The Verb | English Grammar for Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Verbs? |

|
| Objects of the Verb |

|
| Kinds of Verbs |

|
| Direct and Indirect Objects |

|
| Verbs: Main and Auxilliary |

|
| Strong and Weak Verbs |

|
What are Verbs?
A verb is a word that tells us something about the subject. It shows what someone or something is doing, what they are, or what they have.
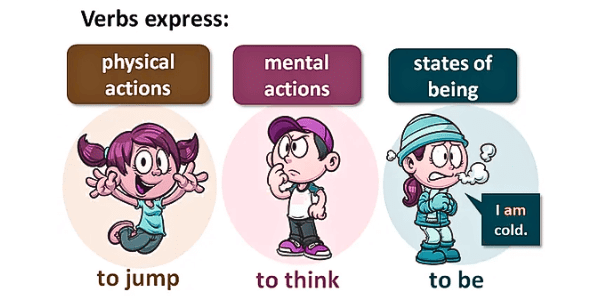
Action Verbs: These verbs tell us what someone is doing.
- Example 1: "Ankita kept the books in the shelf."
- Here, "kept" is the action verb because it shows what Ankita did with the books.
- Example 2: "The teacher teaches the students in the classroom."
- "Teaches" is the action verb because it shows what the teacher does in the classroom.
Being Verbs: These verbs describe what someone or something is.
- Example 1: "This river is quite shallow."
- "Is" is the being verb because it tells us about the river's condition.
- Example 2: "Shakespeare was the greatest poet and dramatist."
- "Was" is the being verb because it tells us about Shakespeare.
Possession Verbs: These verbs show what someone has.
- Example 1: "The nightingale has a sweet voice."
- "Has" shows possession, meaning the nightingale has something.
- Example 2: "Priya has blue eyes."
- "Has" shows possession, meaning Priya owns something (blue eyes).
Objects of the Verb
The object of a verb is the person or thing that receives the action. You can find the object by asking "what?" or "whom?" after the verb.
Examples:
"The table needs repairs."
- Ask: "Needs what?" Answer: "Repairs."
- So, "repairs" is the object of the verb "needs."
"The lion killed the deer."
- Ask: "Killed what?" Answer: "The deer."
- So, "the deer" is the object of the verb "killed."
"My parents love me."
- Ask: "Love whom?" Answer: "Me."
- So, "me" is the object of the verb "love."
"Vinay helps the needy."
- Ask: "Helps whom?" Answer: "The needy."
- So, "the needy" is the object of the verb "helps."
Kinds of Verbs
Verbs are words that show action or a state of being. There are three main types of verbs: Transitive Verbs, Intransitive Verbs, and Linking Verbs.
1. Transitive Verbs
A transitive verb needs an object to complete its meaning. The object is the person or thing that receives the action.
Example 1: "The woman filled the pail with water."
- Here, "filled" is the transitive verb. The object is "pail"
- What did the woman fill? The pail.
Example 2: "The boy flew a kite."
- "Flew" is the transitive verb, and "kite" is the object
- What did the boy fly? A kite.
Example 3: "She wrote a letter."
- "Wrote" is the transitive verb, and "letter" is the object
- What did she write? A letter.
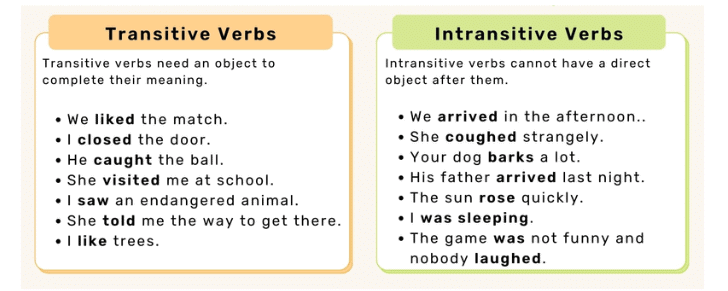
2. Intransitive Verbs
An intransitive verb does not need an object to make sense. It can stand alone and still make complete sense.
Example 1: "He knelt to pray."
- "Knelt" is the intransitive verb.
- It doesn’t need an object to complete its meaning.
Example 2: "The bird flew away."
- "Flew" is the intransitive verb.
- There is no object needed.
Example 3: "The rain stopped."
- "Stopped" is the intransitive verb.
- It makes sense on its own.
3. Linking Verbs
Linking verbs (also called verbs of incomplete predication) connect the subject to more information about the subject, often an adjective or a noun. They do not show action but instead describe a state of being.
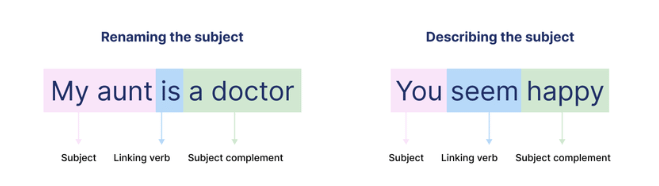
Example 1: "This river is quite shallow."
- "Is" is the linking verb. It links the subject "river" to the adjective "shallow," which describes the river.
Example 2: "Shakespeare was the greatest poet."
- "Was" is the linking verb. It connects "Shakespeare" to "the greatest poet," which describes him.
Example 3: "You appear happy today."
- "Appear" is the linking verb. It connects "you" to the adjective "happy," which describes your state.
Direct and Indirect Objects
In a sentence, some verbs need two objects to complete their meaning. These are called direct and indirect objects.
Example:
- The magician gave the king a golden lamp.
Questions to ask:
- Gave what? - a golden lamp (This is the direct object.)
- Gave whom? - the king (This is the indirect object.)
Direct and Indirect Objects
- Direct Object: Answers the question "what?" after the verb. It is the thing that is being acted upon.
- Indirect Object: Answers the question "whom?" or "for whom?" after the verb. It is the person or thing receiving the direct object.
Examples:
Mother gave Ankita a glass of juice.
- Direct Object: a glass of juice (What did Mother give?)
- Indirect Object: Ankita (Whom did Mother give the glass of juice to?)
The teacher handed the student a book.
- Direct Object: a book (What did the teacher hand?)
- Indirect Object: the student (Whom did the teacher hand the book to?)
Placement of Objects
Indirect Object Before Direct Object: The indirect object usually comes before the direct object.Example:
- The king gave the soldiers a reward.
- Mother made her little sister a pizza.
Reversing the Position: You can also place the direct object first and use a preposition like "to" or "for" before the indirect object.
Examples:
- The king gave a reward to the soldiers.
- She made a pizza for her little sister.
Important NoteNot all verbs work with the prepositions "to" or "for" when using two objects.
Examples:
- The library fined me twenty rupees. (Correct)
- The library fined twenty rupees to me. (Incorrect)
- The library fined twenty rupees for me. (Incorrect)
In sentences like these, the indirect object must come before the direct object without using "to" or "for."
More Examples:
- My friend sent me a postcard.
- Direct Object: a postcard
- Indirect Object: me
- My friend sent a postcard to me. (Correct)
- She taught us a new song.
- Direct Object: a new song
- Indirect Object: us
- She taught a new song to us. (Correct)
Verbs: Main and Auxilliary
Verbs are crucial in sentences because they tell us what the subject is doing or what is happening. They are mainly classified into two categories: Main (Principal) Verbs and Auxiliary (Helping) Verbs.
1. Main (Principal) Verbs
Main verbs are the verbs that show the main action or state of being in a sentence. They can stand alone or be used with other verbs.
Examples:
- Run: She runs every morning.
- Dance: They danced at the party.
- Eat: He eats an apple.
- Work: She works at a bank.
- Jump: The kids jumped on the trampoline.
Changing Forms: Main verbs can change form to show different tenses, such as past or future.
Examples:
Run becomes ran in the past tense.
- Present: I run to school.
- Past: I ran to school yesterday.
Dance becomes danced in the past tense.
- Present: They dance every Friday.
- Past: They danced at the wedding last month.
2. Auxiliary (Helping) Verbs
Auxiliary verbs help the main verbs to form different tenses, questions, or negatives. They are also known as helping verbs.
Common Auxiliary Verbs:
- Be (am, is, are, was, were)
- Do (do, does, did)
- Have (has, have, had)
Examples:
Forms of "Be":
- Present Tense: am, is, are
- I am happy.
- She is reading a book.
- They are playing soccer.
- Past Tense: was, were
- He was tired.
- We were at the park.
- Present Tense: am, is, are
Forms of "Do":
- Present Tense: do, does
- I do my homework.
- She does not like spinach.
- Past Tense: did
- They did their chores yesterday.
- Present Tense: do, does
Forms of "Have":
- Present Tense: has, have
- She has a cat.
- We have finished our project.
- Past Tense: had
- He had a bicycle when he was young.
- Present Tense: has, have
How Auxiliary Verbs Work
Auxiliary verbs are used with main verbs to create verb phrases. They can help show when something is happening or to form questions and negatives.
Examples:
- He is swimming in the pool. (Here, is is the auxiliary verb helping swimming (the main verb).)
- She has eaten lunch. (Here, has is the auxiliary verb helping eaten (the main verb).)
- Do you like ice cream? (Here, do helps form the question with the main verb like.)
- I am not going to the party. (Here, am helps form the negative with the main verb going.)
Auxiliary Verbs as Main Verbs: Sometimes, auxiliary verbs can also act as main verbs on their own.
Examples:
- He is happy. (Here, is is a main verb showing the state of being.)
- She has a book. (Here, has is a main verb showing possession.)
Strong and Weak Verbs
Verbs change their form to show different tenses, like present and past. They can be classified into two main types based on how they change their form:
1. Weak Verbs
Weak Verbs form their past tense by adding the same endings to the base form. These endings are usually -ed, -d, or -t.
Examples:
- Present Tense: watch
- Past Tense: watched (We just add -ed)
- Present Tense: laugh
- Past Tense: laughed (We just add -ed)
- Present Tense: learn
- Past Tense: learned or learnt (Some weak verbs can have two forms)
How to Identify: If a verb in the past tense ends with -ed, -d, or -t that was not in the present tense, it is a weak verb.
Examples:
- Present Tense: play
- Past Tense: played (added -ed)
- Present Tense: love
- Past Tense: loved (added -ed)
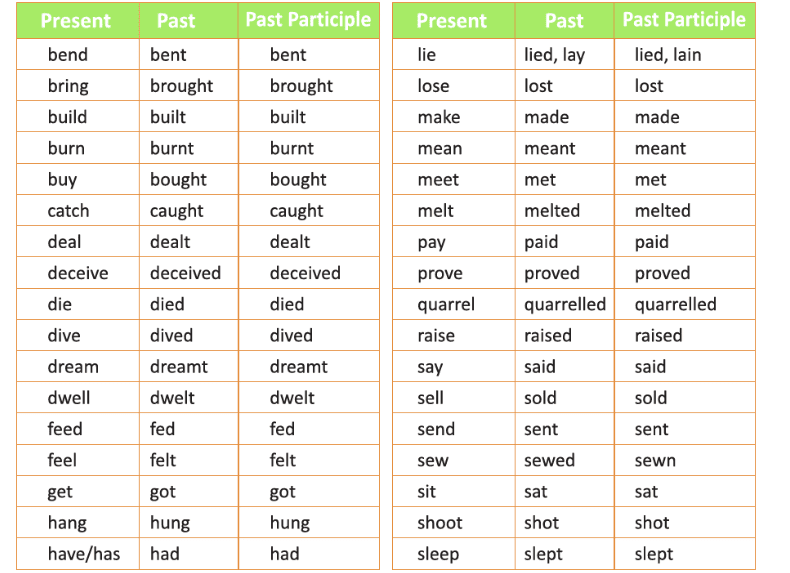
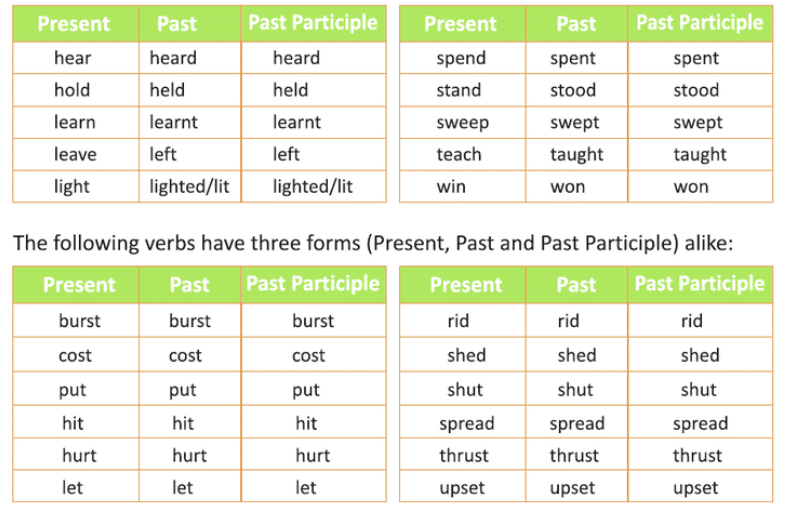
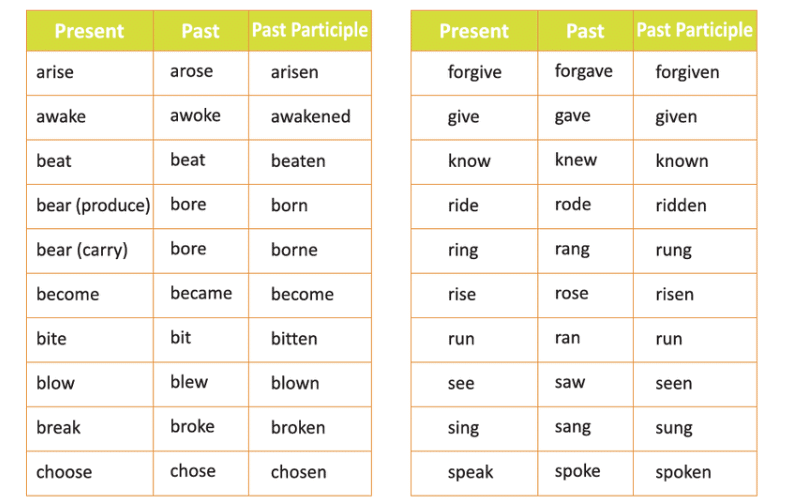
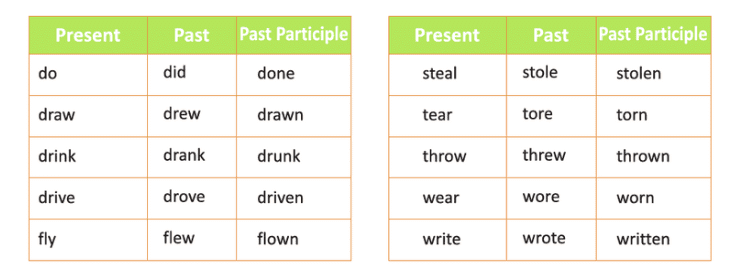
2. Strong Verbs
Strong Verbs form their past tense by changing the vowel in the middle of the word. They do not use -ed, -d, or -t.
Examples:
- Present Tense: rise
- Past Tense: rose (the vowel changes from i to o)
- Present Tense: know
- Past Tense: knew (the vowel changes from o to e)
- Present Tense: speak
- Past Tense: spoke (the vowel changes from ea to o)
How to Identify: If the past tense of a verb changes the vowel sound but does not add -ed, -d, or -t, it is a strong verb.
Examples:
- Present Tense: buy
- Past Tense: bought (the vowel changes from u to ou)
- Present Tense: catch
- Past Tense: caught (the vowel changes from a to au)
|
50 videos|520 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on The Verb - English Grammar for Class 6
| 1. What are the different kinds of verbs? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between direct and indirect objects of a verb? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between main and auxiliary verbs? |  |
| 4. What are strong and weak verbs? |  |
| 5. How are objects of the verb important in sentence construction? |  |
















