The Four Aims of Human Life | Religion, Philosophy & Ethics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| The Four Aims of Human Life |

|
| Dharma |

|
| Kama |

|
| Artha |

|
| Moksha |

|
| Summary Table of the Four Aims |

|
| What is Dharma? |

|
| The Four Stages of Life (Ashramas) |

|
| Types of Dharma |

|
The Four Aims of Human Life
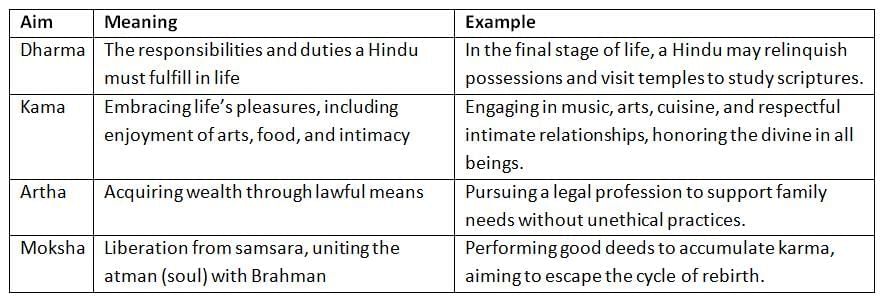
In Hinduism, the purpose of life is to pursue four key goals, known as Purusharthas. These aims guide Hindus toward a moral and ethical existence, fostering a fulfilling life. The four aims are Dharma, Kama, Artha, and Moksha. By adhering to these principles, Hindus seek to live virtuously, accumulate good karma, and ultimately break free from the cycle of samsara (rebirth) to attain spiritual liberation.
Dharma
- Dharma represents an individual’s true purpose, encompassing their duties and the actions they undertake to live righteously.
- Each Hindu has a personal dharma, unique to their life circumstances, which emphasizes making morally sound decisions.
- This pursuit of righteous living helps generate good karma, which is essential for escaping the cycle of samsara.
Kama
- Kama refers to love, desire, and pleasure, forming a practical aspect of Hindu life. Hindus seek pleasure through various avenues, such as sports, cultural activities, and notably, sexual enjoyment, which is considered a natural human instinct.
- Kama, particularly in the context of intimate relationships, is valued as it fosters connection and leads to procreation.
- Hinduism, being a practical religion, embraces kama as an integral part of personal life.
Artha
- Artha signifies prosperity and the pursuit of material wealth. For many Hindus, acquiring wealth is a legitimate goal, as it supports their journey toward moksha.
- However, attachment to material possessions is discouraged, as true liberation requires detachment from worldly concerns. While only a few may forgo material wealth entirely, most Hindus view artha as a necessary component of a balanced life.
Moksha
- Moksha is the ultimate goal of Hindu life, representing liberation from the cycle of samsara and union with Brahman, the divine essence. Achieving moksha requires accumulating good karma through virtuous actions in both past and present lives.
- By consistently making ethical choices, Hindus work toward breaking free from the cycle of rebirth, attaining spiritual salvation.
Summary Table of the Four Aims
What is Dharma?
- Dharma encompasses the duties a Hindu must perform, which vary based on their family background, occupation, and stage of life. It includes worshipping God, performing one’s job diligently, practicing non-violence toward people and animals, and maintaining honesty.
- Hindus are encouraged to prioritize their duty to act ethically over chasing material wealth or fleeting pleasures. The Katha Upanishad (2.1-2) emphasizes this: “There is the path of joy, and there is the path of pleasure.
- Both attract the soul. Who follows the first comes to good; who follows pleasure reaches not the End. The two paths lie in front of man. Pondering on them, the wise man chooses the path of joy; the fool takes the path of pleasure.”
The Four Stages of Life (Ashramas)
Hinduism outlines four stages of life, known as ashramas, each with specific duties and samskaras (rites of passage). These stages guide Hindus in fulfilling their dharma and earning good karma.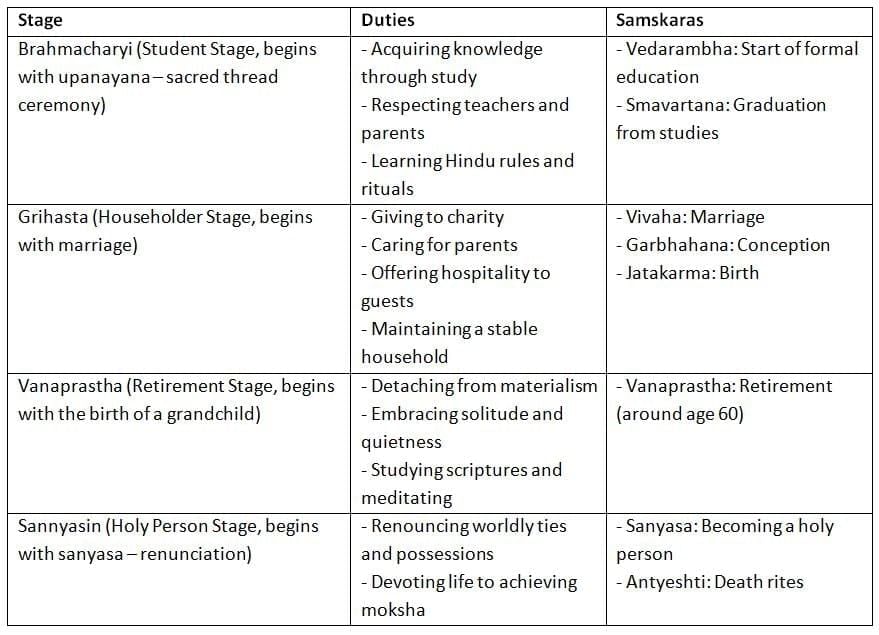
By following the duties and samskaras of each ashrama, Hindus align with their dharma, fostering good karma and progressing toward moksha.
Types of Dharma
Dharma varies depending on an individual’s circumstances, including their stage of life and social role. There are personal and universal duties that guide Hindu life.
Sanatana Dharma
Sanatana dharma, meaning “eternal truth,” is a universal principle applicable to all people at all times. Many Hindus prefer this term over “Hinduism,” as it encapsulates their core beliefs. Following sanatana dharma involves:
- Living ethically and making moral choices.
- Engaging in worship and prayer to stay connected with God.
- Studying scriptures to deepen understanding of Hindu teachings.
- Striving for moksha, the ultimate liberation from samsara.
- Caring for all living beings, including plants, animals, and the environment.
- Supporting those in need with compassion and respect.
Varnashrama Dharma
Varnashrama dharma refers to personal duties based on an individual’s stage of life (ashrama) and caste (varna). In traditional Hindu society, caste determines roles and responsibilities, with four main castes and numerous sub-castes (jatis):
- Teachers and priests (head): Closest to achieving moksha, they guide spiritual learning.
- Warriors and leaders (upper body): Protect and govern society.
- Merchants, traders, and farmers (legs): Support economic stability.
- Manual workers and laborers (feet): Provide essential services.
The Rig Veda likens society to a human body, with each group contributing to its functioning. However, the caste system, particularly the exclusion of Dalits (over 15% of India’s population), is controversial. Dalits, meaning “the broken” or “oppressed,” are outside the caste system and have faced discrimination, though laws in India now prohibit employment discrimination. Despite this, caste-based inequalities persist, raising human rights concerns about fairness and equality.
|
172 docs|3 tests
|














