Testes, Ovaries & Other Hormone Secreting Organs | Biology for JAMB PDF Download
Other Organs Which Secrete Hormones
(A) Kidney :– Main function of kidney is excretion, but it secretes some hormones also. These are as follows :-
1. Renin :– It is secreted by Juxtamedullary nephron. Renin hormone acts as protein digesting enzyme.
It digests a plasma protein called Angiotensinogen and converts it into Angiotensin-II.
- Renin hormone increases reabsorption of water and Na+ ions in uriniferous tubules.
- It stimulates the secretion of aldosterone hormone from adrenal cortex.
2. Erythrogenin :– The hormone reacts with plasmaprotein (Globulin) and forms a new hormone erythropoietin.
Erythropoietin stimulates bone marrow to form RBCs.
3. Renomedullary prostaglandins :– It is the most active renal hormone. It makes relaxation in unstriated muscles of blood vessels of kidneys. It enhances the excretion of Na+ ions by urine (diuretic effect), renal vasodilation & decreases tubular reabsorption.
(B) Skin :– Due to the effect of ultraviolet rays of sunlight steroids like argosterol and cholesterol are changed into argocalciferol and cholecalciferol vitamin D respectively in the skin, it reaches to its target organ by blood stream.
- Vit. D is supposed to be a hormone. It acts as a co hormone with parathormone.
- It helps in bone formation and teeth formation. It increases the absorption of calcium and phosphorus by intestine.
- 'Rickets' disease is observed in children due to the deficiency of vitamin D as a result of which bones become weak, thin, deshaped and ugly.
- In adulthood, its deficiency causes Osteomalacia. Bones become weak and brittle.
(C) Gonads :–
(i) Testes (Male gonad) :–
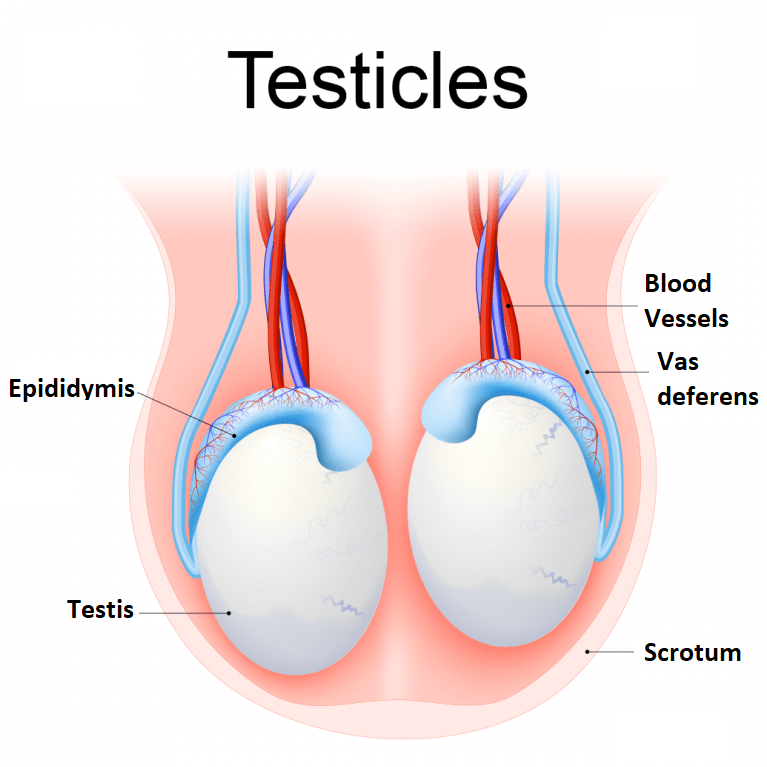
- Leydig's cells or Interstitial cells of connective tissue of seminiferous tubules of testes secrete male hormones androgens.
- Main androgens are testosterone and androsterone.
- These are steroid in nature.
- Testes also secrete inhibin/activin.
WORKS OF TESTOSTERONE
- Testosterone is the main androgen (30 to 100 ng/ml).
- This Hormone stimulates the development of secondary sex organ. Such as epididymus, vas deferens, seminal vesicle.
- This Hormone stimulates the number of sebaceous gland on the face which causes Acne & pimples.
- It increases the development of beard & moustache.
- It also stimulates the growth of hair on the upper limb, lower limb, thoracic, abdominal part, armpits & near to the external genital organ.
(ii) Ovary (Female gonad) :–
- Estrogen/Oestrogen :– The hormone is secreted by the inner layer - theca interna of graafian follicles . Estrogen includes estradiol, estrone and estriol.
- Estrogen is steroid in nature.
- This Hormone stimulates the development of sec. organ such as fallopian tube, uterus, vagina.
- Promotes the development of mammary gland.
- It develops the high pitch of voice which is also called as FEMININE voice.
- This Hormone removes the hair from face, upper & lower limb, thorax & abdominal part. But stimulates growth of hair near the external genetial organ & armpits.
- It also develops the growth of skeletal muscle & bone.
- It increase the diameter of pelvic bone.
- It stimulates the blood formation but decreases the cholesterol level in the blood. It stimulates the rate of growth of hair of head.
- It also changes the sexual behaviour, means attraction towards the male.
Corpus Luteum :– (Temporary endocrine gland).
After ovulation graafian follicle changed into a yellow gland in the ovary, it is called corpus luteum. Regulation and control of its production is done by LH. Corpus luteum is an endocrine gland. Following are the hormones secreted by this.
(1) Progesterone :–
- The hormone stimulates the developmental characters of pregnancy.
- Due to the effect of this hormone, uterine wall endometrium become thick and blood circulation is increased in it. Fats and glycogen are deposited in its cells.
- Mammary glands become highly developed, as a result of this breasts become enlarged.
- It helps in implantation of embryo in the uterine wall.
- The hormone maintains pregnancy, so it is also called "Pregnancy hormone" Progesterone inhibits the contractions in uterine wall muscles, so it is also called "anti abortion hormone".
(2) Relaxin :– Perhaps corpus luteum also secretes it, but it is secreted at the end of pregnancy/gestation period.
(3) Estrogen
(4) Inhibin
(D) Placenta :– (Temporary endocrine gland).
Placenta connects the embryo and uterus of mother at the time of embryo development. It secretes some hormones –
(i) Chorionic gonadotropin hormone (CGH) OR Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) It is a protein hormone. It helps to maintain the pregnancy and controls the secretory action of corpus luteum.
- At the initial stage of pregnancy CGH or HCG is secreted in excess amount by placenta and it is excreted by urine. At this stage presence of CGH of HCG in the urine is tested by urine test.
- It is a positive test for pregnancy. (Gravidex test)
- HCG or CGH is tested in urine test for pregnancy test.
(ii) Placental lactogen or human chorionic somatomammotropin :– It is also a protein hormone, and stimulates the mammary glands for milk production.
(iii) Estrogen :– It is a steroid, It controls extra development of breast during pregnancy.
(iv) Progesterone :– It is also a steroid. It controls the slow action of slowly abolishing corpus luteum and maintains the pregnancy.
(v) Relaxin :- It is a protein hormone. At the time of parturition, it helps to expand the pubic symphysis of pelvic girdle to facilitate the child birth in females.
Hormones which always remain in tissue fluid :– There are some hormones which never reach upto blood stream but always remain in ECF.
These are as follows :-
(1) Neurohormone :– These are secreted in the nodes of axons of nerve cells. Acetylcholine and Norepinephrine are the main neurohormones.
(2) Prostaglandin :– These are fatty acids. These are most active substances among all the known substances.
- Prostaglandin are of so many types. Kidneys, gonads, seminal vesicles, thymus, brain etc. organs and their cells secrete these hormones in ECF.
- These prostaglandins are first of all observed in semen of man. These stimulate contraction of unstriated muscles.
- These prostaglandins are secreted by seminal vesicles and reach upto vagina of female through semen of male, and then these activate the muscles of uterus of female.
(3) Kinins :– These are chemicals which are secreted by any organ of body at the time of chemical change in ECF, and reduce the B.P. by expanding blood vessels. These also reduce the time of blood clotting.
Kinins are also called as "Firstaid hormone".
(4) Pheromones or Ectohormones :–
- The term "Pheromone" was coined by Karlson and Butenandt.
- These are secreted by exocrine glands. These are also called "Samio- chemical".
- These chemicals are secreted by animals and effect the other animal's behaviour and mode of life of the same species.
- Just like hormones, their target place is far from place of origin.
- first of all, pheromone Bombicol was studied. It is pheromone of silk moth. Pheromones are volatile in nature, and travel through air from place to place.
Pheromones are of 3 types :-
(1) Sex - Pheromone :– These attract male and female animals for reproduction. Female silk moth secretes Bombicol or Gyplure from its body which attracts male for mating.
(a) Muskone :– It is secreted by Musk - deers.
(b) Civetone :– It is secreted by cats.
(2) Aggregation pheromone :– This pheromone is secreted by one member of social insects and pheromone sends messages to other members of that society. Thus helps in aggregation. e.g. :- Geradial pheromone in honeybee.
(3) Alarm pheromones :– These pheromones are secreted by one member of the insect species and alarm the other members of the same species. e.g :- Secretion of formic acid in ants insects etc.
SPECIAL POINT
- Heterocrine gland :- These are those endocrine glands which are involved in hormone secretion as well as some other function eg. pancreas, gonads, placenta, GI mucosa and kidneys.
- In females prolactin induce maternalism i.e. strong emotional attachment.
- In male prolactin promotes paternalism i.e. protective attitudes towards family members and intensive food gathering for the family.
- Contrary to thyroid dwarf (cretins), the pituitary dwarf have a normal mental development and proportionate body.
- Sporadic cases of simple goitre (sporadic goitre) in a population are normally due to genetic defect.
- Muller organ and subneural gland is homologous to pituitary gland.
- Tropic hormone :- A hormone which stimulates another endocrine gland to secrete its hormone is called trophic hormone.
- Simmond's disease :- This condition is due to atrophy of the anterior lobe of pituitary gland.
- Pheochromocytoma :- It is due to hypersecretion of adrenaline causes, high blood pressure, high level of sugar in blood and urine, high metabolic rate, nervousness and sweating.
- True sexual precocity :- True sexual precocity is early maturation of ovaries and testes with production, of ova before the age of 9 years in girls, or sperm before 10 years in boys, occurs without evident cause.
- Sexual pseudoprecocity results from adrenal cortex, testes, ovary or from other sources, including extragonadial tumours.
- Eunuchoidism :- Failure of testosterone secretion in male causes eunuchoidism.
(A) Eunuch has an undeveloped secondary sex organs like prostrate, seminal vesicle and penis
(B) lacks external sex character such as beard, moustache and low pitch and
(C) does not produce sperm.
- Growth hormone :- Stimulate the liver to form "Somatomedins" ("Insulin like growth factors"). This somatomedins potent effect to bone growth.
- In heart CGMP has antagonistic effect to CAMP, CAMP mediate muscle contraction in response to adrenaline, while CGMP slow down muscle contraction is response to acetylcholine (NCERT).
- CGMP used in second messanger in atrial natriuretic peptide and nitric oxide.
|
225 videos|175 docs|156 tests
|
FAQs on Testes, Ovaries & Other Hormone Secreting Organs - Biology for JAMB
| 1. What are the functions of the testes in the male reproductive system? |  |
| 2. What are the functions of the ovaries in the female reproductive system? |  |
| 3. How do the hormones secreted by the ovaries and testes affect the body? |  |
| 4. Can hormonal imbalances in the testes and ovaries lead to health problems? |  |
| 5. How can one maintain hormonal balance in the testes and ovaries? |  |

















