Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Class 7 Oxford Science: Chapter Notes, Worksheets & Tests > Textbook Solution: Heat and Temperature
Textbook Solution: Heat and Temperature | Class 7 Oxford Science: Chapter Notes, Worksheets & Tests PDF Download
A. Choose the correct option.
1.
Ans: (c)
2.
Ans: (b)
3.
Ans: (b)
4.
Ans: (a)
5.
Ans: (a)
6.
Ans: (b)
7.
Ans: (a)
B. Match the following.
1.
Ans: 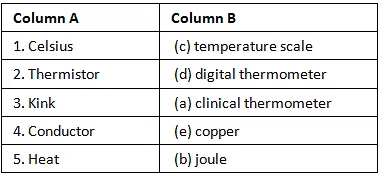
C.
1.
Ans:
1. Temperature (It is a measure, not a mode of heat transfer like the rest)
2. Kink (It is a part of a thermometer, not a substance or a measure like the rest)
3. Wood (It is an insulator, not a conductor like the rest)
4. Celsius (It is a unit of temperature, not of energy like the rest)
D. Answer the following questions.
1.Ans:
(a) Temperature scales: Temperature scales are units for measuring temperature. The most commonly used temperature scales are the Celsius scale and the Fahrenheit scale. In the Celsius scale, the melting point of ice is taken as 0°C and the boiling point of water as 100°C. In the Fahrenheit scale, the melting point of ice is taken as 32°F and the boiling point of water as 212°F.
(b) Modes of heat transfer: The processes by which heat is transferred are called modes of heat transfer. There are three modes of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction is the primary mode of heat transfer in solids and occurs when two bodies are in contact. Convection is the primary mode of heat transfer in air and water, and other liquids and gases. Radiation is the mode of heat transfer that can occur through vacuum or through any medium.
(c) Heat energy: The type of energy that flows from a hot body to a cold body is called heat or heat energy. Heat energy always travels from a body at a higher temperature to a body at a lower temperature.
(d) Radiation of heat: Heat energy from the sun reaches the Earth by a form of heat transfer known as radiation. All warm bodies give out heat energy in the form of radiation, even human beings.
(e) Clinical thermometer: A clinical thermometer is used to measure body temperature. It has a kink present near the bulb which prevents the mercury in the tube from contracting and flowing back into the bulb before the temperature is read.
2.
Ans:
The conversion formula from Celsius to Fahrenheit is F = (C × 9/5) + 32.
(a) 55°C = (55 × 9/5) + 32 = 131°F
(b) 100°C = (100 × 9/5) + 32 = 212°F
(c) 0°C = (0 × 9/5) + 32 = 32°F
(d) 20°C = (20 × 9/5) + 32 = 68°F
3.
Ans:
The conversion formula from Fahrenheit to Celsius is C = 5/9 (F-32).
(a) 58°г = Not applicable as this isn't a recognized temperature scale.
(b) 75°F = 5/9 (75-32) = 24°C
(c) 5°F = 5/9 (5-32) = -15°C
(d) 140°F = 5/9 (140-32) = 60°C
4.
Ans:
(a) Celsius scale: There are 100 divisions between the melting point of ice and the boiling point of water.
(b) Fahrenheit scale: There are 180 divisions between the melting point of ice and the boiling point of water.
5.
Ans: Reading a clinical thermometer correctly involves the following steps:
- Wash the thermometer with antiseptic liquid before and after use.
- Hold the thermometer by the end opposite the bulb.
- Read the temperature by the height of the thin line of mercury or alcohol inside the tube, which expands and rises with temperature.
- Ensure to read the thermometer at eye level and straight on.
6.
Ans:
- Conduction: It is the primary mode of heat transfer in solids and happens when two bodies are in contact. For example, when a spoon is left in a hot soup, it gets hot due to conduction.
- Convection: It is the primary mode of heat transfer in liquids and gases. For example, when heating water in a pot, the water at the bottom gets hot first and rises, allowing the cooler water to sink and get heated. This cycle continues until all the water is heated.
- Radiation: It is the mode of heat transfer that can occur through vacuum or through any medium. For example, we feel heat from the sun even though it is far away because heat is transferred through radiation.
7.
Ans: Sea breeze and land breeze are set up due to the uneven heating of land and water. During the day, the sun heats up the land faster than water. As a result, the warm air above the land rises and the cooler air above the sea rushes in to replace it, creating a sea breeze. At night, the land cools down faster than the sea. The air above the land becomes cooler than the air above the sea and moves towards the sea, creating a land breeze.
The document Textbook Solution: Heat and Temperature | Class 7 Oxford Science: Chapter Notes, Worksheets & Tests is a part of the Class 7 Course Class 7 Oxford Science: Chapter Notes, Worksheets & Tests.
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
139 videos|151 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Textbook Solution: Heat and Temperature - Class 7 Oxford Science: Chapter Notes, Worksheets & Tests
| 1. What is the difference between heat and temperature? |  |
Ans. Heat is the energy transferred between objects due to a temperature difference, while temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance.
| 2. How is heat transferred between objects? |  |
Ans. Heat can be transferred through conduction (direct contact), convection (through fluids like air or water), or radiation (through electromagnetic waves).
| 3. How does temperature affect the behavior of particles in a substance? |  |
Ans. As temperature increases, the particles in a substance move faster, leading to expansion and changes in state (solid to liquid, liquid to gas).
| 4. What is specific heat capacity and how does it relate to heat transfer? |  |
Ans. Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius. It determines how easily a substance can absorb or release heat.
| 5. How does insulation help in maintaining temperature in buildings? |  |
Ans. Insulation reduces heat transfer by trapping air and preventing it from moving, thus helping to maintain a consistent temperature inside buildings.
Related Searches
















