The Cell | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Cell Theory |

|
| Basic Types of Cells |

|
| Cell Cycle and Cell Division |

|
Introduction
- In 1665, English scientist Robert Hooke observed small chamber-like structures in cork, which he called "cells."
- A cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of all living organisms.
- Some organisms are unicellular (made up of a single cell), while others, like humans, are multicellular (composed of billions of cells).
- All cells have three basic structures: the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus.
- These structures are living components.
- The combined content of the cytoplasm and nucleoplasm inside the cell is called protoplasm, known as the physical basis of life.
- The non-living inclusions within a cell are collectively referred to as deutoplasm.
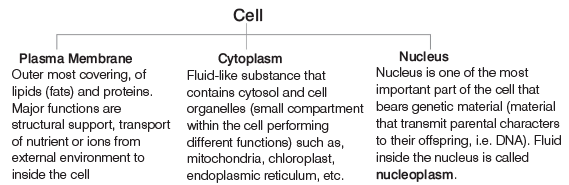
These differences can be easily visualised by the following diagrams
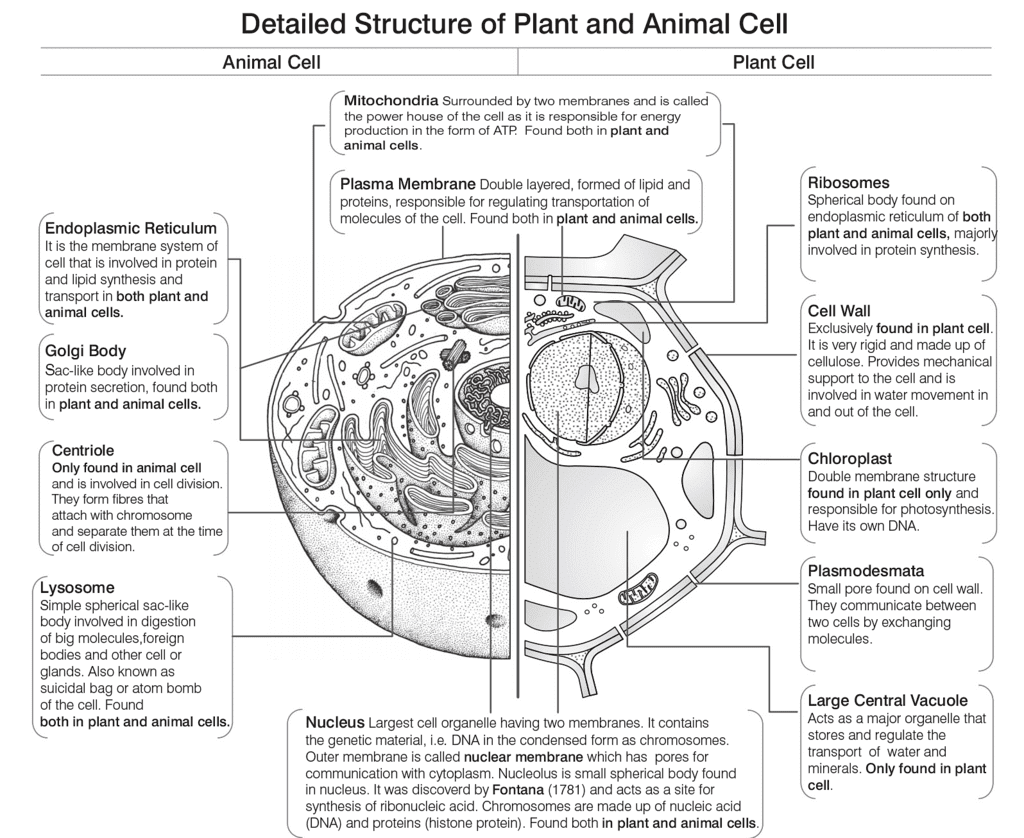
Cell Theory
German botanist M. Schleiden and British zoologist T. Schwann formulated the cell theory, with contributions from Rudolf Virchow. The main principles of cell theory are:
- All living organisms are composed of cells and their products.
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells (Omnis cellula e cellula).
- Cells are the basic building units of life.
However, viruses do not follow cell theory. Plant cells differ from animal cells in several ways.
In 2016, the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Japanese cell biologist Yoshinori Ohsumi for his work on autophagy, the process by which cells destroy and recycle cellular components using lysosomes.
Basic Types of Cells
There are two primary types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic.
Differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
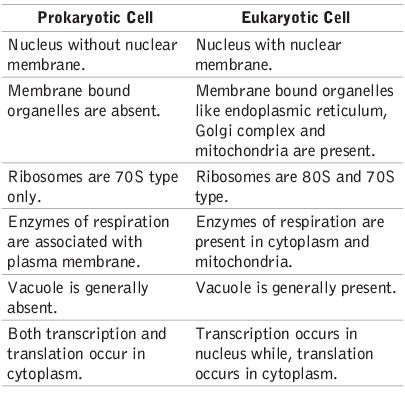
Chromosomes
- Chromosomes are the condensed form of DNA, facilitated by special proteins called histones.
- When DNA is not condensed, it is referred to as chromatin.
- During cell division, chromosomes display chromatids held together at a point called the centromere.
- The ends of chromosomes are called telomeres.
- Based on the position of the centromere, chromosomes can be metacentric (centered), submetacentric (slightly off-center), acrocentric (near the end), or telocentric (at the end).
Types of Chromosomes
- Lampbrush Chromosomes: Discovered by Balbiani in 1882, resembling a lamp brush.
- Polytene Chromosomes: Discovered by Balbiani in 1881 in the salivary glands of Chironomus larvae.
Genes
- Chromosomes contain genes, which act as units of inheritance, controlling the transfer of genetic information from one generation to the next.
Karyotype and Idiogram
- A karyotype refers to the number and appearance of chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. It can also refer to the complete set of chromosomes. An idiogram is a diagrammatic representation of the chromosomes of a species or population.
Cell Cycle and Cell Division
The cell cycle is an ordered set of stages for cell growth and division into daughter cells.
The stages are as follows:- G1 (Gap 1)
- S (Synthesis, where DNA replication occurs)
- G2 (Gap 2)
- M (Mitosis, or division phase)
During the M-stage, the nucleus divides (karyokinesis), followed by the division of the cytoplasm (cytokinesis). Cells that do not re-enter the cell cycle remain in the G0 stage (quiescent stage).
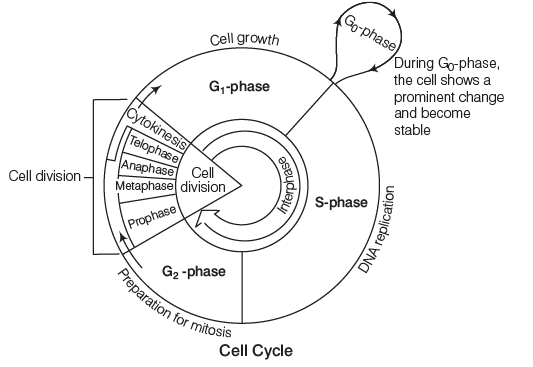
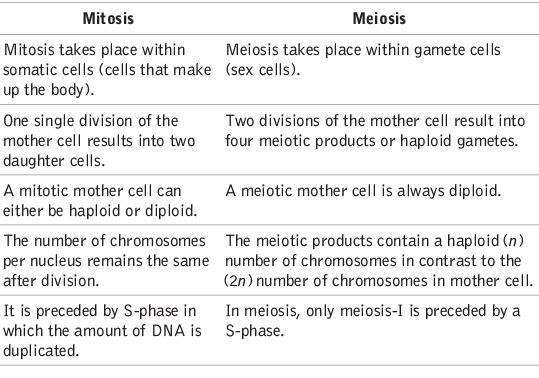
There are two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis.
Major differences between Mitosis and Meiosis
 Transcriptome
Transcriptome
A transcriptome is the full range of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules expressed by an organism. It describes the array of mRNA transcripts produced in a particular cell or tissue.
|
528 videos|2113 docs|339 tests
|
FAQs on The Cell - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What is the Cell Theory? |  |
| 2. What are the basic types of cells? |  |
| 3. What is the Cell Cycle and Cell Division? |  |
| 4. How does the process of cell division contribute to growth and repair in multicellular organisms? |  |
| 5. What are the key differences between mitosis and meiosis in cell division? |  |




















