SSC CGL Exam > SSC CGL Notes > SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year > The spread of Indian culture abroad
The spread of Indian culture abroad | SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year PDF Download
The spread of Indian culture abroad
Asian Countries
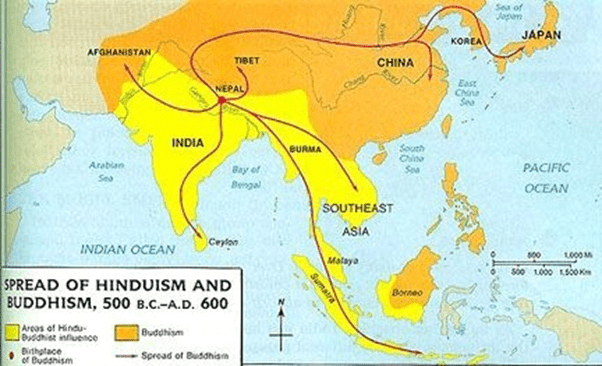
- The spread of Indian culture and civilization to the other parts of Asia constitutes an important chapter in the history of India.
- India had established commercial contacts with other countries from the earliest times.
- It had inevitably resulted in the spread of Indian languages, religions, art and architecture, philosophy, beliefs, customs and manners.
- Indian political adventurers even established Hindu kingdoms in some parts of South East Asia.
- However, this did not lead to any kind of colonialism or imperialism in the modern sense.
- On the other hand, these colonies in the new lands were free from the control of the mother country.
- But they were brought under her cultural influence.
Central Asia
- Central Asia was a great centre of Indian culture in the early centuries of the Christian era.
- Several monuments have been unearthed in the eastern part of Afghanistan. Khotan and Kashkar remained the most important centres of Indian culture.
- Several Sanskrit texts and Buddhist monasteries were found in these places.
- Indian cultural influence continued in this region till the eighth century. Indian culture had also spread to Tibet and China through Central Asia.
India and China
- China was influenced both by the land route passing through Central Asia and the sea route through Burma.
- Buddhism reached China at the beginning of the first century A.D. A number of Chinese pilgrims like Fahien and Hiuen Tsang visited India.
- On the other side, hundreds of Buddhist monks like Gunabhadra, Vajrabothi, Dharmadeva and Dharmagupta visited China. Indian scholars translated many Sanskrit works at the request of Chinese emperors.
- This contact with China continued even in the thirteenth century when the Mongols established their empire in China.
- Chinese art had also been influenced by Indian art.
India and Tibet
- Tibet was influenced by India from the seventh century.
- The famous Buddhist king Gampo founded the city of Lhasa and introduced Buddhism.
- The Tibetan alphabet was devised with the help of Indian scholars. Later, the Indian scholars helped with the establishment of Lamaism in Tibet.
- In the eleventh century, the Pala dynasty of Bengal had close contacts with Tibet.
- When Bengal was attacked by the Muslim rulers, many Buddhist monks sought shelter in Tibet.
India and Sri Lanka
- Despite having different political history, Sri Lanka experienced a great cultural influence from India.
- Buddhist missionaries had spread not only the religious faith but also cultural traditions.
- The art of stone carving went to Sri Lanka from India. In the fifth century, Buddha Ghosha visited Sri Lanka and consolidated there the Hinayana Buddhism.
- The famous paintings of Sigiriya were modelled on the Ajantha paintings.
Indian Culture in South East Asia
- Indian culture had extended its mighty influence in the South East Asian region consisting of the Malay Archipelago and Indo-China.
- They are located across the Bay of Bengal.
- Being fertile and rich in minerals, these lands attracted the attention of the Indians.
- Moreover, the east coast of India is studded with numerous ports and Indians undertook frequent voyages to these lands.
- The ancient traditions refer to traders' voyages to Suvarnabhumi, (the land of gold) a name generally given to all the countries of East Asia. Indians began to colonize East Asia in the Gupta period.
- It was further encouraged by the Pallavas.
- The Indian colonists established great kingdoms and some of them lasted for more than a thousand years.
- A number of dynasties with Indian names ruled in various parts.
- Till the arrival of Islam in the fifteenth century, Indian culture dominated this region.
Cambodia (Kambhoja)
- They influenced the native people called the Khemers.
- The ruling dynasty was known as Kambojas and their country was Kamboja or modern Cambodia.
- Under the early rulers, Saivism and Vaishnavism made steady progress. The Kamboja empire at its greatest extent included Laos, Siam, part of Burma and the Malay peninsula.
- Numerous Sanskrit inscriptions give us a detailed history of its kings. A number of Hindu literary works like the Vedas, the Ramayana, the Mahabharata, Panini's grammar, Hindu philosophical treatises were all known to the people of Cambodia.
- Like the Pallava kings, they were called Varmans. Yasovarman and Suryavarman II were two well-known rulers. Temples were built in South Indian style.
- There are plenty of Sanskrit inscriptions.
- The most famous of these temples was the temple (wat) of Vishnu built by Suryavarman II in his capital city Angkor.
- It was popularly called as the Angkorwat Temple.


- It is standing on top of a terraced structure.
- Each terrace is a sort of a covered gallery that contains numerous relief sculptures.
- The temple is constructed on the Dravidian style and the sculptures depict episodes from the Ramayana and the Mahabharata.
- The Kambhoja kingdom declined only in fifteenth century.
Champa
- Champa or South Annam is situated to the east of Cambodia.
- The first Hindu dynasty was established by Sri Mara in the second century A.D.
- A number of Sanskrit inscriptions throw light on the history of Champa.
- Twelve Indian dynasties ruled over Champa and by the thirteenth century, Champa was annexed to Cambodia.
- Under its Hindu rulers the Hindu religion and culture, customs and manners were introduced in Champa.
- Saivism and Vaishnavism flourished. Buddhism also existed side by side. Various works on Hindu philosophy, grammar, fine arts and astrology were written.
 |
Download the notes
The spread of Indian culture abroad
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Siam or Thailand
- There were several states in Siam following Indian culture.
- Thai script was developed with the help of Indian scholars.

- The traditional laws of that country were composed on the model of Dharmasastras.
- The temples at Bangkok contain many sculptures depicting the Ramayana.
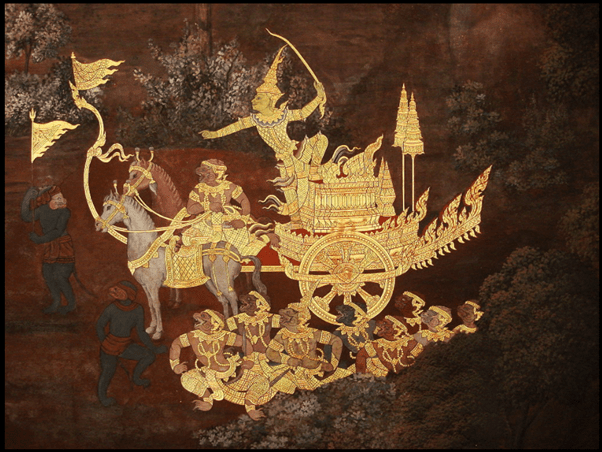 Rama with the monkey army adorning the walls of temple in Thailand
Rama with the monkey army adorning the walls of temple in Thailand
Sumatra and Java
- The Malay Archipelago had remained an important link between India and the Far East.
- Several Hindu kingdoms existed here between the fifth to fifteenth centuries A.D.
- The most important Hindu kingdom in the big island of Sumatra was Sri Vijaya.
- It was a great centre of trade and culture in the seventh century.
- Subsequently, the Sri Vijaya kingdom developed into a powerful maritime and commercial power known as the Sailendra empire extending its sway over the neighbouring islands of Java, Bali, Borneo and over Cambodia.
- The Sailendra rulers were Mahayana Buddhists and maintained cordial relations with the Indian kingdoms of the Palas of Bengal and the Cholas of Tamil Nadu.
- Rajaraja Chola allowed the Sailendra king Maravijayottungavarman to build a Buddhist monastery at Nagapattinam. His son Rajendra conquered the Sailendra kingdom for some time.
- Later they became independent. The Sailendra empire continued intact till the eleventh century A.D.
- A Hindu kingdom was established in Java as early as the fourth century A.D.
- In Central Java arose the kingdom of Mataram which became a strong centre of Hindu religion and culture.
- It was conquered by the Sailendras of Sumatra.
- Till the ninth century, Java continued to be a part of the Sailendra empire.
- Later it regained its independence. Java attained greatness and splendour in art under Sailendra rule.
- The greatest monument of Indo-Java art is the Borobudur which was built during A.D. 750-850 under the patronage of the Sailendras.
- It is situated on the top of a hill.
- It consists of nine successive terraces, crowned by a bell-shaped stupa at the centre of the topmost terrace.
- The open galleries in the terraces contain 2000 bas-reliefs (small carved stone figures) illustrating various incidents in the life of the Buddha.
- The lower parts are rich in decoration while the upper portions are plain and unadorned.
- Borobudur is described as an epic in stone, the most wonderful Buddhist stupa in the world.
 Borobudur Temple
Borobudur Temple
- In the twelfth century, eastern Java with Kadiri as its capital developed into the leading kingdom of Java.
- In the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries which marked the golden age of Javanese culture, Majapahit became the capital of the far-flung Javanese empire which included the neighbouring islands.
- Indian art and literature flourished in Java to an extent unknown elsewhere.
- Still, ruins of hundreds of temples and manuscripts based on the Sanskrit language are found in Java.
- The Ramayana and the Mahabharata were popular and even today furnish the theme for their popular shadow-play.
- The fall of Majapahit brought to an end all artistic activity in Java.
Bali
- Bali came under the rule of Hindu dynasties as early as the sixth century.
- I-Tsing refers to the prevalence of Buddhism there in the seventh century.
- The stone and copper plate inscriptions from that island show that it was colonised directly from India.
- Later it became subordinate to Java.
- Its people continue to be Hindus and even today we find the prevalence of the caste system there.

Myanmar
- The cultural contacts between India and Burma (now Myanmar) dates back to the period of Asoka, who sent his missionaries there to preach Buddhism.
- Many Hindu kingdoms existed in Burma. Pali and Sanskrit were the languages of Burma till the thirteenth century.
- Both Hinayana and Mahayana Buddhism were followed by the Burmese.
- Thus for nearly fifteen hundred years Hindu kings were ruling over numerous islands of the Malay Archipelago and over the Indo-China peninsula.
- Indian religions and Indian culture moulded the lives of the primitive inhabitants of these regions who were elevated to a higher plan of civilization.
Other Countries
- India has interacted with the rest of the world since the middle of the third millennium B. C.
- Indian travelled abroad and leave the footprints of their Culture. They also bought to the soil ideas, impressions, customs, traditions and knowledge of the distant lands.
- Indian Culture and Civilization is spread in various parts of the world by means of voluntary acceptance of cultural and spiritual values of India not merely by conquest or threat to life.
- In ancient times, traders from India went to distant lands such as China, Rome, Indonesia and Cambodia for business.
- During the time of emperor Ashoka, Kingdom Kalinga had trade relations with Sri Lanka. Traders established trade relations and cultural links.
- The universities were the most important centres of cultural interaction like Nalanda and Valabhi where Chinese pilgrim Huien Tsang visited.
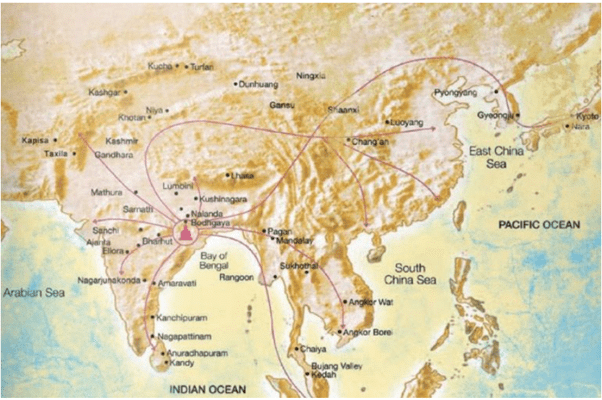 Nalanda university location and impact on the world
Nalanda university location and impact on the world
- Acharya Kamalasheel of Nalanda University was invited by the King of Tibet. In the eleventh century, the head of the Vikramashila University Acharya Ateesha went to Tibet and gave foundation to Buddhism in Tibet.
- A large number of Tibetans embraced Buddhism. Even the king became a Buddhist. He declared Buddhism as the State Religion.
- In Europe, the groups of Indian wanderers were famous as GYPSIES while they called themselves ROMAS and their language as Romani.
- The Romas are known for their dance and music and it is said that every Roma musician is a splendid artist.
- They use to travel through Iran, Iraq, Turkey, Persia, Europe and other countries. Now they are settled in Greece, Bulgaria, Romania, Hungary, Russia and Switzerland.
- India maintained commercial contact with China, Central Asia, West Asia and the Roman Empire.
- The Silk Route was primarily opened for trade and later it was used by scholars, monks and missionaries.
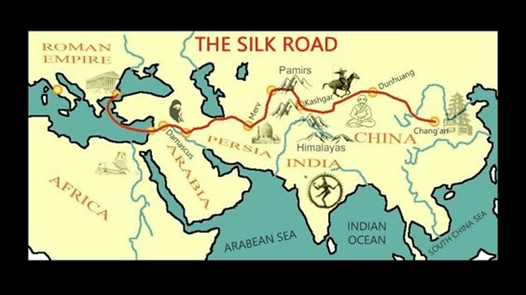
- This route served as a channel for Cultural Transmission and Indian Culture was spread in Central Asia.
- Kuchi in Central Asia was an important centre of Indian Culture. Discoveries of Ancient Stupas, temples, monasteries, images and paintings are the evidence of the Cultural exchange that took place between India and the Countries of Central Asia.
- Indian Culture first entered China with two monk scholars – Kashyapa Martanga and Dharmarakshita who went to China with the invitation of Chinese Emperor Ming Ti.
- The Chinese people were highly cultured people and they wrote about Indians and Indian Culture which became the most important source of India History.
- Buddhism was declared as the State Religion by Wei Dynasty. Thousands of Sanskrit Books were translated into Chinese.
- Korea received Indian Cultural elements through China.
- Sundo was the first Buddhist Monk who entered Korea.
- Indian monks brought philosophy, religion, art of making images, paintings and metallurgy. Monasteries and temples acted as centres of devotion and learning all over Korea.
- it՚s more than fifteen hundred years that Indian Culture came into link with Japan It was the Korean emperor who sent a Buddhist statue, sutras, instruments for worship, artists, sculptors, paintings and architects as gifts for the Japanese Emperor. In Japan, Sanskrit was soon accepted as a sacred language.
- King Ashoka made great efforts to propagate Buddhism outside India. He also sent his Children to Sri Lanka to spread Buddha՚s message which was transmitted orally. The first monasteries built in Sri Lanka were Mahavihara and Agbayani. Pali became their literary language. Indian Art forms, themes, styles, techniques of paintings, dance, folklore and architecture also reached Sri Lanka.
- People and Culture Of India began to reach Myanmar which is situated en route to China. Indian tradition was quite strong. Court, Astrologers, soothsayers and professors were known to be Brahmins called ponnas.
- Indian Culture began to reach Thailand by Indian Traders, teachers and missionaries. Sanskrit names were given to Thai Kingdoms such as Dwaravati, Shrivijay, sukhodaya and Ayutthiya. Even the street names such as Rajaram, Rajarani , Mahajaya remind of Ramayana. In the capital city of Thailand, Bangkok has 400 and more temples.
- Indian Culture was carried to the distant land of Vietnam by traders and princes who migrated and established themselves as pioneers in the field of politics and economics in Vietnam and Cambodia.
- Indian Culture also travelled to Indonesia.

- Prambanan is the largest Shiva Temple built in Indonesia՚s Island of Java. The stories of Ramayana and Krishna were carved on the walls of the temples.
- India՚s links with West Asia by land as well as sea route goes back to ancient times. The ties between the two-culture zone became close with rising and spread of Islamic Civilizations in West Asia. Indian contributions to Arab civilization was Mathematics as the Arabs acknowledged their debt to India by calling Mathematics “Hindisa” . A number of Arab sources dating back to the tenth and thirteenth century inform us about Indian work on medicine and therapeutics.
- Southern India had the monopoly of the products that were in great demand in the west represented mainly by the Roman Empire which became India՚s best customer.
- Items like pepper, betel, spices, scents and precious stones like beryl, gem, diamond, ruby, pearls, ivory, silk and muslins were in great demand.
- Trade thus became a very important mode that helped in the spread of Indian Culture abroad. Indian ships sailed across the seas and reach foreign shores to establish commercial ties with several countries.
- The Literature, Art and sculpture of the neighbouring countries clearly show the influence of Indian Culture and Civilization.
The document The spread of Indian culture abroad | SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year is a part of the SSC CGL Course SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year.
All you need of SSC CGL at this link: SSC CGL
|
1366 videos|1313 docs|1016 tests
|
FAQs on The spread of Indian culture abroad - SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year
| 1. What are some examples of Indian cultural elements that have spread abroad? |  |
| 2. How has Bollywood contributed to the spread of Indian culture abroad? |  |
Ans. Bollywood films have played a significant role in spreading Indian culture abroad. These films are known for their vibrant music, dance sequences, and colorful costumes, which have captured the interest of audiences worldwide. Bollywood movies have helped showcase Indian traditions, values, and storytelling techniques to a global audience.
| 3. Why has yoga gained popularity around the world as part of Indian culture? |  |
Ans. Yoga has gained popularity worldwide due to its numerous health benefits and ability to promote physical and mental well-being. Originating in ancient India, yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation. Its holistic approach to wellness has resonated with people across different cultures and backgrounds.
| 4. How has Indian cuisine influenced global food culture? |  |
Ans. Indian cuisine has had a significant influence on global food culture. The use of aromatic spices, diverse flavors, and vegetarian options in Indian dishes has attracted food enthusiasts worldwide. Popular Indian dishes like curry, biryani, samosas, and naan have become staples in many international cuisines, reflecting the growing appreciation for Indian culinary traditions.
| 5. What role does Indian diaspora play in spreading Indian culture abroad? |  |
Ans. The Indian diaspora, consisting of people of Indian origin living outside of India, plays a crucial role in spreading Indian culture abroad. They carry their cultural practices, traditions, and values to different parts of the world, thereby promoting Indian art, music, dance, festivals, and other cultural aspects. Indian diaspora communities often organize events, cultural festivals, and workshops that showcase various facets of Indian culture, contributing to its spread globally.
Related Searches























