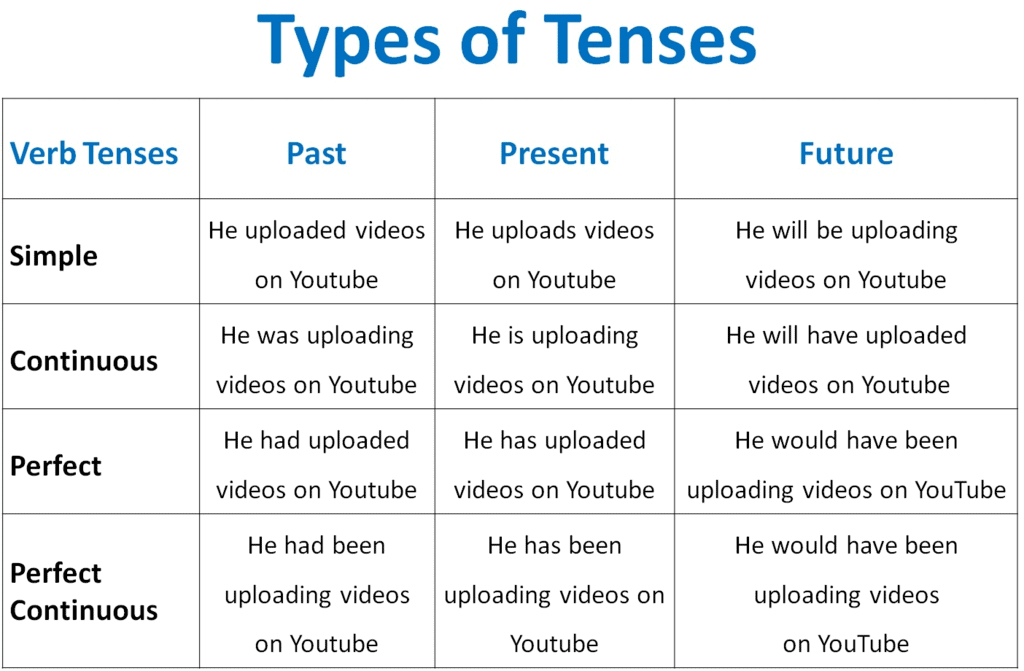
Types of Tenses
1. Present Tense (वर्तमान काल)
It is used to describe actions that are happening currently or habits that are ongoing.a. Simple Present (सामान्य वर्तमान) - Describes general facts or habits.
I eat. (मैं खाता हूँ।)
b. Present Continuous (वर्तमान अव्ययीभाव) - Describes actions that are currently happening.
I am eating. (मैं खा रहा हूँ।)
c. Present Perfect (पूर्ण वर्तमान) - Describes actions that have recently been completed.
I have eaten. (मैंने खा लिया।)
d. Present Perfect Continuous (समाप्त वर्तमान जारी काल)-Describes actions that started in the past and continue to the present.
He/she has been eating (वह खाते/खाती जा रहा/रही है I )
2. Past Tense (भूत काल)
It is used to describe actions that have already happened.a. Simple Past (सामान्य भूत) - Describes actions that happened in the past and are completed.
I ate (मैंने खाया।)
b. Past Continuous (भूत अव्ययीभाव) - Describes actions that were happening in the past.
I was eating. (मैं खा रहा था।)
c. Past Perfect (पूर्ण भूत) - Describes actions that were completed before another action in the past.
I had eaten. (मैंने खा लिया था।)
d. Past Perfect Continuous (समाप्त भूत जारी काल)-Describes actions that were ongoing in the past before another past action.
I had been eating. (मैं खाते/खाती जा रहा/रही था/थी। – I had been eating.)
3. Future Tense (भविष्य काल)
It is used to describe actions that will happen in the future. a. Simple Future (सामान्य भविष्य) - Describes actions that will happen in the future.
I will eat. (मैं खाऊंगा।)
b. Future Continuous (भविष्य अव्ययीभाव) - Describes actions that will be happening in the future.
I will be eating. (मैं खा रहा होऊंगा।)
c. Future Perfect (पूर्ण भविष्य) - Describes actions that will be completed before another action in the future.
I will have eaten. (मैंने खा लिया होगा।)
d. Future Perfect Continuous (समाप्त भविष्य जारी काल)- Describes actions that will have been ongoing before another future action.
I will have been eating. (मैं खाते/खाती जा रहा/रही होऊंगा/होगी। )
Rules Related to Tenses
1. Simple Present Tense: This tense is used to express general truths, habits, or routines. The verb remains in its base form.
- Rule 1: The subject is singular, add 's' or 'es' to the verb.
Example: He works every day. - Rule 2: For plural subjects, or 'I' and 'you,' no change is made to the verb.
Example: They work every day.
2. Present Continuous Tense: This tense indicates an action that is currently happening. The verb is formed by adding 'is/are/am' + present participle (-ing form).
- Rule: Add 'is' for singular subjects, 'are' for plural subjects, and 'am' for 'I.'
Example: She is working. They are working. I am working.
3. Simple Past Tense: This tense expresses actions that have already occurred in the past. The verb is changed to its past form.
- Rule: Regular verbs take '-ed' in the past tense, while irregular verbs have different forms.
Example: She worked yesterday. They ate breakfast.
4. Past Continuous Tense: This tense is used to describe an ongoing action in the past. The verb is formed by adding 'was/were' + present participle (-ing form).
- Rule: Use 'was' for singular subjects and 'were' for plural subjects.
Example: He was working when she called.
5. Simple Future Tense: This tense is used to express actions that have not yet occurred but will happen in the future. The verb is formed using 'will' + base form of the verb.
- Rule: Use 'will' for all subjects.
Example: They will work tomorrow.
6. Future Continuous Tense: This tense indicates an ongoing action that will occur in the future. The verb is formed by adding 'will be' + present participle (-ing form).
- Rule: Use 'will be' for all subjects.
Example: She will be working when you arrive.
7. Present Perfect Tense: This tense is used to describe actions that have been completed at an unspecified time in the past. The verb is formed by adding 'has/have' + past participle.
- Rule: Use 'has' for singular subjects and 'have' for plural subjects.
Example: She has worked here for five years.
8. Past Perfect Tense: This tense is used to describe actions that were completed before another past action. The verb is formed by adding 'had' + past participle.
- Rule: Use 'had' for all subjects.
Example: They had eaten before the movie started.
9. Future Perfect Tense: This tense is used to describe actions that will be completed before another future action. The verb is formed by adding 'will have' + past participle.
- Rule: Use 'will have' for all subjects.
Example: She will have finished her work by the time you arrive.
10. Present Perfect Continuous Tense: This tense is used to describe actions that started in the past and continue to the present. The verb is formed by adding 'has/have' + been + present participle (-ing form).
- Rule: Use 'has been' for singular subjects and 'have been' for plural subjects.
Example: She has been working here for five years.
11. Past Perfect Continuous Tense: This tense is used to describe actions that were ongoing in the past and were completed before another past action. The verb is formed by adding 'had been' + present participle (-ing form).
- Rule: Use 'had been' for all subjects.
Example: They had been waiting for two hours when the bus finally arrived.
12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense: This tense is used to describe actions that will be ongoing in the future and will be completed before another future action. The verb is formed by adding 'will have been' + present participle (-ing form).
- Rule: Use 'will have been' for all subjects.
Example: She will have been working for three hours by the time you arrive.
Functions of Tenses
1. Simple Present Tense (साधारण वर्तमान काल)
- Function: It is used to express a general truth, habitual actions, and present states.
Example: She writes a letter. वह पत्र लिखती है। (Vah patra likhti hai.)
2. Present Continuous Tense (वर्तमान क्रिया प्रवाह काल)
- Function: It is used to express an action that is happening right now, at the moment of speaking.
- Example: She is writing a letter. वह पत्र लिख रही है। (Vah patra likh rahi hai.)
3. Present Perfect Tense (समाप्त वर्तमान काल)
- Function: It is used to describe an action that has recently occurred or just been completed.
- Example: She has written a letter. वह पत्र लिख चुकी है। (Vah patra likh chuki hai.)
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense (समाप्त वर्तमान प्रवाह काल)
- Function: It is used to describe an action that began in the past and is still ongoing.
- Example: She has been writing a letter. वह पत्र लिखते जा रही है। (Vah patra likhte ja rahi hai.)
5. Simple Past Tense (साधारण भूत काल)
- Function: It is used to describe a completed action in the past.
- Example: She wrote a letter. वह पत्र लिखी। (Vah patra likhi.)
6. Past Continuous Tense (भूत क्रिया प्रवाह काल)
- Function: It is used to describe an action that was ongoing in the past.
- Example: She was writing a letter. वह पत्र लिख रही थी। (Vah patra likh rahi thi.)
7. Past Perfect Tense (समाप्त भूत काल)
- Function: It is used to describe an action that was completed before another action in the past.
- Example: She had written a letter. वह पत्र लिख चुकी थी। (Vah patra likh chuki thi.)
8. Past Perfect Continuous Tense (समाप्त भूत प्रवाह काल)
- Function: It is used to describe an action that had been ongoing for some time before another action in the past.
- Example: She had been writing a letter. वह पत्र लिखते जा रही थी। (Vah patra likhte ja rahi thi.)
9. Simple Future Tense (साधारण भविष्य काल)
- Function: It is used to describe an action that will occur in the future.
- Example: She will write a letter. वह पत्र लिखेगी। (Vah patra likhegi.)
10. Future Continuous Tense (भविष्य क्रिया प्रवाह काल)
- Function: It is used to describe an action that will be ongoing in the future.
- Example: She will be writing a letter. वह पत्र लिख रही होगी। (Vah patra likh rahi hogi.)
11. Future Perfect Tense (समाप्त भविष्य काल)
- Function: It is used to describe an action that will be completed before another action in the future.
- Example: She will have written a letter. वह पत्र लिख चुकी होगी। (Vah patra likh chuki hogi.)
12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense (समाप्त भविष्य प्रवाह काल)
- Function: It is used to describe an action that will have been ongoing for some time before another action in the future.
- Example: She will have been writing a letter. वह पत्र लिखते जा रही होगी। (Vah patra likhte ja rahi hogi.)
Solved Exercises
1. Present Simple Tense:
Exercise: Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb in brackets.
(a) She always _______ (drink) coffee in the morning.
She always drinks coffee in the morning.
We use the present simple tense for habits and routines. The verb "drink" is changed to "drinks" because it is the third person singular (she).
(b) They _______ (live) in London.
They live in London.
We use the present simple tense for facts and general truths. The verb "live" remains the same because it's in the plural form (they).
(c) He _______ (work) as a teacher.
He works as a teacher.
We use the present simple tense for occupations. The verb "work" is changed to "works" because it is the third person singular (he).
2. Past Simple Tense:
Exercise: Rewrite the sentences in the past simple tense.
(a) She eats pizza.
She ate pizza.
We change the verb "eats" to its past simple form "ate" to show that the action happened in the past.
(b) They travel to Paris.
They traveled to Paris.
We change the verb "travel" to its past simple form "traveled" to show that the action happened in the past.
(c) He writes a letter.
He wrote a letter.
We change the verb "writes" to its past simple form "wrote" to show that the action happened in the past.
3. Present Continuous Tense:
Exercise: Change the sentences into the present continuous tense.
(a) She reads a book.
She is reading a book.
We change the verb "reads" to its present continuous form "is reading" to show that the action is happening now.
(b) They play football.
They are playing football.
We change the verb "play" to its present continuous form "are playing" to show that the action is happening now.
(c) He cooks dinner.
He is cooking dinner.
We change the verb "cooks" to its present continuous form "is cooking" to show that the action is happening now.
4. Past Continuous Tense:
Exercise: Complete the sentences with the past continuous form of the verbs in brackets.
(a) She ________ (watch) TV when the phone rang.
She was watching TV when the phone rang.
We use the past continuous tense to show that an action was in progress when another action occurred. The verb "watch" is changed to "was watching" to show the past continuous tense.
(b) They ________ (eat) dinner when the guests arrived.
They were eating dinner when the guests arrived.
We use the past continuous tense for actions that were happening when another action occurred. The verb "eat" is changed to "were eating" to show the past continuous tense.
(c) He ________ (drive) when it started to rain.
He was driving when it started to rain.
We use the past continuous tense for actions that were happening when another action occurred. The verb "drive" is changed to "was driving" to show the past continuous tense.
|
40 videos|97 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Tenses (काल) - Basic English Grammar for Competitive Exams - Bank Exams
| 1. Tenses क्या होते हैं और इन्हें क्यों सीखना जरूरी है? |  |
| 2. Tenses के कितने प्रकार होते हैं? |  |
| 3. Tenses के नियम क्या हैं? |  |
| 4. Tenses का उचित उपयोग कैसे किया जा सकता है? |  |
| 5. क्या Tenses से संबंधित कोई अभ्यास उपलब्ध है? |  |




















