Delhi Police Constable Exam > Delhi Police Constable Notes > The Mauryan Empire (322-185 BCE)
The Mauryan Empire (322-185 BCE) - Delhi Police Constable PDF Download
≫ Mauryan Empire – Rise of the Mauryas
- The last of the Nanda rulers, Dhana Nanda was highly unpopular due to his oppressive tax regime.
- Also, post-Alexander’s invasion of North-Western India, that region faced a lot of unrest from foreign powers.
- Some of these regions came under the rule of the Seleucid Dynasty, founded by Seleucus Nicator I. He was one of the generals of Alexander the Great.
- Chandragupta, with the help of an intelligent and politically astute Brahmin, Kautilya usurped the throne by defeating Dhana Nanda in 321 BC.
≫ Important Rulers of Mauryan Empire
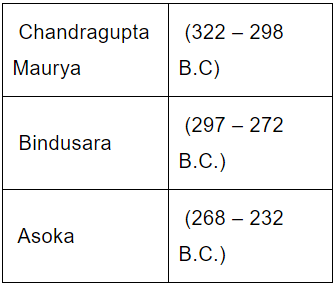
The Mauryan Empire had rulers who were famous for their reign. The table below gives the list of Mauryan Empire rulers:
Mauryan Empires – Rulers
≫ Founder of Mauryan Empire – Chandragupta Maurya
- Chandragupta’s origins are shrouded in mystery. The Greek sources (which are the oldest) mention him to be of non-warrior lineage. The Hindu sources also say he was a student of Kautilya of humble birth (probably born to a Shudra woman). Most Buddhist sources say he was a Kshatriya.
- It is generally accepted that he was an orphaned boy born into a humble family who was trained by Kautilya.
- Greek accounts mention him as Sandrokottos.
- Alexander had abandoned his India conquest in 324 BC and within a year, Chandragupta had defeated some of the Greek-ruled cities in the north-western part of the country.
- Kautilya provided the strategy while Chandragupta executed it. They had raised a mercenary army of their own.
- Then, they moved eastward into Magadha.
- In a series of battles, he defeated Dhana Nanda and laid the foundations of the Maurya Empire in about 321 BC.
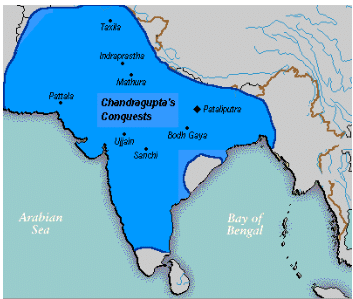
- In 305 BC, he entered into a treaty with Seleucus Nicator in which Chandragupta acquired Baluchistan, eastern Afghanistan and the region to the west of Indus. He also married Seleucus Nicator’s daughter. In return, Seleucus Nicator got 500 elephants. Seleucus Nicator avoided a full-scale war with the mighty Chandragupta and in return got war assets that would lead him to victory against his rivals in the Battle of Ipsus, fought in 301 BC
- Megasthenes was the Greek ambassador at Chandragupta’s court.
- Chandragupta led a policy of expansion and brought under one control almost the whole of present India barring a few places like Kalinga and the extreme South.
- His reign lasted from 321 BC to 297 BC.
- He abdicated the throne in favour of his son, Bindusara, and went to Karnataka with Jain monk Bhadrabahu. He had embraced Jainism and is said to have starved himself to death according to the Jain tradition at Shravanabelagola.
≫ Second Ruler of the Mauryan Empire – Bindusara
- Son of Chandragupta.
- He ruled from 297 BC to 273 BC.
- Also called Amitraghata (Slayer of foes) or Amitrochates in Greek sources.
- Deimachus was a Greek ambassador at his court.
- He had appointed his son, Ashoka as the governor of Ujjain.
- Bindusara is believed to have extended the Mauryan Empire to Mysore as well.
≫ Chanakya
- Teacher of Chandragupta Maurya, who was also his Chief Minister.
- He was a teacher and scholar at Taxila. Other names are Vishnugupta and Kautilya.
- He was also a minister in the court of Bindusara.
- He is credited to be the master strategist behind the usurping of the Nanda throne and the rise of the Mauryan Empire through his student, Chandragupta.
- He wrote Arthashastra which is a treatise on statecraft, economics, and military strategy.
- Arthashastra was rediscovered by R Shamasastry in 1905 after it had disappeared in the 12th century.
- The work contains 15 books and 180 chapters. The main theme is divided into:
(i) King, Council of Ministers and Departments of the Government
(ii) Civil and criminal law
(iii) Diplomacy of war - It also contains information on trade and markets, a method to screen ministers, spies, duties of a king, ethics, social welfare, agriculture, mining, metallurgy, medicine, forests, etc.
- Chanakya is also called ‘Indian Machiavelli”.
The document The Mauryan Empire (322-185 BCE) - Delhi Police Constable is a part of Delhi Police Constable category.
All you need of Delhi Police Constable at this link: Delhi Police Constable
FAQs on The Mauryan Empire (322-185 BCE) - Delhi Police Constable
| 1. What was the extent of the Mauryan Empire? |  |
Ans. The Mauryan Empire was one of the largest empires in ancient India, stretching from present-day Afghanistan in the west to Bangladesh in the east and covering most of the Indian subcontinent.
| 2. Who founded the Mauryan Empire? |  |
Ans. The Mauryan Empire was founded by Chandragupta Maurya, who overthrew the Nanda dynasty and established his rule in 322 BCE.
| 3. What were the major accomplishments of the Mauryan Empire? |  |
Ans. The Mauryan Empire witnessed several significant accomplishments, such as the establishment of a centralized administration, the construction of extensive road networks, the spread of Buddhism under Emperor Ashoka, and the compilation of the Arthashastra, an influential treatise on governance and economics.
| 4. How did the Mauryan Empire decline? |  |
Ans. The decline of the Mauryan Empire began after the death of Emperor Ashoka. Internal conflicts, succession disputes, and regional rebellions weakened the empire. The final blow came with the invasion of the Sunga dynasty in 185 BCE, leading to the collapse of the Mauryan Empire.
| 5. How did the Mauryan Empire contribute to the spread of Buddhism? |  |
Ans. Emperor Ashoka played a significant role in spreading Buddhism during the Mauryan Empire. After his conversion to Buddhism, Ashoka promoted the principles of non-violence, religious tolerance, and social welfare through his edicts and missionary activities. His efforts resulted in the widespread acceptance and growth of Buddhism within and beyond the empire's borders.
Download as PDF
Related Searches




















