The Battle of Buxar (1764) | SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year PDF Download
INTRODUCTION
With the advent of Europeans in India, the British East India Company gradually conquered Indian territories. The Battle of Buxar is one such confrontation between the British army and their Indian counterparts which paved the way for the British to rule over India for the next 183 years.
BATTLE OF BUXAR
It was a battle fought between the English Forces, and a joint army of the Nawab of Oudh, Nawab of Bengal, and the Mughal Emperor. The battle was the result of misuse of trade privileges granted by the Nawab of Bengal and also the colonialist ambitions of East India Company. Battle of Buxar
Battle of Buxar
BACKGROUND OF THE BATTLE OF BUXAR
Before the battle of Buxar, one more battle was fought. It was the Battle of Plassey, that gave the British a firm foothold over the region of Bengal. As a result of the Battle of Plassey, Siraj-Ud-Daulah was dethroned as the Nawab of Bengal and was replaced by Mir Jafar (Commander of Siraj’s Army.) After Mir Jafar became the new Bengal nawab, the British made him their puppet but Mir Jafar got involved with Dutch East India Company. Mir Qasim (son-in-law of Mir Jafar) was supported by the British to become the new Nawab and under the pressure of the Company, Mir Jafar decided to resign in favour of Mir Kasim. A pension of Rs 1,500 per annum was fixed for Mir Jafar.
A few reasons which were the key to the Battle of Buxar are given below:
- Mir Qasim wanted to be independent and shifted his capital to Munger Fort from Calcutta.
- He also hired foreign experts to train his army, some of whom were in direct conflict with the British.
- He treated Indian merchants and English as same, without granting any special privileges for the latter.
- These factors fuelled the English to overthrow him and war broke out between Mir Kasim and the Company in 1763.
COMBATANTS OF THE BATTLE OF BUXAR
The table below will inform the participants of the battle of Buxar and their significance on the battle:
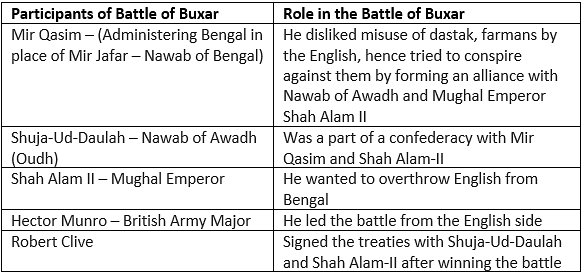
[Question: 962059]
COURSE OF BATTLE OF BUXAR
Mir Qasim's Retreat:
- In 1763, as the Battle of Buxar broke out, Mir Qasim faced successive defeats at Katwah, Murshidabad, Giria, Sooty, and Munger against the English.
- Fleeing from Bengal, Mir Qasim sought refuge in Awadh (Oudh).
Formation of Confederacy:
- In Awadh, Mir Qasim formed a confederacy with Shuja-Ud-Daulah (Nawab of Awadh) and Shah Alam II (Mughal Emperor).
- Their collective aim was to overthrow the English and regain control of Bengal.
Engagement with English Forces:
- In 1764, Mir Qasim's forces engaged with the English army led by Major Munro.
- The joint armies of Mir Qasim confronted the British troops in a bid to reclaim Bengal.
Defeat of the Confederacy:
- The battle concluded with the defeat of the confederate forces by the British.
- While engaged in the conflict, Mir Qasim absconded from the battlefield, leaving his soldiers defeated.
Surrender and Conclusion:
- In the aftermath, the Nawab of Awadh, Shuja-Ud-Daulah, and the Mughal Emperor, Shah Alam II, surrendered to the English army.
- The Battle of Buxar concluded with the surrender of the confederate leaders.
Treaty of Allahabad (1765):
- The Battle of Buxar paved the way for the Treaty of Allahabad in 1765.
- As a result, the defeated leaders ceded significant territories to the British, marking a crucial turning point in the consolidation of British power in India.
RESULT OF BATTLE OF BUXAR
Outcome (October 22, 1764):
- The Battle of Buxar, fought on October 22, 1764, concluded with the defeat of the joint forces led by Mir Qasim, Shuja-Ud-Daula, and Shah Alam-II.
Decisive Victory by Major Hector Munro and Robert Clive:
- Major Hector Munro played a crucial role as the British military commander, securing a decisive victory.
- Robert Clive, a prominent British military and political figure, contributed significantly to the English triumph, ensuring success on the battlefield.
English Ascendancy in Northern India:
- The Battle of Buxar played a pivotal role in establishing English ascendancy in northern India.
- The victory solidified British influence and marked them as a dominant power in the region.
Territorial Concessions and Trade Privileges:
- Mir Jafar, the Nawab of Bengal, conceded key districts like Midnapore, Burdwan, and Chittagong to the English.
- In return for these territorial gains, the English were granted significant trade privileges, including duty-free trade in Bengal with a nominal duty of two percent on salt.
Controlled Administration under Najimud-Daula:
- Following Mir Jafar's death, his minor son, Najimud-Daula, assumed the position of Nawab.
- Despite his nominal rule, actual administrative power remained in the hands of the naib-subahdar, who could be appointed or dismissed by the English.
Political Settlements in the Treaty of Allahabad:
- Robert Clive conducted political negotiations with Emperor Shah Alam II and Shuja-Ud-Daula of Awadh.
- The Treaty of Allahabad, resulting from these negotiations, outlined significant agreements that shaped the political dynamics in the region, solidifying English influence and control.
TREATY OF ALLAHABAD (1765)
Treaty Between Robert Clive & Shuja-Ud-Daulah:
Surrender of Allahabad and Kara:
- Context: Shuja-Ud-Daulah, the Nawab of Awadh, had allied with Shah Alam II and Mir Qasim to challenge the British.
- Allahabad and Kara, two crucial strategic locations, were surrendered to Shah Alam II by Shuja-Ud-Daulah.
War Indemnity Payment:
- Context: The conflict preceding the treaty involved the Battle of Buxar, where the British, led by Major Hector Munro, emerged victorious.
- Shuja-Ud-Daulah was compelled to pay a war indemnity of Rs 50 lakh to the East India Company as compensation for the expenses incurred during the war.
Granting Full Possession to Balwant Singh:
- Context: Balwant Singh, the Zamindar of Banaras, was an important local figure.
- Shuja-Ud-Daulah agreed to ensure that Balwant Singh gained full possession of his estate in Banaras, possibly as a gesture of local political reorganization.
Treaty Between Robert Clive & Shah Alam-II:
Residence at Allahabad:
- Context: The treaty aimed to establish the position and residence of Shah Alam II, the Mughal Emperor.
- Shah Alam II was directed to reside at Allahabad, and the East India Company provided protection to the emperor within this arrangement.
Diwani of Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa:
- Context: The treaty marked a significant shift in the economic control of the specified provinces.
- Shah Alam II issued a Farman, granting the Diwani rights (revenue and civil jurisdiction) of Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa to the East India Company.
Annual Payment and Nizamat Functions:
- Context: The financial arrangements aimed to secure the Company's economic interests and control over administrative functions.
- Shah Alam II agreed to make an annual payment of Rs 26 lakh to the East India Company for the Diwani rights.
- An additional payment of Rs 53 lakh was agreed upon for the Nizamat functions, including military defence, police, and administration of justice in the specified provinces.
The Treaty of Allahabad consolidated the East India Company's authority over key regions and economic matters. It significantly influenced the power dynamics in colonial India, establishing a framework for British control over revenue, administration, and territorial arrangements.
 Treaty of Allahabad
Treaty of Allahabad
KEY - FACTS ABOUT BATTLE OF BUXAR
- After the Battle of Buxar, English did not annex Awadh even after Shuja-Ud-Daulah was defeated because it would have placed the Company under an obligation to protect an extensive land frontier from the Afghan and the Maratha invasions.
- Shuja-Ud-Daulah became a firm friend of British and made Awadh a buffer state between English and foreign invasions.
- The treaty of Allahabad with Mughal Emperor Shah Alam-II made emperor a useful ‘Rubber stamp’ of the Company. Besides, the emperor’s Farman legalised the political gains of the Company in Bengal.
|
1365 videos|1312 docs|1010 tests
|
FAQs on The Battle of Buxar (1764) - SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year
| 1. What was the significance of the Battle of Buxar? |  |
| 2. Who were the combatants in the Battle of Buxar? |  |
| 3. How did the Battle of Buxar unfold? |  |
| 4. What were the outcomes of the Battle of Buxar? |  |
| 5. How did the Treaty of Allahabad impact British control over India? |  |
|
1365 videos|1312 docs|1010 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for SSC CGL exam
|

|


















